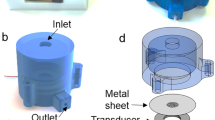
Abstract
This study presents a peristaltic piezoelectric micropump system to transport deionized water and whole blood, and deliver phosphated buffered saline (PBS) into the vein of a rat, thus simulating insulin injections for diabetes. The proposed system comprises a micropump, a 12 V battery, an ATmega 8535 microprocessor, a 12–180 V DC-to-DC converter based on transformerless technology, three differential amplifiers, an IC 7805, a phase controller, an A/D converter, a keyboard and an LCD module. The system can generate step-function signals of the 3-, 4-, and 6-phase actuation sequences with voltages of up to 228 Vpp (± 114 V) and frequencies ranging from 10 Hz to 100 kHz, as the inputs for the pump. It is portable and programmable with a package size of 22 × 12.8 × 9 cm. Additionally, a protocol of the PEOU (N-(triethosilylpropyl)-O-polyethylene oxide urethane) coating is developed to form a self-assembly monolayer, thus increasing the hemocompatibility of the micropump, and keeping blood flowing smoothly through the micropump without blocking. This study performs the circuit testing and fluid pumping, and reveals the effects of actuation sequences and liquid on pump performance. The flow rates for pumping DI water and whole blood are 16.6–121.6 μl/min and 8.6–50.2 μl/min, respectively when the voltages are changed from 80 Vpp (± 40 V) to 140Vpp (± 70 V). And the maximum backpressures are 3.2 and 1.8 kPa for DI water and whole blood at 150 Vpp (± 75 V), respectively. The mean artery pressure (MAP) and heart rates of the rate are 63–69 mmHg and 266–279 beats/min, respectively, throughout the injection process, indicating an insignificant change in physiological reactions of rats.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.H. Ahn, M.G. Allen, in Proceedings of the IEEE Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), 1995, pp. 408–412
H. Andersson, Wouter van der Wijngaarta, P. Nilssonb, P. Enokssona, G. Stemme, Sens. Actuators B 72, 259–265 (2001)
M. Bu, T. Melvin, G. Ensell, J.S. Wilkinson, A.G.R. Evans, J. Micromechanics Microengineering 13(4), S125–S130 (2003)
L. Cao, S. Mantell, D. Polla, Sens. Actuators A 94, 117–125 (2001)
J.J. Carr, J.M. Brown, Introduction to Biomedical Equipment Technology, 4th edn. (Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ, 2001)
O. Francais, I. Dufour, Sens. Actuators A 70, 56–60 (1998)
B. Husband, M. Bu, A.G.R. Evans, T. Melvin, J. Micromechanics Microengineering 14, S64–S69 (2004)
G.S. Jan, Sens. Actuators A 21–23, 203–206 (1990)
D.J. Laser, J.G. Santiago, J. Micromechanics Microengineering 14(6), R35–R64 (2004)
D.-S. Lee, J.S. Ko, Y.T. Kim, Bidirectional pumping properties of a peristaltic piezoelectric micropump with simple design and chemical resistance. Thin Solid Films 486, 285–290 (2004)
C.-S. Liao, G.-B. Lee, J.-J. Wu, C.-C. Chang, T.-M. Hsieh, F.-C. Huang, C.-H. Luo, Biosens. Bioelectron. 20, 1341–1348 (2005)
A.J. Masys, W. Ren, G. Yang, B.K. Mukherjee, J. Appl. Phys. 94(2), 1155–1162 (2003)
Z. Miqin, T. Desai, M. Ferrari, Biomaterials 19, 953–960 (1998)
N.-T. Nguyen, X. Huang, T.K. Chuan, Trans. Am. Soc. Mech. Eng. 124, 384–391 (2002)
S.Y. Oha, H.S. Choia, H.S. Jiea, J.K. Parkb, Mater. Sci. Eng. C 24, 91–94 (2004)
F. Rodes, in EDN Design Ideas (2004) pp. 83–86
D. Satakea, H. Ebia, N. Okub, K. Matsudaa, H. Takaoc, M. Ashikic, M. Ishidac, Sens. Actuators B 83, 77–81 (2002)
Y.-C. Shu, Mater. Trans. 43(5), 1037–1044 (2002)
J.G. Smits, Sens. Actuators A 21–23, 203–206 (1990)
H. Takaoa, K. Miyamurab, H. Ebib, M. Ashikia, K. Sawadaa, M. Ishidaa, Sens. Actuators A 119, 468–475 (2005)
R. Tanabe, S. Hata, A. Shimokohbe, Microelectron. Eng. 83, 1646–1650 (2006)
S.P. Timoshenko, W. Weaver, Vibration Problems in Engineering, 4th edn. (Wiley: New York, 1974)
J.-H. Tsai, L. Lin, Sens. Actuator A 97–98, 665–671 (2002)
J. Xie, J. Shih, Q. Lin, B. Yang, Y.C. Tai, Lab Chip 4, 495–501 (2004)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Science Council (NSC 94-2215-E-006-051) and Chi Mei Hospital of Taiwan (CMFHR9421). Additionally, this work made use of Shared Facilities supported by the Program of Top 100 Universities Advancement, Ministry of Education, Taiwan. The authors also would like to thank the Center for Micro/Nano Science and Technology, National Cheng Kung University, and National Nano Device Laboratories, Tainan, Taiwan, for equipment access and technical support. Moreover, the authors would like to thank Dr. Ching-Cheng Hou’s assistance for animal tests in Chi Mei Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jang, LS., Kan, WH. Peristaltic piezoelectric micropump system for biomedical applications. Biomed Microdevices 9, 619–626 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-007-9075-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-007-9075-1