Abstract
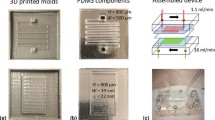
In this paper, we present a new method for the creation of a smaller dialyzer and do so by incorporating polymeric nanofiber web, which is known to have good filtration efficiency for broad particle sizes, into a poly (dimethylsiloxane)-based microplatform. We have developed a process that makes possible the efficient production of polyethersulfone and polyurethane nanofiber web and that, itself, incorporates an electrospinning method. We have combined the nanofiber web with the PDMS-based microfluidic platform to create a chip-based portable hemodialysis system. With the dialyzing chip, we evaluated the filtration capability of molecules in broad ranges of sizes and compared the filtration capability of nanofiber membranes with that of PES and polyvinylidene fluoride porous membranes (sheet type): we discovered that the nanofiber membranes have better filtration performance than the other membranes. Blood cells were not mechanically affected during their filtration and their transportation through the chip. In conclusion, we have demonstrated the feasibility of chip-based hemodialysis, and we expect that our method suggested in this paper will be applied to the development of small light-weight dialyzers for the realization of portable hemodialysis systems.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.H. Ahn, J.W. Choi, G. Beaucage, J.H. Nevin, J.B. Lee, A. Puntambekar, and J.Y. Lee, Proc. of IEEE 92, 154 (2004).
K.J. Baik, J.Y. Kim, H.K. Lee, and S.C. Kim, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 74, 2113 (1999).
R.H. Barth, Replacement of Renal Function by Dialysis 4th ed. (Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1996), p. 418.
D.J. Beebe, G.A. Mensing, and G.M. Walker, Biomed. Eng. 4, 261 (2002).
J.W. Choi, K.W. Oh, J.H. Thomas, W.R. Heineman, H.B. Halsall, J.H. Nevin, A.J. Helmicki, H.T. Henderson, and C.H. Ahn, Lab. Chip. 2, 27 (2002).
J. Gardeniers and A. Van Den Berg, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 378, 1700 (2004).
T.H. Grafe and K.M. Graham, In Proceedings of 5th International Conference (Stuttgart, 2003).
B.L. Hogan, S.M. Lunte, J.F. Stobaugh, and C.E. Lunte, Anal. Chem. 66, 596 (1994).
J.W. Hong, V. Studer, G. Hang, W.F. Anderson, and S.R. Quake, Nat. Biotech. 22, 435 (2004).
W.H. Hőrl, K.M. Koch, R.M. Lindsay, C. Ronco, and J.F. Winchester, Replacement of Renal Function by Dialysis 5th ed. (Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2004), Sec. II, p. 313.
P.J. Hung, P.J. Lee, P. Sabounchi, R. Lin, and L.P. Lee, Biotechnol. Bioeng. 89, 1 (2005).
D. Janasek, J. Franzke, and A. Manz, Nature 442, 374 (2006).
M.K. Ng. Jessamine, I. Giltin, A.D. Stroock, and G.M. Whitesides, Electrophoresis 23, 3461 (2002).
R. Kaazempur-Mofrad, J.P. Vacanti, N.J. Krebs, and J.T. Borenstein, In Proceedings of the Solid-State Sensor, Actuator and Microsystems Workshop (South Carolina, 2004), p. 67.
D.S. Kim, S.H. Lee, C.H. Ahn, J.Y. Lee, and T.H. Kwon, Lab. Chip. 6, 784 (2006).
B. Krause, M. Storr, T. Ertl, R. Buck, H. Hildwein, R. Deppisch, and H. Göhl, Chem. Ing. Tech. 11, 1725 (2003).
M. Külz, B. Nederlof, and H. Schneider, Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 17, 1475 (2002).
S.H. Lee, W.J. Jeong, and D.J. Beebe, Lab. Chip. 3, 164 (2003).
K.H. Lee, H.Y. Kim, Y.J. Ryu, K.W. Kim, and S.W. Choi, J. Polym. Sci. Part B: Polym. Phys. 41, 1256 (2003).
J.M.K. Ng, I. Gitlin, A.D. Stroock, and G.M. Whitesides, Electrophoresis 23, 3461 (2002).
A.R. Nissenson, C. Ronco, G. Pergamit, M. Edelstein, and R. Watts, Blood Purif. 23, 269 (2005).
J.Y. Park and S.H. Lee, J. Micromech. Microeng. 15, 1015 (2005).
M. Pulat and A. Akdoğan, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 85, 193 (2002).
C. Ronco, A. Brendolan, A. Lupi, G. Metry, and N.W. Levin, Kidney Int. 58, 809 (2000).
M.H. Rosner, South. Med. J. 98, 785 (2005).
S. Song, A.K. Singh, T.J. Shepodd, and B.J. Kirby, Anal. Chem. 76, 2367 (2004).
A.J. Tüdos, G.A.J. Besselink, and R.B.M. Schasfoort, Lab. Chip. 1, 83 (2002).
G.M. Whitesides, Nature 442, 368 (2006).
P. Yager, T. Edwards, E. Fu, K. Helton, K. Nelson, M.R. Tam, and B.H. Weigl, Nature 442, 412 (2006).
M.C. Yang and W.C. Lin, J. Polym. Res. 9, 61 (2002).
S.H. Ye, J. Watanabe, M. Takai, Y. Iwasaki, and K. Ishihara, Biomaterials 26, 5032 (2005).
J.D. Zahn, A.A. Deshmukh, A.P. Papavasiliou, A.P. Pisano, and D. Liepmann, In Proceedings of 2001 ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition (New York, 2001).
Y. Zhang, H. Ouyang, C.T. Lim, S. Ramakrishna, and Z.M. Huang, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 72, 156 (2005).
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by two grants of the Korea Health 21 R&D Project, Ministry of Health &; Welfare, Republic of Korea. (0405-ER01–0304-0001) and (02-PJ3-PG6-EV09–0001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, K.H., Kim, D.J., Min, B.G. et al. Polymeric nanofiber web-based artificial renal microfluidic chip. Biomed Microdevices 9, 435–442 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-007-9047-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-007-9047-5