Abstract
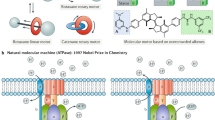
In this paper, construction of hybrid device by integrating nanowires with F1-ATPase motors is described. The nickel nanowires and multi-segment nanowires, including gold and nickel, were fabricated by electrochemical deposition in nanoporous templates. The nickel nanowires functionalized by biotinylated peptide can be assembled directly onto F1-ATPase motors to act as the propellers. If the multi-component nanowires, including gold and nickel, were selectively functionalized by the thiol group modified ssDNA and the synthetic peptide, respectively, the biotinylated F1-ATPase motors can be attached to the biotinylated peptide on nickel segment of the nanowires. Then, the multi-component nanowires can also be used as the propellers, and one may observe the rotations of the multi-component nanowires driven by F1-ATPase motors. Therefore, introduction of multiple segments along the length of a nanowire can lead to a variety of multiple chemical functionalities, which can be selectively bound to cells and special biomolecules. This method provides an insight for the construction of other hybrid devices with its controlling arrangement of different biomolecule on designed nanometer scale structures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.P. Abrahams, A.G.W. Leslie, R. Lutter, and J.E. Walker, Nature 370, 621–628 (1994).
G.D. Bachand and C.D. Montemagno, Biomedical Microdevices 2, 179–184 (2000).
R. Berry and J. Armitage, Advances in Microbial Physiology 41, 291–337 (1999).
S.M. Block, Cell 93, 5–8 (1998).
P.D. Boyer, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1140, 215–250 (1993).
G.B. Cox, A.L. Fimmel, F. Gibson, and L. Hatch, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 849, 62–69 (1986).
I. Dobbie, M. Linari, G. Piazzesi, M. Reconditi, N. Koubassova, M. A. Ferenczi, V. Lombardi, and M. Irving, Nature 396, 383–387 (1998).
T.M. Duncan, V.V. Bulygin, Y. Zhou, M.L. Hutcheon, and R.L. Cross, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 92, 10964–10968 (1995).
S. Engelbrecht and W. Junge, FEBS Lett. 414, 485–491 (1997).
J. Fritz, M.K. Baller, H.P. Lang, H. Rothuizen, P. Vettiger, E. Meyer, H.J. Güntherodt, C. Gerber, and J.K. Gimzewski, Science 288, 316–318 (2000).
I.R. Gibbons and J. Biol. Chem. 263, 15837–15840 (1988).
G. Groth and J. Walker, FEBS Lett. 410, 117–123 (1997).
T.J. Huang, B. Brough, C.M. Ho, Y. Li, A.H. Flood, P.A. Bonvallet, H.R. Tseng, J.F. Stoddart, M. Baller, and S. Magonov, Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 5391–5393 (2004).
A.J. Hunt, F. Gittes, and J. Howard, Biophysical Journal 67, 766–781 (1994).
L. Jia, S.G. Moorjani, T.N. Jackson, and W.O. Hancock, Biomedical Microdevices 6, 67–74 (2004).
D. Kaiser, Curr. Biol. 10, 777–780 (2000).
K. Kitamura, M. Tokunaga, A.H. Iwane, and T. Yanagida, Nature 397, 129–134 (1999).
C. Lapoinet, A. Hltgren, D.M. Silevitch, E.J. Felton, D.H. Reich, and R.L. Leheny, Science 303, 652–655 (2004).
B.S. Lee, S.C. Lee, and L.S. Holliday, Biomedical Microdevices 5, 269–280 (2003).
T. Matsui and M. Yoshida, Biochimica et Biophysica ACTA-Bioenergetics 1231, 139–146 (1995).
C.D. Montemagno and G.D. Bachand, Nanotechnology 10, 225–231 (1999).
K. Nishio, A. Iwamoto-Kihara, A. Yamamoto, Y. Wada, and M. Futai, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 99, 13448–13452 (2002).
H. Noji, R. Yasuda, M. Yoshida, and K. Jr. Kinosita, Nature 386, 299–302 (1997).
I. Ogilvie, R. Aggeler, and R.A. Capaldi, J. Biol. Chem. 272, 16652–16656 (1997).
H. Omote, N. Sambonmatsu, K. Saito, Y. Sambongi, A.I. Kihara, T. Yanagida, Y. Wada, and M. Futai, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 96, 7780–7784 (1999).
G. Oster and H. Wang, Trends Cell Biol. 13, 114–121 (2003).
O. Pänke, K. Gumbiowski, W Junge, and S. Engelbrecht, FEBS Lett. 472, 34–38 (2000).
D.H. Reich, M. Tanase, A. Hultren, L.A. Bauer, C.S. Chen, and G.J. Meyer, J. Appl. Phys. 93, 7275–7280 (2003).
Q. Ren, Y. P. Zhao, L. Han, and H. B. Zhao, Nanotechnology 17, 1778–1785 (2006).
A.K. Salem, J. Chao, K.W. Leong, and P.C. Searson, Advanced Materials 16, 268–271 (2004).
C. Shingyoji, H. Higuchi, M. Yoshimura, E. Katayama, and T. Yanagida, Nature 393, 711–714 (1998).
R.K. Soong, G.D. Bachand, H.P. Neves, A.G. Olkhovets, H.G. Craighead, and C.D. Montemagno, Science 290, 1555–1558 (2000).
R.K. Soong, H.P. Neves, J.J. Schmidt, G.D. Bachand, and C.D. Montemagno, Biomedical Microdevices 3, 71–73 (2001).
L. Stryer, Biochemistry (Freeman, New York, 1995) p. 443.
R. Yasuda, H. Noji, K. Jr. Kinosita, and M. Yoshida, Cell 93, 1117–1124 (1998).
R. Yasuda, H. Noji, M. Yoshida, K. Jr. Kinosita, and H. Itoh, Nature 410, 898–904 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, Q., Zhao, YP., Yue, J.C. et al. Biological application of multi-component nanowires in hybrid devices powered by F1-ATPase motors. Biomed Microdevices 8, 201–208 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-006-8173-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-006-8173-9