Abstract
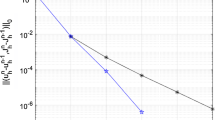
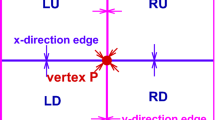
In this paper, we propose and analyze a new structure-preserving finite element method for the stationary magnetohydrodynamic equations with magnetic-current formulation on Lipschitz domains. Using a mixed finite element approach, we discretize the hydrodynamic unknowns by inf-sup stable velocity-pressure finite element pairs, and the current density, the induced electric field and the magnetic field by using the edge-edge-face elements from a discrete de-Rham complex pair. To deal with the divergence-free condition of the magnetic field, we introduce an augmented term to the discrete scheme rather than a Lagrange multiplier in the existing schemes. Thanks to discrete differential forms and finite element exterior calculus, the proposed scheme preserves the divergence-free property exactly for the magnetic induction on the discrete level. The well-posedness of the discrete problem is further proved under the small data condition. Under weak regularity assumptions, we rigorously establish the error estimates of the finite element schemes. Numerical results are provided to illustrate the theoretical results and demonstrate the efficiency of the proposed method.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Adler, J.H., Benson, T.R., Cyr, E.C., Farrell, P.E., MacLachlan, S.P., Tuminaro, R.S.: Monolithic multigrid methods for magnetohydrodynamics. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 43(5), S70–S91 (2021)
Ata, K., Sahin, M.: A facebased monolithic approach for the incompressible magnetohydrodynamics equations. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 92(5), 347–371 (2020)
Boffi, D., Brezzi, F., Fortin, M.: Mixed finite element methods and applications. Springer Series in Computational Mathematics, vol. 44. Springer, Heidelberg (2013)
Brackbill, J.U., Barnes, D.C.: The effect of nonzero \(\nabla \cdot {{\varvec {B}}}\) on the numerical solution of the magnetohydrodynamic equations. J. Comput. Phys. 35(3), 426–430 (1980)
Dai, W., Woodward, P.R.: On the divergence-free condition and conservation laws in numerical simulations for supersonic magnetohydrodynamic flows. Astrophys. J. 494(1), 317 (1998)
Davidson, P.A.: An introduction to magnetohydrodynamics. Cambridge Texts in Applied Mathematics, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2001)
Gao, H., Qiu, W.: A semi-implicit energy conserving finite element method for the dynamical incompressible magnetohydrodynamics equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 346, 982–1001 (2019)
Gerbeau, J.F., Le Bris, C., Lelièvre, T.: Mathematical methods for the magnetohydrodynamics of liquid metals. Numerical Mathematics and Scientific Computation, Oxford University Press, Oxford (2006)
Girault, V., Raviart, P.A.: Finite element methods for Navier-Stokes equations, Springer Series in Computational Mathematics, vol. 5. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (1986). Theory and algorithms
Goedbloed, J.P., Keppens, R., Poedts, S.: Advanced Magnetohydrodynamics: With Applications to Laboratory and Astrophysical Plasmas. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2010)
Goedbloed, J.P.H., Poedts, S.: Principles of Magnetohydrodynamics: With Applications to Laboratory and Astrophysical Plasmas. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2004)
Gunzburger, M.D., Meir, A.J., Peterson, J.S.: On the existence, uniqueness, and finite element approximation of solutions of the equations of stationary, incompressible magnetohydrodynamics. Math. Comput. 56(194), 523–563 (1991)
He, Y.: Unconditional convergence of the Euler semi-implicit scheme for the three-dimensional incompressible MHD equations. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 35(2), 767–801 (2015)
Hecht, F.: New development in FreeFem++. J. Numer. Math. 20(3–4), 251–265 (2012)
Hiptmair, R., Li, L., Mao, S., Zheng, W.: A fully divergence-free finite element method for magnetohydrodynamic equations. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 28(4), 659–695 (2018)
Hu, K., Ma, Y., Xu, J.: Stable finite element methods preserving \(\nabla \cdot {\varvec {B}}=0\) exactly for MHD models. Numer. Math. 135(2), 371–396 (2017)
Hu, K., Xu, J.: Stable magnetic field-current finite element formulation for magnetohydrodynamics system (in Chinese). Sci. Sin. Math. 46(7), 967–980 (2016)
Hu, K., Xu, J.: Structure-preserving finite element methods for stationary MHD models. Math. Comput. 88(316), 553–581 (2019)
John, V.: Finite element methods for incompressible flow problems. Springer Series in Computational Mathematics, vol. 51. Springer, Cham (2016)
Laakmann, F., Farrell, P.E., Mitchell, L.: An augmented Lagrangian preconditioner for the magnetohydrodynamics equations at high Reynolds and coupling numbers. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 44(4), B1018–B1044 (2022)
Li, L., Zhang, D., Zheng, W.: A constrained transport divergence-free finite element method for incompressible MHD equations. J. Comput. Phys. 428(109980), 22 (2021)
Li, X., Li, L.: A conservative finite element solver for the induction equation of resistive MHD: vector potential method and constraint preconditioning. J. Comput. Phys. 466(111416), 20 (2022)
Ma, Y., Xu, J., Zhang, G.D.: Error estimates for structure-preserving discretization of the incompressible MHD system. arXiv: arXiv1608.03034 (2016)
Marioni, L., Bay, F., Hachem, E.: Numerical stability analysis and flow simulation of lid-driven cavity subjected to high magnetic field. Phys. Fluids 28, 057102 (2016)
Phillips, E.G., Elman, H.C., Cyr, E.C., Shadid, J.N., Pawlowski, R.P.: A block preconditioner for an exact penalty formulation for stationary MHD. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 36(6), B930–B951 (2014)
Prohl, A.: Convergent finite element discretizations of the nonstationary incompressible magnetohydrodynamics system. M2AN Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 42(6), 1065–1087 (2008)
Qiu, W., Shi, K.: Analysis of a semi-implicit structure-preserving finite element method for the nonstationary incompressible magnetohydrodynamics equations. Comput. Math. Appl. 80(10), 2150–2161 (2020)
Schötzau, D.: Mixed finite element methods for stationary incompressible magneto-hydrodynamics. Numer. Math. 96(4), 771–800 (2004)
Su, H., Feng, X., Huang, P.: Iterative methods in penalty finite element discretization for the steady MHD equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 304, 521–545 (2016)
Tóth, G.: The \(\nabla \cdot {\varvec {B}}=0\) constraint in shock-capturing magnetohydrodynamics codes. J. Comput. Phys. 161(2), 605–652 (2000)
Yang, J., Mao, S.: Second order fully decoupled and unconditionally energy-stable finite element algorithm for the incompressible MHD equations. Appl. Math. Lett. 121(107467), 8 (2021)
Zhang, G., He, Y., Yang, D.: Analysis of coupling iterations based on the finite element method for stationary magnetohydrodynamics on a general domain. Comput. Math. Appl. 68(7), 770–788 (2014)
Zhang, G., Yang, J., Bi, C.: Second order unconditionally convergent and energy stable linearized scheme for MHD equations. Adv. Comput. Math. 44(2), 505–540 (2018)
Zhang, X., Ding, Q.: Coupled iterative analysis for stationary inductionless magnetohydrodynamic system based on charge-conservative finite element method. J. Sci. Comput. 88(2), 32 (2021)
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the anonymous referees and the associate editor for many constructive comments that improved the paper.
Funding
The first author’s research is supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 12201575 and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation under Grant 2022M722878. The second author’s research is supported in part by Xinjiang Graduate Student Research Innovation Project under Grant XJ2023G081.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XZ: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, writing, review. SD: visualization, validation, review. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Dong, S. New structure-preserving mixed finite element method for the stationary MHD equations with magnetic-current formulation. Bit Numer Math 63, 55 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10543-023-00995-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10543-023-00995-7