Abstract
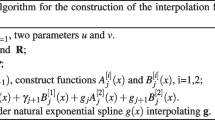
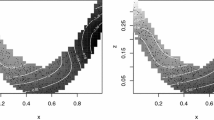
In this paper a special class of one-dimensional L-splines of order 4 is studied, which naturally appear in the computation of interpolation and smoothing with multivariate polysplines. Fast algorithms are provided for interpolation and smoothing with this class of L-splines, as well as a generalization of the Reinsch algorithm to this setting. The explicit description of all mathematical expressions permits a simple and direct numerical implementation. Applications are provided to financial data of the index S&P500, for the fast calculation of statistically interesting quantities, as cross validation (scores), generalized cross validation (scores) for finding the best smoothing parameter \(\alpha \), and the residual sum of squares.








Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Data downloaded via https://finance.yahoo.com website. From all S&P500 prices we have subtracted the value 2500 to avoid working with big numbers.
References
Ayalon, Z., Dyn, N., Levin, D.: Piecewise L-splines of order 4: interpolation and \(L^{2}\)-error bounds for splines in tension. J. Approx. Theory 161, 421–431 (2009)
Buhmann, M.: Radial Basis Functions. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2003)
Coddington, E.A., Levinson, N.: Theory of Ordinary Differential Equations. McGraw-Hill, New York (1955)
de Boor, C.: A Practical Guide to Splines. Springer, Berlin (2001)
Fasshauer, G., McCourt, M.: Kernel-Based Approximation Methods Using MATLAB. World Scientific Publishers, Singapore (2015)
Golub, G., Van Loan, Ch.: Matrix Computations. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore (2012)
Green, P., Silverman, B.: Nonparametric Regression and Generalized Linear Models. Chapman and Hall, London (1994)
Gu, Ch.: Smoothing Spline ANOVA Models. Springer, New York (2013)
Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R., Friedman, J.: The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction. Springer, Berlin (2013)
Horn, R.A., Johnson, Ch.R.: Matrix Analysis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1985)
Kounchev, O.: Multivariate Polysplines: Applications to Numerical and Wavelet Analysis. Academic Press, San Diego (2001)
Kounchev, O., Render, H.: The approximation order of polysplines. Proc. Am. Math. Soc. 132, 455–461 (2004)
Kounchev, O., Render, H.: Cardinal interpolation with polysplines on annuli. J. Approx. Theory 137, 89–107 (2005)
Kounchev, O., Render, H.: Polyharmonic splines on grids \(Z\times Z^{n}\) and their limits. Math. Comput. 74, 1831–1841 (2005)
Lyche, T., Schumaker, L.L.: Computation of smoothing and interpolating natural splines via local bases. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 10(6), 1027–1038 (1973)
McCartin, B.J.: Computation of exponential splines. SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comput. 11(2), 242–262 (1990)
McCartin, B.J.: Theory of exponential splines. J. Approx. Theory 66, 1–23 (1991)
Pontryagin, L.: Ordinary Differential Equations. Addison-Wesley, Reading (1962)
Pruess, S.: Properties of splines in tension. J. Approx. Theory 17, 86–96 (1976)
Ramsay, J., Silverman, B.W.: Functional Data Analysis. Springer, Berlin (2005)
Schultz, M.H., Varga, R.S.: L-splines. Numer. Math. 10, 345–369 (1967)
Schumaker, L.: Spline Functions: Basic Theory. Academic Press, San Diego (2007)
Stoer, J., Bulirsch, R.: Introduction to Numerical Analysis. Springer, Berlin (2003)
Wahba, G.: Spline Models for Observational Data. SIAM, Philadelphia (1990)
Wendland, H.: Scattered Data Approximation. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Tom Lyche.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
O. Kounchev was partially supported by the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation, Bonn, while all were supported by Grant DN-02-13 and Grant KP-06-H32-8 with Bulgarian NSF.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kounchev, O., Render, H. & Tsachev, T. On a class of L-splines of order 4: fast algorithms for interpolation and smoothing. Bit Numer Math 60, 879–899 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10543-020-00801-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10543-020-00801-8