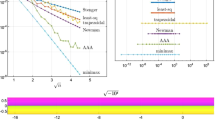
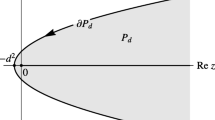
Abstract
Many computational problems can be solved with the aid of contour integrals containing e z in the integrand: examples include inverse Laplace transforms, special functions, functions of matrices and operators, parabolic PDEs, and reaction-diffusion equations. One approach to the numerical quadrature of such integrals is to apply the trapezoid rule on a Hankel contour defined by a suitable change of variables. Optimal parameters for three classes of such contours have recently been derived: (a) parabolas, (b) hyperbolas, and (c) cotangent contours, following Talbot in 1979. The convergence rates for these optimized quadrature formulas are very fast: roughly O(3-N), where N is the number of sample points or function evaluations. On the other hand, convergence at a rate apparently about twice as fast, O(9.28903-N), can be achieved by using a different approach: best supremum-norm rational approximants to e z for z∈(–∞,0], following Cody, Meinardus and Varga in 1969. (All these rates are doubled in the case of self-adjoint operators or real integrands.) It is shown that the quadrature formulas can be interpreted as rational approximations and the rational approximations as quadrature formulas, and the strengths and weaknesses of the different approaches are discussed in the light of these connections. A MATLAB function is provided for computing Cody–Meinardus–Varga approximants by the method of Carathéodory–Fejér approximation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. I. Aptekarev, Sharp constants for rational approximation of analytic functions, Sb. Math., 193 (2002), pp. 1–72.
D. Calvetti, E. Gallopoulos, and L. Reichel, Incomplete partial fractions for parallel evaluation of rational matrix functions, J. Comput. Appl. Math., 59 (1995), pp. 349–380.
A. J. Carpenter, A. Ruttan, and R. S. Varga, Extended computations on the ‘1/9’ conjecture in rational approximation theory, in Rational Approximation and Interpolation, P. R. Graves-Morris, E. B. Saff, and R. S. Varga, eds., Lect. Notes Math., vol. 1105, pp. 383–411, Springer, Berlin, 1984.
J. C. Cavendish, W. E. Culham, and R. S. Varga, A comparison of Crank–Nicolson and Chebyshev rational methods for numerically solving linear parabolic equations, J. Comput. Phys., 10 (1972), pp. 354–368.
W. J. Cody, G. Meinardus, and R. S. Varga, Chebyshev rational approximations to e -x in [0,+∞) and applications to heat-conduction problems, J. Approximation Theory, 2 (1969), pp. 50–65.
E. Gallopoulos, A partial fraction decomposition approach to improved efficiency of some parabolic solvers, Technical report 874, Ctr. for Supercomputing Res. Dev., University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, May 1989.
E. Gallopoulos and Y. Saad, On the parallel solution of parabolic equations, Proc. 1989 ACM Internat. Conf. on Supercomputing, pp. 17–28, Heraklion, Greece, 1989.
E. Gallopoulos and Y. Saad, Efficient solution of parabolic equations by Krylov approximation methods, SIAM J. Sci. Statist. Comput., 13 (1992), pp. 1236–1264.
I. P. Gavrilyuk and V. L. Makarov, Exponentially convergent parallel discretization methods for the first order evolution equations, Comput. Meth. Appl. Math., 1 (2001), pp. 333–355.
I. P. Gavrilyuk and V. L. Makarov, Exponentially convergent algorithms for the operator exponential with applications to inhomogeneous problems in Banach spaces, SIAM J. Numer. Anal., 43 (2005), pp. 2144–2171.
A. Gil, J. Segura, and N. M. Temme, Computing special functions by using quadrature rules, Numer. Algorithms, 33 (2003), pp. 265–275.
A. A. Gonchar and E. A. Rakhmanov, Equilibrium distributions and degree of rational approximation of analytic functions, Mat. Sb., 134 (1987), pp. 306–352 (English transl. in Math. USSR-Sb. 62 (1989)).
G. H. Halphen, Traité des fonctions elliptiques et de leurs applications, I, Théorie des fonctions elliptiques et de leurs développement en séries, Gauthier-Villars, Paris, 1886 (http://moa.cit.cornell.edu/).
A.-K. Kassam, Solving reaction-diffusion equations ten times faster, Numer. Anal. Rep. NA 03/16, Oxford U. Computing Lab., Oxford, 2003.
A.-K. Kassam and L. N. Trefethen, Fourth-order time-stepping for stiff PDE, SIAM J. Sci. Comput., 26 (2005), pp. 1214–1233.
J. D. Lawson and D. A. Swayne, High-order near best uniform approximations to the solution of heat conduction problems, Information Processing 80, pp. 741–746, North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1980.
M. López-Fernández, C. Lubich, C. Palencia, and A. Schädle, Fast Runge–Kutta approximation of inhomogeneous parabolic equations, Numer. Math., 102 (2005), pp. 277–291.
M. López-Fernández and C. Palencia, On the numerical inversion of the Laplace transform in certain holomorphic mappings, Appl. Numer. Math., 51 (2004), pp. 289–303.
M. López-Fernández, C. Palencia, and A. Schädle, A spectral order method for inverting sectorial Laplace transforms, SIAM J. Numer. Anal., 44 (2006), pp. 1332–1350.
Y. Y. Lu, Exponentials of symmetric matrices through tridiagonal reductions, Linear Algebra Appl., 279 (1998), pp. 317–324.
C. Lubich and A. Schädle, Fast convolution for nonreflecting boundary conditions, SIAM J. Sci. Comput., 24 (2002), pp. 161–182.
Y. L. Luke, The Special Functions and Their Approximations, vol. 1–2, Academic Press, New York, 1969.
Y. L. Luke, Error estimation in numerical inversion of Laplace transforms using Padé approximation, J. Franklin Inst., 305 (1978), pp. 259–273.
A. P. Magnus, Asymptotics and super asymptotics of best rational approximation error norms for the exponential function (the ‘1/9’ problem) by the Carathéodory–Fejér method, in Nonlinear Methods and Rational Approximation, II, A. Cuyt et al., eds., pp. 173–185, Kluwer, Dordrecht, 1994.
W. McLean and V. Thomée, Time discretization of an evolution equation via Laplace transforms, IMA J. Numer. Anal., 24 (2004), pp. 439–463.
G. Meinardus, Approximation of Functions: Theory and Numerical Methods, Springer, Berlin, 1967.
C. Moler and C. Van Loan, Nineteen dubious ways to compute the exponential of a matrix, twenty-five years later, SIAM Rev., 45 (2003), pp. 3–49.
R. Piessens, On a numerical method for the calculation of transient responses, J. Franklin Inst., 292 (1971), pp. 57–64.
R. Piessens, Gaussian quadrature formulas for the numerical integration of Bromwich’s integral and the inversion of the Laplace transform, J. Eng. Math., 5 (1971), pp. 1–9.
V. M. Rjabov, Application of Padé approximations to Laplace transformation inversion, Vestn. Leningrad. Univ. Math., 2 (1970), p. 119 (Russian).
A. J. Rodrigues, Properties of constants for a quadrature formula to evaluate Bromwich’s integral, J. Inst. Math. Appl., 18 (1976), pp. 49–56.
E. B. Saff and V. Totik, Logarithmic Potentials with External Fields, Springer, Berlin, 1997.
H. E. Salzer, Orthogonal polynomials arising in the numerical evaluation of inverse Laplace transforms, Math. Comput., 9 (1955), p. 164–177.
A. Schädle, M. López-Fernández, and C. Lubich, Fast and oblivious convolution quadrature, SIAM J. Sci. Comput., 28 (2006), pp. 421–438.
T. Schmelzer and L. N. Trefethen, Computing the gamma function using contour integrals and rational approximations, SIAM J. Numer. Anal., submitted.
A. Schönhage, Zur rationalen Approximierbarkeit von e -x über [0,∞), J. Approximation Theory, 7 (1973), pp. 395–398.
D. Sheen, I. H. Sloan, and V. Thomée, A parallel method for time-discretization of parabolic problems based on contour integral representation and quadrature, Math. Comput., 69 (2000), pp. 177–195.
D. Sheen, I. H. Sloan, and V. Thomée, A parallel method for time discretization of parabolic equations based on Laplace transformation and quadrature, IMA J. Numer. Anal., 23 (2003), pp. 269–299.
R. B. Sidje, Expokit: A software package for computing matrix exponentials, ACM Trans. Math. Softw., 24 (1998), pp. 130–156.
H. Stahl and V. Totik, General Orthogonal Polynomials, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1992.
A. Talbot, The accurate numerical inversion of Laplace transforms, J. Inst. Math. Appl., 23 (1979), pp. 97–120.
N. M. Temme, Special Functions, Wiley, New York, 1996.
L. N. Trefethen, Chebyshev approximation on the unit disk, in Computational Aspects of Complex Analysis, H. Werner et al., eds., pp. 309–323, D. Reidel Publishing, Dordrecht, 1983.
L. N. Trefethen, Matlab programs for CF approximation, in Approximation Theory V, pp. 599–602, Academic Press, Boston, 1986.
L. N. Trefethen, Is Gauss quadrature better than Clenshaw-Curtis?, SIAM Rev., submitted.
L. N. Trefethen and M. H. Gutknecht, The Carathéodory–Fejér method for real rational approximation, SIAM J. Numer. Anal., 20 (1983), pp. 420–436.
L. N. Trefethen and J. A. C. Weideman, The fast trapezoid rule in scientific computing, manuscript in preparation.
R. S. Varga, On higher order stable implicit methods for solving parabolic partial differential equations, J. Math. Phys., 40 (1961), pp. 220–231.
J. Vlach, Numerical method for transient responses of linear networks with lumped, distributed or mixed parameters, J. Franklin Inst., 288 (1969), pp. 99–113.
J. A. C. Weideman, Optimizing Talbot’s contours for the inversion of the Laplace transform, SIAM J. Numer. Anal., to appear.
J. A. C. Weideman and L. N. Trefethen, Parabolic and hyperbolic contours for computing the Bromwich integral, Math. Comput., to appear.
V. Zakian, Properties of IMN and JMN approximants and applications to numerical inversion of Laplace transforms and initial value problems, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 50 (1975), pp. 191–222.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
In memory of Germund Dahlquist (1925–2005).
AMS subject classification (2000)
65D30, 41A20
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trefethen, L., Weideman, J. & Schmelzer, T. Talbot quadratures and rational approximations . Bit Numer Math 46, 653–670 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10543-006-0077-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10543-006-0077-9