Abstract
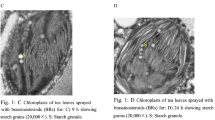
Brassinolide (BL) alleviates salt injury in cotton seedlings; however, little is known about the molecular mechanisms of this response. In this study, digital gene expression analysis was performed to better understand the regulatory pathways of BL in NaCl-stressed cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Compared with control plants (CK), a total of 1 162 and 7 659 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were detected in the leaves and roots of NaCl-treated plants, respectively. Most of the DEGs in NaCl-treated plants, compared to CK, were regulated by BL. Moreover, expression patterns of DEGs in BL+NaCl treated plants were similar to those in CK plants; however, the responses of DEGs in the leaves and roots of NaCl-treated plants to BL differed. In the roots, BL-regulated DEGs were involved in protein biosynthesis, whereas in the leaves, BL promoted photosynthesis in NaCl-stressed cotton. BL treatment also significantly increased the overall biomass, chlorophyll a + b content in leaves, and the protein content in roots in NaCl-stressed cotton. The downregulation of stress-responsive genes in BL+NaCl-stressed leaves was also found. These results suggest that BL can alleviate NaCl injury in cotton plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BL:
-
brassinolide
- BRs:
-
brassinosteroids
- Chl:
-
chlorophyll
- CK:
-
control
- DEG:
-
differentially expressed gene
- EBR:
-
epibrassinolide
- GO:
-
gene ontology
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes
- L:
-
leaf
- RT-qPCR:
-
reverse transcriptase quantitative polymerase chain reaction
- R:
-
root
References
Anders, S., Huber, W.: Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. — Genome Biol. 11: 1–12, 2010.
Anuradha, S., Rao, S.S.R.: Application of brassinosteroids to rice seeds (Oryza sativa L.) reduced the impact of salt stress on growth, prevented photosynthetic pigment loss and increased nitrate reductase activity. — Plant Growth Regul. 40: 29–32, 2003.
Bajguz, A., Hayat, S.: Effects of brassinosteroids on the plant responses to environmental stresses. — Plant Physiol. Biochem. 47: 1–8, 2009.
Clouse, S.D., Sasse, J.: Brassinosteroids: essential regulators of plant growth and development. — Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 49: 427–451, 1998.
Dhaubhadel, S., Krishna, P.: Identification of differentially expressed genes in brassinosteroid-treated Brassica napus seedlings. — J. Plant Growth Regul. 27: 297–300, 2008.
Divi, U.K., Krishna, P.: Brassinosteroid: a biotechnological target for enhancing crop yield and stress tolerance. — New Biotechnol. 36: 131–136, 2009.
Dobrikova, A.G., Vladkova, R.S., Rashkov, G.D., Todinova, S.J., Krumova, S.B., Apostolova, E.L.: Effects of exogenous 24-epibrassinolide on the photosynthetic membranes under non-stress conditions. — Plant Physiol. Biochem. 80: 75–82, 2014.
Fariduddin, Q., Yusuf, M., Ahmad, I., Ahmad, I.: Brassinosteroids and their role in response of plants to abiotic stress. — Biol. Plant. 58: 9–17, 2014.
Goetz, M., Godt, D.E., Roitsch, T.: Tissue-specific induction of the mRNA for an extracellular invertase isoenzyme of tomato by brassinosteroids suggests a role for steroid hormones in assimilate partitioning. — Plant J. 22: 515–522, 2000.
Hershkovitz, V., Sela, N., Taha-Salaime, L., Liu, J., Rafael, G., Kessler, C., Aly, R., Levy, M., Wisniewski, M., Droby, S.: De-novo assembly and characterization of the transcriptome of Metschnikowia fructicola reveals differences in gene expression following interaction with Penicillium digitatum and grapefruit peel. — BMC Genomics 14: 168–181, 2013.
Janeczko, A., Oklestkova, J., Pociecha, E., Koscielniak, J., Mirek, M.: Physiological effects and transport of 24-epibrassinolide in heat-stressed barley. — Acta. Physiol. Plant. 33: 1249–1259, 2011.
Kanehisa, M., Araki, M., Goto, S., Hattori, M., Hirakawa, M., Itoh, M., Katayama, T., Kawashima, S., Okuda, S., Tokimatsu, T., Yamanishi, Y.: KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. — Nucl. Acids Res. 36: 480–484, 2008.
Kosmas, S.A., Argyrokastritis, A., Loukas, M.G., Eliopoulos, E., Tsakas, S., Kaltsikes, P.J.: Isolation and characterization of drought-related trehalose 6-phosphate-synthase gene from cultivated cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L). — Planta 223: 329–339, 2006.
Krumova, S., Zhiponova, M., Dankov, K., Velikova, V., Balashev, K., Andreeva, T., Russinova, E., Taneva, S.: Brassinosteroids regulate the thylakoid membrane architecture and the photosystem II function. — J. Photochem. Photobiol. B. 126: 97–104, 2013.
Li, B., Dewey, C.: RSEM: accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. — BMC Bioinformatics 12: 323, 2011.
Li, F., Fan, G., Wang, K., Sun, F., Yuan, Y., Song, G., Li, Q., Ma, Z., Lu, C., Zou, C., Chen, W., Liang, X., Shang, H., Liu, W., Shi, C., Xiao, G., Gou, C., Ye, W., Xu, X., Zhang, X., Wei, H., Li, Z., Zhang, G., Wang, J., Liu, K., Kohel, R.J., Percy, R.G., Yu, J.Z., Zhu, Y.X., Wang, J., Yu, S.: Genome sequence of the cultivated cotton Gossypium arboretum. — Nat. Genet. 46: 567–574, 2014.
Liu, B., Yue, Y.M., Li, R., Shen, W.J., Wang, K.L.: Plant leaf chlorophyll content retrieval based on a field imaging spectroscopy system. — Sensors 14: 19910–19925, 2014.
Livak, K.J., Schmittgen, T.D.: Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCt method. — Methods 25: 402–408, 2001.
Mao, X., Cai, T., Olyarchuk, J.G., Wei, L.: Automated genome annotation and pathway identification using the KEGG Orthology (KO) as a controlled vocabulary. — Bioinformatics 21: 3787–3793, 2005.
Mortazavi, A., Williams, B.A., McCue, K., Schaeffer, L., Wold, A.: Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. — Nat. Methods. 5: 621–628, 2008.
Peng, Z., He, S., Gong, W., Sun, J., Pan, Z., Xu, F., Lu, Y., Du, X.: Comprehensive analysis of differentially expressed genes and transcriptional regulation induced by salt stress in two contrasting cotton genotypes. — BMC Genomics 15: 760, 2014.
Sharma, I., Ching, E., Saini, R., Bhardwaj, S., Pati, P.K.: Exogenous application of brassinosteroid offers tolerance to salinity by altering stress responses in rice variety Pusa Basmati-1. — Plant Physiol. Biochem. 69: 17–26, 2013.
Shu, H., Guo, S., Gong, Y., Ni, W.: [Effects of brassinolide on leaf physiological characteristics and differential gene expression profiles of NaCl-stressed cotton.] — Chin. J. appl. Ecol. 27: 150–156, 2016. [In Chin.]
Shu, H., Ni, W., Guo, S., Gong, Y., Shen, X., Zhang, X., Xu, P., Guo, Q.: Root-applied brassinolide can alleviate the NaCl injuries on cotton. — Acta Physiol. Plant. 37: 75, 2015.
Storey, J.D., Tibshirani, R.: Statistical significance for genomewide studies. — Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA. 100: 9440–9445, 2003.
Wang, K., Wang, Z., Li, F., Ye, W., Wang, J., Song, G., Yue, Z., Cong, L., Shang, H., Zhu, S., Zou, C., Li, Q., Yuan, Y., Lu. C., Wei. H., Gou, C., Zheng, Z., Yin, Y., Zhang, X., Liu, K., Wang, B., Song, C., Shi, N., Kohel, R.J., Percy, R.G., Yu, J.Z., Zhu, Y.X., Wang, J., Yu, S.: The draft genome of a diploid cotton Gossypium raimondii. — Nat. Genetics 44: 1098–1103, 2012.
Wu, C.Y., Trieu, A., Radhakrishnan, P., Kwok, S.F., Harris, S., Zhang, K., Wang, J., Wan, J., Zhai, H., Takatsuto, S., Matsumoto, S., Fujioka, S., Feldmann, K.A., Pennella, R.I.: Brassinosteroids regulate grain filling in rice. — Plant Cell 20: 2130–2145, 2008.
Xu, P., Liu, Z., Fan, X., Gao, J., Zhang, X., Zhang, X., Shen, X.: De novo transcriptome sequencing and comparative analysis of differentially expressed genes in Gossypium aridum under salt stress. — Gene 525: 26–34, 2013.
Yao, D., Zhang, X., Zhao, X., Liu, C., Wang, C., Zhang, Z., Zhang, C., Wei, Q., Wang, Q., Yan, H., Li, F., Su, Z.: Transcriptome analysis reveals salt-stress-regulated biological processes and key pathways in roots of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). — Genomics 98: 47–55, 2011.
Young, M.D., Wakefield, M.J., Smyth, G.K., Oshlack, A.: Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: accounting for selection bias. — Genome Biol. 11: 1–12, 2010.
Zhang, T., Hu, Y., Jiang, W., Fang, L., Guan, X., Chen, J., Zhang, J., Saski, CA., Scheffler, B.E., Stelly, D.M., Hulse-Kemp, A.M., Wan, Q., Liu, B., Liu, C., Wang, S., Pan, M., Wang, Y., Wang, D., Ye, W., Chang, L., Zhang, W., Song, Q., Kirkbride, R.C., Chen, X., Dennis, E., Llewellyn, D.J., Peterson, D.G., Thaxton, P., Jones, D.C., Wang, Q., Xu X., Zhang, H., Wu, H., Zhou, L., Mei, G., Chen, S., Tian, Y., Xiang, D., Li, X., Ding, J., Zuo, Q., Tao, L., Liu, Y., Li, J., Lin, Y., Hui, Y., Cao, Z., Cai, C., Zhu, X., Jiang, Z., Zhou, B., Guo, W., Li, R., Chen, Z.J.: Sequencing of allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L. acc.TM-1) provides a resource for fiber improvement. — Nat. Biotechnol. 33: 531–537, 2015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Acknowledgments: This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31201139), the National Transgenic Program (2016ZX08005-001), and the Jiangsu Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Funds (CX (13) 5011).
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shu, H.M., Guo, S.Q., Gong, Y.Y. et al. RNA-seq analysis reveals a key role of brassinolide-regulated pathways in NaCl-stressed cotton. Biol Plant 61, 667–674 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-017-0736-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-017-0736-5