Abstract
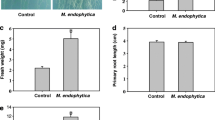
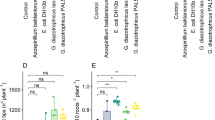
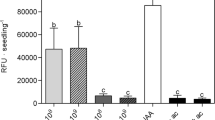
A wide range of microorganisms found in the rhizhosphere are able to regulate plant growth and development, but little is known about the mechanism by which epiphytic microbes inhibit plant growth. Here, an epiphytic bacteria Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, named as LZMBW216, were isolated and identified from the potato (Solanum tuberosum L. cv. Da Xi Yang) leaf surface. They could decrease primary root elongation and lateral root numbers in Arabidopsis seedlings. The inhibitory effects of LZMBW216 on plant growth were not due to a reduced indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) content, as exogenously applied IAA did not recover the inhibition. Furthermore, LZMBW216 did not affect the expression of DR5::GUS and CycB1;1::GUS. However, we found that LZMBW216 exhibited little effect on the primary root elongation in the pin2 mutant and on the lateral root numbers in the aux1-7 mutant. Moreover, LZMBW216 decreased expressions of AUX1 and PIN2 proteins. Together, these results suggest that root system architecture alterations caused by LZMBW216 may involve polar auxin transport.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACC:
-
1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid
- ET:
-
ethylene
- GFP:
-
green fluorescent protein
- IAA:
-
indole-3-acetic acid
- GUS:
-
ß-glucuronidase
- KB:
-
King’s B medium
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- YFP:
-
yellow fluorescent protein
References
Abanda-Nkpwatt, D., Müsch, M., Tschiersch, J., Boettner, M., Schwab, W.: Molecular interaction between Methylobacterium extorquens and seedlings: growth promotion, methanol consumption, and localization of the methanol emission site. — J. exp. Bot. 57: 4025–4032, 2006.
Alabadí, D., Gil, J., Blázquez, M., García-Martínez, J.: Gibberellins repress photomorphogenesis in darkness. — Plant Physiol. 134: 1050–1057, 2004.
Alström, S., Burns, R.: Cyanide production by rhizobacteria as a possible mechanism of plant growth inhibition. — Biol. Fertil. Soils 7: 232–238, 1989.
Arase, F., Nishitani, H., Egusa, M., Nishimoto, N., Sakurai, S., Sakamoto, N., Kaminaka, H.: IAA8 involved in lateral root formation interacts with the TIR1 auxin receptor and ARF transcription factors in Arabidopsis. — PloS ONE 7: e43414, 2012.
Arkhipova, T.N., Veselov, S.U., Melentiev, A.I., Martynenko, E.V., Kudoyarova, G.R.: Ability of bacterium Bacillus subtilis to produce cytokinins and to influence the growth and endogenous hormone content of lettuce plants. — Plant Soil 272: 201–209, 2005.
Badri, D.V., Vivanco, J.M.: Regulation and function of root exudates. — Plant Cell Environ. 32: 666–681, 2009.
Bais, H.P., Weir, T.L., Perry, L.G., Gilroy, S., Vivanco, J.M.: The role of root exudates in rhizosphere interactions with plants and other organisms. — Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 57: 233–266, 2006.
Blom, D., Fabbri, C., Eberl, L., Weisskopf, L.: Volatilemediated killing of Arabidopsis thaliana by bacteria is mainly due to hydrogen cyanide. — Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77: 1000–1008, 2011.
Boerjan, W., Cervera, M.T., Delarue, M., Beeckman, T., Dewitte, W., Bellini, C., Caboche, M., Van Onckelen, H., Van Montagu, M., Inzé, D.: Superroot, a recessive mutation in Arabidopsis, confers auxin overproduction. — Plant Cell 7: 1405–1419, 1995.
Brown, R.L., Kazan, K., McGrath, K.C., Maclean, D.J., Manners, J.M.: A role for the GCC-box in jasmonate-mediated activation of the PDF1.2 gene in Arabidopsis. — Plant Physiol. 132: 1020–1032, 2003.
Calderon Villalobos, L.I., Lee, S., De Oliveira, C., Ivetac, A., Brandt, W., Armitage, L., Sheard, L.B., Tan, X., Parry, G., Mao H.: A combinatorial TIR1/AFB-Aux/IAA co-receptor system for differential sensing of auxin. — Natur. Chem. Biol. 8: 477–485, 2012.
Camehl, I., Sherameti, I., Venus, Y., Bethke, G., Varma, A., Lee, J., Oelmueller, R. Ethylene signalling and ethylene-targeted transcription factors are required to balance beneficial and nonbeneficial traits in the symbiosis between the endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica and Arabidopsis thaliana. - New Phytol. 185: 1062–1073. 2010.
Casimiro, I., Marchant, A., Bhalerao, RP., Beeckman, T., Dhooge, S., Swarup, R., Graham, N., Inzé, D., Sandberg, G., Casero, P.J., Bennett, M.: Auxin transport promotes Arabidopsis lateral root initiation. — Plant Cell 13: 843–852, 2001.
Celenza, J.L., Grisafi, P.L., Fink, G.R.: A pathway for lateral root formation in Arabidopsis thaliana. — Genes Dev. 9: 2131–2142, 1995.
Cesarz, S., Fender, A.-C., Beyer, F., Valtanen, K., Pfeiffer, B., Gansert, D., Hertel, D., Polle, A., Daniel, R., Leuschner, C.: Roots from beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) and ash (Fraxinus excelsior L.) differentially affect soil microorganisms and carbon dynamics. — Soil Biol. Biochem. 61: 23–32, 2013.
Chao, Q., Rothenberg, M., Solano, R., Roman, G., Terzaghi, W.: Activation of the ethylene gas response pathway in Arabidopsis by the nuclear protein ETHYLENE-INSENSITIVE3 and related proteins. — Cell 89: 1133–1144, 1997.
Chang, C., Kwok, S.F., Bleecker, A.B., Meyerowitz, E.M.: Arabidopsis ethylene-response gene ETR1: similarity of product to two-component regulators. — Science 262: 539–544, 1993.
Clark, D.G., Gubrium, E.K., Barrett, J.E., Nell, T.A., Klee, H.J.: Root formation in ethylene-insensitive plants. — Plant Physiol. 121: 53–60, 1999.
Colón-Carmona, A., You, R., Haimovitch-Gal, T., Doerner, P.: Spatio-temporal analysis of mitotic activity with a labile cyclin-GUS fusion protein. — Plant J. 20: 503–508, 1999.
Contesto, C., Milesi, S., Mantelin, S., Zancarini, A., Desbrosses, G., Varoquaux, F., Bellini, C., Kowalczyk, M., Touraine, B.: The auxin-signaling pathway is required for the lateral root response of Arabidopsis to the rhizobacterium Phyllobacterium brassicacearum. — Planta 232: 1455–1470, 2010.
Contreras-Cornejo, H.A., Macías-Rodríguez, L., Cortés-Penagos, C., López-Bucio, J.: Trichoderma virens, a plant beneficial fungus, enhances biomass production and promotes lateral root growth through an auxin-dependent mechanism in Arabidopsis. — Plant Physiol. 149: 1579–1592, 2009.
D'Haeze, W., De Rycke, R., Mathis, R., Goormachtig, S., Pagnotta, S., Verplancke, C., Capoen, W., Holsters, M.: Reactive oxygen species and ethylene play a positive role in lateral root base nodulation of a semiaquatic legume. — Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 100: 11789–11794, 2003.
Dharmasiri, N., Dharmasiri, S., Estelle, M.: The F-box protein TIR1 is an auxin receptor. — Nature 435: 441–445, 2005a.
Dharmasiri, N., Dharmasiri, S., Weijers, D., Lechner, E., Yamada, M., Hobbie, L., Ehrismann, J.S., Jurgens, G., Estelle, M.: Plant development is regulated by a family of auxin receptor F box proteins. — Dev. Cell 9: 109–119, 2005b.
Ditengou, F.A., Béguiristain, T., Lapeyrie, F.: Root hair elongation is inhibited by hypaphorine, the indole alkaloid from the ectomycorrhizal fungus Pisolithus tinctorius, and restored by indole-3-acetic acid. — Planta 211: 722–728, 2000.
Dreher, KA., Brown, J., Saw, RE., Callis, J.: The Arabidopsis Aux/IAA protein family has diversified in degradation and auxin responsiveness. — Plant Cell 18: 699–714, 2006.
Felten, J., Kohler, A., Morin, E., Bhalerao, R.P., Palme, K., Martin, F., Ditengou, F.A., Legué, V.: The ectomycorrhizal fungus Laccaria bicolor stimulates lateral root formation in poplar and Arabidopsis through auxin transport and signaling. — Plant Physiol. 151: 1991–2005, 2009.
Friml, J., Yang, X., Michniewicz, M., Weijers, D., Quint, A., Tietz, O., Benjamins, R., Ouwerkerk, P.B., Ljung, K., Sandberg, G.: A PINOID-dependent binary switch in apical-basal PIN polar targeting directs auxin efflux. — Science 306: 862–865, 2004.
Fujimoto, S.Y., Ohta, M., Usui, A., Shinshi, H., Ohme-Takagi, M.: Arabidopsis ethylene-responsive element binding factors act as transcriptional activators or repressors of GCC box-mediated gene expression. — Plant Cell 12: 393–404, 2000.
Fujita, H., Syono, K.: Genetic analysis of the effects of polar auxin transport inhibitors on root growth in Arabidopsis thaliana. — Plant Cell Physiol. 37: 1094–1101, 1996.
Glick, B.R.: Modulation of plant ethylene levels by the bacterial enzyme ACC deaminase. — FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 251: 1–7, 2005.
Gray, E.J., Smith, D.L.: Intracellular and extracellular PGPR: commonalities and distinctions in the plant-bacterium signaling processes. — Soil Biol. Biochem. 37: 395–412, 2005.
Guilfoyle, T.J., Hagen, G.: Auxin response factors. — Curr Opin Plant Biol. 10: 453–460, 2007.
Hall, A.E., Chen, Q.G., Findell, J.L., Schaller, G.E., Bleecker, A.B.: The relationship between ethylene binding and dominant insensitivity conferred by mutant forms of the ETR1 ethylene receptor. — Plant Physiol. 121: 291–300, 1999.
Hao, D., Ohme-Takagi, M., Sarai, A.: Unique mode of GCC box recognition by the DNA-binding domain of ethylene-responsive element binding factor (ERF domain) in plants. — J. biol. Chem. 273: 26857–26861, 1998.
Hirsch, A.M., Fang, Y., Asad, S., Kapulnik, Y.: The role of phytohormones in plant-microbe symbioses. — Plant Soil 194: 171–184, 1997.
Hua, J., Chang, C., Sun, Q., Meyerowitz, EM.: Ethylene insensitivity conferred by Arabidopsis ERS gene. — Science 269: 1712–1714, 1995a.
Hua, J., Meyerowitz, E.M.: Ethylene responses are negatively regulated by a receptor gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. — Cell 94: 261–271, 1998.
Hua, J., Sakai, H., Nourizadeh, S., Chen, Q.G., Bleecker, A.B., Ecker, J.R., Meyerowitz E.M.: EIN4 and ERS2 are members of the putative ethylene receptor gene family in Arabidopsis. — Plant Cell 10: 1321–1332, 1998b.
Ivanchenko, M.G., Muday, G.K., Dubrovsky, J.G.: Ethylene-auxin interactions regulate lateral root initiation and emergence in Arabidopsis thaliana. — Plant J. 55: 335–347, 2008.
Johnson, D., Martin, F., Cairney, J.W.G., Anderson, I.C.: The importance of individuals: intraspecific diversity of mycorrhizal plants and fungi in ecosystems. — New Phytol. 194: 614–628, 2012.
Karadeniz, A., Topcuoglu, S.F., Inan, S.: Auxin, gibberellin, cytokinin and abscisic acid production in some bacteria. — World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 22: 1061–1064, 2006.
Kieber, J.J., Rothenberg, M., Roman, G., Feldmann, K.A., Ecker, J.R.: CTR1, a negative regulator of the ethylene response pathway in Arabidopsis, encodes a member of the Raf family of protein kinases. — Cell 72: 427–441, 1993.
Lewis, D.R., Negi, S., Sukumar, P., Muday, G.K.: Ethylene inhibits lateral root development, increases IAA transport and expression of PIN3 and PIN7 auxin efflux carriers. — Development 138: 3485–3495, 2011.
Lincoln, C., Britton, J.H., Estelle, M.: Growth and development of the axr1 mutants of Arabidopsis. — Plant Cell 2: 1071–1080, 1990.
Lindow, S.E., Brandl, M.T.: Microbiology of the phyllosphere. — Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 69: 1875–1883, 2003.
Ljung K.: Auxin metabolism and homeostasis during plant development. — Development 140: 943–950, 2013.
Long, H.H., Sonntag, D.G., Schmidt, D.D., Baldwin, I.T.: The structure of the culturable root bacterial endophyte community of Nicotiana attenuata is organized by soil composition and host plant ethylene production and perception. - New Phytol. 185: 554–567. 2010.
López-Bucio, J., Campos-Cuevas, J.C., Hernández-Calderón, E., Velásquez-Becerra, C., Farías-Rodríguez, R., Macías-Rodríguez, L.I., Valencia-Cantero, E. Bacillus megaterium rhizobacteria promote growth and alter root-system architecture through an auxin-and ethylene-independent signaling mechanism in Arabidopsis thaliana. - Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 20: 207–217, 2007.
López-Bucio, J., Cruz-Ramírez, A., Herrera-Estrella, L.: The role of nutrient availability in regulating root architecture. — Curr. Opin. Plant. Biol. 6: 280–287, 2003.
López-Bucio, J., Hernández-Abreu, E., Sánchez-Calderón, L., Nieto-Jacobo, M.F., Simpson, J., Herrera-Estrella, L.: Phosphate availability alters architecture and causes changes in hormone sensitivity in the Arabidopsis root system. — Plant Physiol. 129: 244–256, 2002.
Meldau, D.G., Long, H.H., Baldwin, I.T.: A native plant growth promoting bacterium, Bacillus sp. B55, rescues growth performance of an ethylene-insensitive plant genotype in nature. — Front. Plant Sci. 3: 1–13, 2012.
Misaghi, I., Donndelinger, C.: Endophytic bacteria in symptom-free cotton plants. — Phytopathology 80: 808–811, 1990.
Morgan, J.A.W., Bending, G.D., White, P.J.: Biological costs and benefits to plant-microbe interactions in the rhizosphere. — J. exp. Bot. 56: 1729–1739, 2005.
Negi, S., Ivanchenko, M.G., Muday, G.K.: Ethylene regulates lateral root formation and auxin transport in Arabidopsis thaliana. — Plant J. 55: 175–187, 2008.
Ohta, M., Ohme-Takagi, M., Shinshi, H.: Three ethylene-responsive transcription factors in tobacco with distinct transactivation functions. — Plant J. 22: 29–38, 2000.
Oldroyd, G.E.D., Downie, J.A.: Coordinating nodule morphogenesis with rhizobial infection in legumes. — Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 59: 519–546, 2008.
O'Malley, R.C., Rodriguez, F.I., Esch, J.J., Binder, B.M., O'Donnell, P., Klee, H.J., Bleecker, A.B.: Ethylene-binding activity, gene expression levels, and receptor system output for ethylene receptor family members from Arabidopsis and tomato. — Plant J. 41: 651–659, 2005.
Perrine-Walker, F.M., Jublanc, E.: The localization of auxin transporters PIN3 and LAX3 during lateral root development in Arabidopsis thaliana. — Biol. Plant. 58: 778–782, 2014.
Persello-Cartieaux, F., David, P., Sarrobert, C., Thibaud, M.C., Achouak, W., Robaglia, C., Nussaume, L.: Utilization of mutants to analyze the interaction between Arabidopsis thaliana and its naturally root-associated Pseudomonas. — Planta 212: 190–198, 2001.
Ping, L., Boland, W.: Signals from the underground: bacterial volatiles promote growth in Arabidopsis. — Trends Plant Sci. 9: 263–266, 2004.
Ruegger, M., Dewey, E., Gray, W.M., Hobbie, L., Turner, J., Estelle, M.: The TIR1 protein of Arabidopsis functions in auxin response and is related to human SKP2 and yeast grr1p. — Genes Dev. 12: 198–207, 1998.
Ružicka, K., Ljung, K., Vanneste, S., Podhorská, R., Beeckman, T., Friml, J., Benková, E.: Ethylene regulates root growth through effects on auxin biosynthesis and transportdependent auxin distribution. — Plant Cell 19: 2197–2212, 2007.
Ryu, C.M., Farag, M.A., Hu, C.H., Reddy, M.S., Wei, H.X., Paré, P.W., Kloepper, J.W.: Bacterial volatiles promote growth in Arabidopsis. — Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 100: 4927–4932, 2003.
Ryu, C.M., Hu, C.H., Locy, R., Kloepper, J.: Study of mechanisms for plant growth promotion elicited by rhizobacteria in Arabidopsis thaliana. — Plant Soil 268: 285–292, 2005.
Sakai, H., Hua, J., Chen, Q.G., Chang, C., Medrano, L.J., Bleecker, A.B., Meyerowitz, E.M.: ETR2 is an ETR1-like gene involved in ethylene signaling in Arabidopsis. — Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA. 95: 5812–5817, 1998.
Shkolnik-Inbar, D., Bar-Zvi, D.: ABI4 mediates abscisic acid and cytokinin inhibition of lateral root formation by reducing polar auxin transport in Arabidopsis. — Plant Cell 22: 3560–3573, 2010.
Slankis, V.: Soil factors influencing formation of mycorrhizae. — Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 12: 437–457, 1974.
Stepanova, A.N., Hoyt, J.M., Hamilton, A.A., Alonso, J.M.: A link between ethylene and auxin uncovered by the characterization of two root-specific ethylene-insensitive mutants in Arabidopsis. — Plant Cell 17: 2230–2242, 2005.
Sturz, AV., Christie, B.R., Nowak, J. Bacterial endophytes: potential role in developing sustainable systems of crop production. - Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 19: 1–30, 2000.
Sukumar, P., Legue, V., Vayssieres, A., Martin, F., Tuskan, G.A., Kalluri, U.C.: Involvement of auxin pathways in modulating root architecture during beneficial plantmicroorganism interactions. — Plant Cell Environ. 36: 909–919, 2013.
Swarup, K., Benkova, E., Swarup, R., Casimiro, I., Peret, B., Yang, Y., Parry, G., Nielsen, E., De Smet, I., Vanneste, S., Levesque, M.P., Carrier, D., James, N., Calvo, V., Ljung, K., Kramer, E., Roberts, R., Graham, N., Marillonnet, S., Patel, K., Jones, J.D.G., Taylor, C.G., Schachtman, D.P., May, S., Sandberg, G., Benfey, P., Friml, J., Kerr, I., Beeckman, T., Laplaze, L., Bennett, M.J.: The auxin influx carrier LAX3 promotes lateral root emergence. — Natur. Cell Biol. 10: 946–954, 2008.
Tiwari, S,B., Hagen, G., Guilfoyle, T.: The roles of auxin response factor domains in auxin-responsive transcription. — Plant Cell. 15: 533–543, 2003.
Ulmasov, T., Murfett, J., Hagen, G., Guilfoyle, T.J.: Aux/IAA proteins repress expression of reporter genes containing natural and highly active synthetic auxin response elements. — Plant Cell 9: 1963–1971, 1997.
Wang, J., Zhang, Y., Li, Y., Wang, X., Nan, W., Hu, Y., Zhang, H., Zhao, C., Wang, F., Li, P., Shi, H., Bi, Y.: Endophytic microbes Bacillus sp. LZR216-regulated root development is dependent on polar auxin transport in Arabidopsis seedlings. — Plant Cell Rep. 34: 1075–1087, 2015.
Weijers, D., Benkova, E., Jager, K.E., Schlereth, A., Hamann, T., Kientz, M., Wilmoth, J.C., Reed, J.W., Jurgens, G.: Developmental specificity of auxin response by pairs of ARF and Aux/IAA transcriptional regulators. — EMBO J. 24: 1874–1885, 2005.
Weise, T., Kai, M., Piechulla, B.: Bacterial ammonia causes significant plant growth inhibition. — PloS ONE 8: e63538, 2013.
Wilmoth, J.C., Wang, S., Tiwari, S.B., Joshi, A.D., Hagen, G., Guilfoyle, T.J., Alonso, J.M., Ecker, J.R., Reed, J.W.: NPH4/ARF7 and ARF19 promote leaf expansion and auxin-induced lateral root formation. — Plant J. 43: 118–130, 2005.
Woodward, A.W., Bartel, B.: Auxin: regulation, action, and interaction. — Ann. Bot. 95: 707–735, 2005.
Zamioudis, C., Mastranesti, P., Dhonukshe, P., Blilou, I., Pieterse, C.: Unraveling root developmental programs initiated by beneficial Pseudomonas spp. bacteria. — Plant Physiol. 162: 304–318, 2013.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (2012CB026105), the National High Technology Research and Development Program (2007AA021401), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31170225; 31201145), the Foundation of Science and Technology Program of Gansu Province (1107RJYA005), the Scientific research project of Qinghai-Tibetan DC Interconnection Project in State Grid Corporation of China, and the Foundation of Science and Technology Program of Gansu Province (1208RJZA224). The first two authors contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Zhang, Y., Li, Y. et al. Involvement of polar auxin transport in the inhibition of Arabidopsis seedling growth induced by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia . Biol Plant 60, 299–310 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-016-0585-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-016-0585-7