Abstract
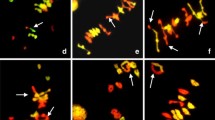
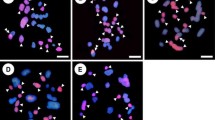
Cryptic intergenomic pairing of genus Zea was induced by the use of a diluted colchicine solution in order to elucidate the phylogenetic relations and differentiation of the homoeologous genomes. Results indicate that in species and hybrids with 2n = 20, there was chromosome pairing between the homoeologous A and B genomes with a maximum of 5IV, with the exception of Zea diploperennis and their interspecific hybrids where cryptic homoeologous chromosome pairing was not induced. In almost all 2n = 30 hybrids, observed cryptic pairing increased to a maximum of 10III although Z. mays × Z. mays with 2n = 30 did not show significant differences between treated and untreated materials. Pairing was also observed in species and hybrids with 2n = 40, in which a maximum of 10IV was observed, with the exception of Z. mays with 2n = 40 where treated and untreated cells did not differ significantly.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A:
-
subgenome A Zea
- B:
-
subgenome B Zea
- Bp1:
-
subgenome Bp1 Zea perennis
- Bp2:
-
subgenome Bp2 Zea perennis
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4 dichlorophenoxyacetic
- I:
-
chromosome monovalent
- II:
-
chromosome bivalent
- III:
-
chromosome trivalent
- IV:
-
chromosome quadrivalent
- pam1 :
-
gene plural abnormalities of meiosis
- Ph :
-
gene pairing homoeologous
- Ph1 :
-
pairing homoeologous 1
References
Bass, H.W., Riera-Lizarazu, O., Ananiev, E.V.B., Bordolini, S.J., Rines, H.W., Phillips, R.L., Sedat, J.W., Agard, D.A., Cande, Z.W.: Evidence for the coincident initiation of homologous pairing and synapsis during the telomereclustering (bouquet) stage of meiotic prophase. — J. Cell Sci. 113: 1033–1042, 2000.
Bozza, C.G., Pawlowsky, W.P.: The cytogenetics of homologous chromosome pairing in meiosis in plants. — Cytogenet. Genet. Res. 120: 313–319, 2008.
Chikashige, Y., Haraguchi, T., Hiraoka, Y.: Nuclear envelope attachment is not necessary for telomere function in fission yeast. — Nucleus 1: 481–486, 2010.
Dobley, J., Iltis, H.H.: Taxonomy of Zea (Gramineae). I. A subgeneric classification with key to taxa. — Amer. J. Bot. 67: 982–993, 1980.
Dover, G.A., Riley, R.: The effect of spindle inhibitors applied before meiosis on meiotic chromosome pairing. — J. Cell. Sci. 12: 143–161, 1973.
Driscoll, C.J., Darvey, N.L.: Chromosome pairing: effect of colchicine on an isochromosome. — Science 169: 290–291, 1970.
Driscoll, C.J., Darvey, N.L., Barber, H.N.: Effect of colchicine on meiosis of hexaploid wheat. — Nature 216: 687–688, 1967.
Feldman, M., Avivi, L.: Genetic control of bivalent pairing in common wheat. The mode of Ph1 action. — In: Brandham, P.E. (ed.) Kew Chromosome Conference III. Pp. 269–279. Royal Botanic Garden, London 1988.
Feldman, F., Liu, B., Segal, G., Abbo, S., Levy. A.: Rapid elimination of low copy DNA sequences in polyploidy wheat: a possible mechanism for differentiation of homeologous chromosomes. — Genetics 147: 1381–1387, 1997.
Fukunaga, K., Hill, J., Vigoroux, Y., Matsuoka, Y., Sanchez G., J., Liu, K., Bucker, E., Doebley, J.: Genetic diversity and population structure of teosinte. — Genetics 169: 2241–2254, 2005.
Furini, A., Jewell, C.: Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration of maize/Tripsacum hybrids. — Maydica 40: 205–210, 1995.
García, M.D., Molina, M. del C.: Embryo rescue and induction of somatic embryogenesis as a method to overcome seed inviability in Zea mays ssp. mays (2n = 40) × Zea mays ssp. parviglumis crosses. — Biol. Plant. 44: 497–501, 2001.
García, M.D., Molina, M. del C., Caso, 0.H.: [Maize (Zea mays ssp. mays) plant regeneration from tissue culture and its applications in maize breeding.] — Rev. Fac. Agron. UNLP 68: 15–25, 1992. [In Spanish]
Goluboskaya, I.N., Harper, L.C., Pawlowski, W.P., Schicnes, D.; Cande, W.Z.: The pam1 gene is required for meiotic bouquet formation and efficient homologous synapsis in maize (Zea mays L.). — Genetics 162: 1979–1993, 2002.
González, G., Poggio, L.: Karyotype of Zea luxurians and Z. mays subsp. mays using FISH/DAPI, and analysis of meiotic behavior of hybrids. — Genome 54: 26–32, 2011.
Harper, L., Golubovskaya, I., Cande, W.Z.: A bouquet of chromosomes. — J. Cell. Sci. 117: 4025–4032, 2004.
Iltis, H.H., Benz B.F: Zea nicaraguensis (Poaceae), a new teosinte from Pacific coastal Nicaragua. — Novon 10: 382–390, 2000.
Iltis, H.H.; Dobley J.: Taxonomy of Zea (Gramineae). II Subspecific categories in the Zea mays comple× and a generic synopsis. — Amer. J. Bot. 67: 994–1004, 1980.
Jackson, R.C.: Polyploidy and diploidy: new perspectives on chromosome pairing and its evolutionary implications. — Amer. J. Bot. 69: 1512–1523, 1982.
Jackson, R.C., Murray, B.G.: Colchicine-induced quadrivalent formation in Helianthus: evidence of ancient polyploidy. — Theor. appl. Genet. 64: 219–222, 1983.
Jenczewski, E., Alix, K.: From diploids to allopolyploids: the emergence of efficient pairing control genes in plants. — Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 23: 21–25, 2004.
Jenkins, G., Chatterjee, R.: Chromosome structure and pairing preferences in tetraploid rye (Secale cereale). — Genome 37: 784–793, 1994.
Molina, M. del C.: Estudios citogenéticos evolutivos del Género Zea. [Cytogenetic Study of Zea Genus Evolution] — PhD Thesis, Polytechnic University of Valencia, Valencia 2011. [In Spanish].
Molina, M. del C., Chorzempa, S.E., García, M.D.: Meiotic pairing in the hybrid (Zea mays × Zea diploperennis) × Zea luxurians. — Maize Genet. Coop. Newslett. 79: 5–7, 2005.
Molina, M. del C., García, M.D.: Influence of ploidy levels on phenotypic and cytogenetic traits in maize and Zea perennis hybrids. — Cytologia 64: 101–109, 1999.
Molina, M. del C., García, M.D.: Meiotic pairing in the interspecific hybrid Zea mays, Z. perennis and Zea diploperennis. — Maize Genet. Coop. Newslett. 74: 42–43, 2000.
Molina, M. del C., García, M.D.: Ploidy levels affect phenotype and cytogenetic traits in Zea mays ssp. mays (2n = 20 or 40) and Zea mays ssp. parviglumis hybrids — Cytologia 66: 189–196, 2001.
Molina, M. del C., García, M.D., López C.G., Moreno Ferrero, V.: Meiotic pairing in the hybrid (Zea diploperennis × Zea perennis) × Zea mays and its reciprocal. — Hereditas 141: 135–141, 2004.
Molina, M. del C., Naranjo, C.A.: Cytogenetic studies in the genus Zea. I. Evidence for five as the basic chromosomes number. — Theor. appl. Genet. 73: 542–550, 1987.
Naranjo, C.A., Molina, M. del C., Poggio, L.: [Evidence of a basic number x = 5 in the genus Zea and its importance in studies of the origin of maize] — Acad. Nac. Cs. Ex. Fis. Nat. 5: 75–84, 1989. [In Spanish].
Naranjo, C.A., Poggio, L., Molina, M. del C., Bernatene, E.: Increase in multivalent frequency in F1 hybrids of Zea diploperennis × Z. perennis by colchicine treatment. — Hereditas 120: 241–244, 1994.
Poggio, L., Molina, M. del C., Naranjo, C.A.: Cytogenetic studies in the genus Zea. 2- colchicine-induced multivalents. — Theor. appl. Genet. 79: 461–464, 1990.
Ruiz, C., Sanchez, J.J., Aguilar, S.M.: Potential geographical distribution of teosinte in Mexico: a GISH approach. — Maydica 46: 105–110, 2001.
Santos, J.L., Lacadena, J.R., Cermeno, M.C., Orellana, J.: Nucleolar organizer activity in wheat-barley chromosome addition lines. — Heredity 53: 425–429, 1984.
Santos, J.L., Orellana, J.: Pairing competition between identical and homologous chromosome in rye and grasshoppers. — Genetics 104: 677–684, 1983.
Schnable, J.C., Freeling, M.: Genes identified by visible mutant phenotypes show increased bias toward one of two subgenomes of maize. — PLoS ONE 6–3: e17855. Doi:101371/journal.pone.0017855, 2011.
Schnable, J.C., Springer, N.M., Freeling, M.: Differentiation of maize subgenome by genome dominance and both ancient and ongoing gene loss. — PNAS 108: 4069–4074, 2011.
Sokal, R.R., Rohlf, Y.: Biometría. — W.H. Freeman and Company, San Francisco 1978.
Swanson-Wagner R., Eichten S., Kumari S., Tiffin P., Stein J., Ware D., Springer N.: Pervasive gene content variation and copy number variation in maize and its undomesticated progenitor. — Genome Res., in press, 2012.
Swigonová, Z., Lai, J., Ma, J., Ramakrisma, W., Llaca, V., Bennetzen, J., Messing, J.: Close split of sorghum and maize genome progenitors. — Genome Res. 14: 1916–1923, 2004.
Wendel, J.: Genome evolution in polyploidy, — Plant mol. Biol. 42: 225–229, 2000.
Zickler, D., Kleckner, N.: The leptotene-zygotene transition of meiosis. — Annu. Rev. Genet. 32: 619–697, 1998.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Acknowedgments: This research was supported by the Universidad Nacional de la Plata, Universidad Nacional de Lomas de Zamora and CONICET.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Molina, M.d.C., López, C.G., Staltari, S. et al. Cryptic homoeology analysis in species and hybrids of genus Zea . Biol Plant 57, 449–456 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-012-0299-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-012-0299-4