Abstract
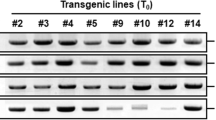
Marker-free transgenic cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) cv. Poinsett 76 SR plants were produced by Agrobacterium mediated transformation. A transformation efficiency of 1.62 was observed on using Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain LBA4404 harbouring Arabidopsis cbf1 gene driven by the inducible promoter RD29A in a binary vector system pCAMBIA. Transgene integration and single copy insert in transgenic cucumber was confirmed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and Southern blot analysis in T0 lines and also confirmed marker-free status in T1 generation. Transgene expression was confirmed by reverse transcription (RT)-PCR in T1 generation transgenic cucumber and advanced to T2 generation. Upon exposure to chilling stress (4 °C), the T2 generation transgenic plants survived up to 36 h; however, wild-type plants could not survive and gradually died. A significant decrease in membrane injury index (MII), increase in activities of antioxidant enzymes (SOD and CAT), free proline content and relative water content (RWC) in the leaves were observed in transgenic cucumber as compared to wild-type under chilling stress. Thus, the transgenic cucumber plants expressing Arabidopsis cbf1 gene conferred protection against chilling stress.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BAP:
-
6-benzylaminopurine
- CAT:
-
catalase
- CBF1:
-
c-repeat binding factor-1
- CTAB:
-
cetyltrimethylammonium bromide
- IBA:
-
indole-3-butyric acid
- MII:
-
membrane injury index
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog’s medium
- NBT:
-
nitroblue tetrazolium chloride
- nptII:
-
neomycin phosphotransferase-II
- RT-PCR:
-
reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
- RWC:
-
relative water content
- SOD:
-
superoxide dismutase
References
Afolabi, A.S., Worland, B., Snape, J., Vain, P.: Multiple T-DNA co-cultivation as a method of producing markerfree (clean gene) transgenic rice (Oryza sativa L.) plant. — Afr. J. Biotechnol. 4: 531–540, 2005.
Ananthakrishnan, G., Xia, X., Elman, C., Singer, S., Paris, H.S., Galon, A., Gaba, V.: Shoot production in squash (Cucurbita pepo) by in vitro organogenesis. — Plant Cell Rep. 21: 739–746, 2003.
Baek, K., Skinner, D.Z., Ling, P., Chen, X.: Molecular structure and organization of the wheat genomic manganese superoxide dismutase gene. — Genome 49: 209–218, 2006.
Baker, S.S., Wilhelm, K.S., Thomoshow, M.F.: The 5′-region of Arabidopsis thaliana COR15a has cis-acting elements that confer cold-, drought- and ABA regulated gene expression. — Plant mol. Biol. 24: 701–713, 1994.
Bates, L.S., Waldren, R.P., Teare, I.D.: Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. — Plant Soil 39: 205–207, 1973.
Beck, E.H., Fetitig, S., Knake, C., Hartig, K., Bhattarai, T.: Specific and unspecific responses of plants to cold and drought stress. — J. Biosci. 32: 501–510, 2007.
Benveniste, R., Davies, J.: Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in bacteria. — Annu. Rev. Biochem. 42: 471–506, 1973.
Bradford, M.: A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein using the principle of protein-dye binding. — Anal. Biochem. 72: 248–254, 1976.
Brasileiro, A.C.M.: Neomicina fosfotransferase II (NPT II). — In: Brasileiro A.C.M., Carneiro V.T.C. (ed.): Manual de Transformação Genética de Plantas. Pp. 143–154. Embrapa-SPI/Embrapa-Cenargen, Brasília 1998.
Chee, P.P.: Transformation of Cucumis sativus tissue by Agrobacterium tumefaciens and the regeneration of transformed plants. — Plant Cell Rep. 9: 245–248, 1990.
Chee, P.P., Slightom, J.L.: Transfer and expression of cucumber mosaic virus coat protein gene in the genome of Cucumis sativus L. — J. amer. Soc. hort. Sci. 116: 1098–1102, 1991.
Choi, P.S., Soh, W.Y., Kim, Y.S., Yoo, O.J., Liu, J.R.: Genetic transformation and plant regeneration of watermelon using Agrobacterium tumefaciens. — Plant Cell Rep. 13: 344–348, 1994.
Compton, M.E.: Interactions between explant size and cultivar affects shoot organogenic competence of watermelon cotyledons. — Hort. Sci. 35: 749–750, 2000.
Djilianov, D., Georgieva, T., Moyankova, D., Atanassov, A., Shinozaki, K., Smeeken, S.C.M., Verma, D.P.S., Murata, N.: Improved abiotic stress tolerance in plants by accumulation of osmoprotactents — gene transfer approach. — Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 19: 63–71, 2005.
Dibax, R., Deschamps, C., Bespalhok Filho, J.C., Vieira, L.G.E., Molinari, H.B.C., De Campos, M.K.F., Quoirin, M.: Organogenesis and Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of Eucalyptus saligna with P5CS gene. — Biol. Plant. 54: 6–12, 2010.
Doyle, J.J., Doyle, J.I.: Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. — Phytochem. Bull. Bot. Soc. Amer. 19: 11–15, 1987.
Fadzilla, N.M., Finch, P.R., Burdon, R.H.: Salinity, oxidative stress and antioxidant responses in shoot culture of rice. — J. exp. Bot. 48: 325–331, 1997.
Ganapathi, A., Perl-Treves, R.: Agrobacterium-mediated transformation in Cucumis sativus L. via direct organogenesis. — Acta Hort. 510: 405–407, 2000.
Gilmour, S.J., Sebolt, A.M., Salazar, M.P., Everard, J.D., Thomashow, M.F.: Overexpression of the Arabidopsis CBF3 transcriptional activator mimics multiple biochemical changes associated with cold acclimation. — Plant Physiol. 124: 1854–1865, 2000.
Gilmour, S.J., Zarka, D.G., Stockinger, E.J., Salazar, M.P., Houghton, J.M., Thomashow, M.F.: Low temperature regulation of the Arabidopsis CBF family of AP2 transcriptional activators as an early step in cold-induced COR gene expression. — Plant J. 16: 433–442, 1998.
Goyary, D., Gupta, N., Khare, N., Anandhan, S., Rathore, M., Ahmed, Z.: In vitro propagation of long melon var. Karnal selection (Cucumis melo L.) from shoot tip. — Int. J. appl. agr. Res. 5: 55–62, 2010.
Hoekstra, F.A., Golovina, E.A., Buitink, J.: Mechanism of plant desiccation tolerance. — Trends Plant Sci. 6: 1360–1385, 2001.
Hsieh, T.H., Lee, J.T., Charng, Y.Y., Chan, M.T.: Tomato plants ectopically expressing Arabidopsis cbf1 show enhanced resistance to water deficit stress. — Plant Physiol. 130: 618–626, 2002.
Jaglo-Ottosen, K.R., Gilmour, S.J., Zarka, D.G., Schabenberger, O., Thomashow, M.F.: Arabidopsis CBF1 over expression induces COR genes and enhances freezing tolerance. — Sciences 280: 104–106, 1998.
Jaleel, C.A., Gopi, R., Manivannan, P., Panneerselvam, R.: Antioxidative potentials as a protective mechanism in Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don. plants under salinity stress. — Turk. J. Bot. 31: 245–251, 2007.
Jia, G.X., Zhu, Z.Q., Chang, F.Q., Li, Y.X.: Transformation of tomato with the BADH gene from Atriplex improves salt tolerance. — Plant Cell Rep. 21: 141–146, 2002.
Kavi, K.P.B., Hong, Z., Miao, G.H., Hu, C.A.A., Verma, D.P.S.: Overexpression of D1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase increases proline production and confers osmotolerance in transgenic plants. — Plant. Physiol. 108: 1387–1394, 1995.
Khan, R.S., Nakamura, I., Mii, M.: Production and selection of marker-free transgenic plants of Petunia hybrida using sitespecific recombination. — Biol. Plant. 54: 265–271, 2010.
Moaed, A., Deshmukh, P.S., Sairam, R.K., Kushwaha, S.R., Singh, T.P.: Protective role of antioxidant enzymes under high temperature stress. — Plant Sci. 117: 382–388, 2006.
Murashige, T., Skoog, F.: A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue culture. — Physiol. Plant. 15: 473–497, 1962.
Nishibayashi, S., Kaneko, H., Hayakawa, T.: Transformation of cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) plants using Agrobacterium tumefaciens and regeneration from hypocotyls explants. — Plant Cell Rep. 15: 809–814, 1996.
Pearce, R.S.: Plant freezing and damage. — Ann. Bot. 87: 417–424, 2001.
Roberto, A., Gaxiola Jisheng, L., Undurraga, S., Dang, L.M., Allen, G.J., Alper, L.S., Fink, G.R.: Drought- and salttolerant plants result from overexpression of the AVP1 H1-pump. — Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 98: 11444–11449, 2001.
Roy, R., Purty, R.S., Agrawal, V., Gupta, S.C.: Transformation of tomato cultivar “Pusa Ruby” with bspA gene from Populus tremula for drought tolerance. — Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 84: 55–67, 2006.
Sarad, N., Rathore, M., Singh, N.K., Kumar, N.: Genetically engineered tomatoes: new vista for sustainable agriculture in high altitude regions. — In: Fisher, T. et al. (ed.): 4th International Crop Science Congress. The Regional Institute, Ltd., Gosford — Brisbane, 2004.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F., Maniatis, T.: Molecular Cloning: a Laboratory Manual. — Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor — New York 1989.
Scandalios, J.G.: Oxygen stress and superoxide dismutase. — Plant Physiol. 10: 17–12, 1993.
Selvaraj, N.: In vitro culture and Agrobacterium mediated genetic transformation in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). — PhD thesis, Bharthidasan University, Trichurapalli 2002.
Shah, P., Singh, N.K., Khare, N., Rathore, M., Anandhan, S., Arif, M., Singh, R.K., Das, S.C., Ahmed, Z., Kumar, N.: Agrobacterium mediated genetic transformation of summer squash ( Cucurbita pepo L. cv. Australian Green) with cbf-1 using a two vector system. — Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 95: 363–371, 2008.
Soniya, E.V., Das, M.R.: In vitro organogenesis and genetic transformation in popular Cucumis sativus L. through Agrobacterium tumefaciens. — Ind. J. exp. Biol. 40: 329–333, 2002.
Stockinger, E.J., Gilmour, S.J., Thomashow, M.F.: Arabidopsis thaliana CBF1 encodes an AP2 domain-containing transcriptional activator that binds to the C-repeat/DRE, a cis-acting DNA regulatory element that stimulates transcription in response to low temperature and water deficit. — Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 94: 1035–1040, 1997.
Thomashow, M.F.: So what’s new in the field of plant cold acclimation? Lots! — Plant Physiol. 125: 89–93, 2001.
Uemura, M., Joseph, R.A., Steponkus, P.L.: Cold acclimation of Arabidopsis thaliana: effect on plasma membrane lipid composition and freeze-induced lesion. — Plant Physiol. 109: 15–30, 1995.
Vasudevan, A., Silvaraj, A., Ganapathi, A., Choi, C.W.: Agrobacterium mediated genetic transformation in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). — Amer. J. Biotechnol. Biochem. 3: 24–32, 2007.
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to DRDO HQ, Ministry of Defence, Govt. of India for the financial assistance. The generous gift of the co-transformation constructs by Dr. A.K. Sharma (Centre for Plant Molecular Biology, University of Delhi, South Campus, India) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, N., Rathore, M., Goyary, D. et al. Marker-free transgenic cucumber expressing Arabidopsis cbf1 gene confers chilling stress tolerance. Biol Plant 56, 57–63 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-012-0016-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-012-0016-3