Abstract
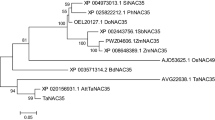
A novel gene induced during hypersensitive reaction (HIR) in wheat was identified using in silico cloning and designated as TaHIR2. The TaHIR2 gene was deduced to encode a 284-amino acid protein, whose molecular mass and isoelectric point (pI) were 31.05 kD and 5.18, respectively. Amino acid sequence analysis demonstrated the presence of stomatins, prohibitin, flotillins, HflK/C (SPFH) domain and prohibitin homologue for the TaHIR2 protein. Phylogenetic analysis of 13 HIR genes from different monocots indicated that TaHIR2 was highly homologous to HvHIR2. Transient expression analysis using particle-mediated bombardment showed that the TaHIR2 fusion protein was located in the onion epidermal cells. Quantitative RT-PCR analyses revealed that TaHIR2 transcripts were significantly accumulated in adult wheat leaves with maximum induction at 18 h post inoculation with the stripe rust, whereas slightly up-regulation could also be observed in the compatible reaction at the seedling stage. These results suggest that TaHIR2 may play an active role in wheat defense against stripe rust.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CT :
-
threshold value
- GS:
-
growth stage
- HIR:
-
hypersensitive induced reaction
- hpi:
-
hour post inoculation
- HR:
-
hypersensitive response
- ORF:
-
open reading frame
- qRT-PCR:
-
quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
- SAR:
-
systemic acquired response
- RT-PCR:
-
reverse transcription PCR
- SPFH:
-
stomatins, prohibitin, flotillins, HflK/C
References
Anand, T., Bhaskaran, R., Raguchander, T., Samiyappan R., Prakasam, V., Gopalakrishnan, C.: Defense responses of chilli fruits to Colletotrichum capsici and Alternaria alternate. — Biol. Plant. 53: 553–559, 2009.
Burland, T.G.: DNASTAR’s laser gene sequence analysis software. — Methods mol. Biol. 132: 71–91, 2000.
Flor, H.H.: Current status of the gene for gene concept. — Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 9: 275–296, 1971.
Greenberg, J.T.: Programmed cell death in plant-pathogen interactions. — Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant mol. Biol. 48: 525–545, 1997.
Heath, M.C.: Hypersensitive response-related death. — Plant mol. Biol. 44: 321–334, 2000.
Hipskind, J.D., Nicholson, R.L., Goldsbrough, P.B.: Isolation of a cDNA encoding a novel leucine-rich repeat motif from Sorghum bicolor inoculated with fungi. — Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 9: 819–825, 1996.
Jung, H., Hwang, B.K.: The leucine-rich repeat (LRR) protein, CaLRR1, interacts with the hypersensitive induced reaction (HIR) protein, CaHIR1, and suppresses cell death induced by the CaHIR1 protein. — Mol. Plant Pathol. 8: 503–514, 2007.
Jung, H.W., Lim, C.W., Lee, S.C., Choi, H.W., Hwang, C.H., Hwang, B.K.: Distinct roles of the pepper hypersensitive induced reaction protein gene CaHIR1 in disease and osmotic stress, as determined by comparative transcriptome and proteome analyses. — Planta 227: 409–425, 2008.
Kang, Z.S., Li, Z.Q.: [Discovery of a normal T. type new pathogenic strain to Lovrin10.] — Acta Cllegii Septentrionali Occidentali Agr. 4: 18–28, 1984. [In Chinese]
Karrer, E.E., Beachy, R.N., Holt, C.A.: Cloning of tobacco genes that elicit the hypersensitive response. — Plant mol. Biol. 36: 681–690, 1998.
Kozak, M.: Downstream secondary structure facilitates recognition of initiator codons by eukaryotic ribosomes. — Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 87: 8301–8305, 1990.
Lam, E., Kato, N., Lawton, M.: Programmed cell death, mitochondria and the plant hypersensitive response. — Nature 411: 848–853, 2001.
McClung, J.K., Jupe, E.R., Liu, X.T., Dell’Orco, R.T.: Prohibitin: potential role in senescence, development, and tumor suppression. — Exp. Gerontol. 30: 99–124, 1995.
Métraux, J.P., Nawrath, C., Genoud, T.: Systemic acquired resistance. — Euphytica 124:237-243, 2002.
Nadimpalli, R., Yalpani, N., Johal, G.S., Simmons, C.R.: Prohibitins, stomatins, and plant-disease response genes compose a protein superfamily that controls cell proliferation, ion channel regulation, and death. — J. biol. Chem. 275: 29579–29586, 2000.
Peng, S.M., Luo, T., Zhou, J.Y., Niu, B., Lei, N.F., Tang, L., Chen, F.: Cloning and quantification of expression levels of two MADS-box genes from Momordica charantia. — Biol. Plant. 52: 222–230, 2008.
Pfaffl, M.W.: A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. — Nucl. Acids Res. 29 (Suppl.): e45, 2001.
Rostoks, N., Schmierer, D., Kudrna, D., Kleinhofs, A.: Barley putative hypersensitive induced reaction genes: genetic mapping, sequence analyses and differential expression in disease lesion mimic mutants. — Theor. appl. Genet. 107: 1094–1101, 2003.
Tavernarakis, N.M., Driscoll, M., Kyrpides, N.C.: The SPFH domain: implicated in regulating targeted protein turnover in stomatins and other membrane-associated proteins. — Trends Biochem. Sci. 24: 425–427, 1999.
Tamura, K., Dudley, J., Nei, M., Kumar, S.: MEGA4: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. — Mol. Biol. Evol. 24: 1596–1599, 2007.
Wang, C.F., Huang, L.L., Buchenauer, H., Han, Q.M., Zhang, H.C., Kang, Z.S.: Histochemical studies on the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (O2 − and H2O2) in the incompatible and compatible interaction of wheat- Puccinia striiformis f. sp. Tritici. — Physiol. mol. Plant Pathol. 71: 230–239, 2007.
Xia, N., Zhang, G., Liu, X.Y., Deng, L., Cao, G.L., Zhang, Y., Wang, X.J., Zhao, J., Huang, L.L., Kang, Z.S.: Characterization of a novel wheat NAC transcription factor gene involved in defense response against stripe rust pathogen infection and abiotic stresses. — Mol. Biol. Rep. 37: 3703–3712, 2010.
Yu, X.M., Yu, X.D., Qu, Z.P., Huang, X.J., Guo, J., Han, Q.M., Zhao, J., Huang, L.L., Kang, Z.S.: Cloning of a putative hypersensitive induced reaction gene from wheat infected by stripe rust fungus. — Gene. 407: 193–198, 2008.
Zadoks, J.C., Chang, T.T., Konzak, C.F.: A decimal code for the growth stages of cereals. — Weed Res. 14: 415–421, 1974.
Zhang, G., Dong, Y.L., Zhang, Y., Li, Y.M., Wang, X.J., Han, Q.M., Guo, J., Huang, L.L., Kang, Z.S.: Cloning and characterization of a novel hypersensitive induced-reaction gene from wheat infected by stripe rust pathogen. — J. Phytopathol. 157: 722–728, 2009.
Zhou, H.B., Li, S.F., Deng, Z.Y., Wang, X.P., Chen, T., Zhang, J.S., Chen, S.Y., Ling, H.Q., Zhang, A.M., Wang, D.W., Zhang, X.Q.: Molecular analysis of three new receptor-like kinase genes from hexaploid wheat and evidence for their participation in the wheat hypersensitive response to stripe rust fungus infection. — Plant J. 52: 420–434, 2007.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30930064 and 30800712), the National Basic Research Program of China (2006CB708208), the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program, 2006AA10A104), the earmarked fund for Modern Agro-industry Technology Research System, the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University, Ministry of Education of China (200558), and the 111 Project from the Ministry of Education of China (B07049). The first two authors contributed equally to this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, G., Li, Y.M., Sun, Y.F. et al. Molecular characterization of a gene induced during wheat hypersensitive reaction to stripe rust. Biol Plant 55, 696–702 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-011-0170-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-011-0170-z