Abstract
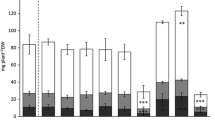
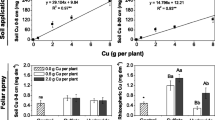
The accumulation of calcium (Ca), copper (Cu) and cadmium (Cd) in roots and stem of Norway spruce (Picea abies [L.] Karst) was examined. Two-year-old Norway spruce seedlings were treated with elevated concentrations of Ca, Cd or Cu, or as combinations of Ca with Cu or Cd in nutrient solutions for three months. The stem was divided into bark, wood formed during the treatment period (new wood), and wood formed before the treatment period (old wood). The accumulation of the metals in stem and roots increased with addition of the respective metal into nutrient solution. Addition of Cu decreased the accumulation of Ca in roots and wood, and Ca addition decreased the accumulation of Cu in the new wood. By adding Ca in combination with Cu the accumulation of Cu in the stem was decreased even more by Ca and the negative effect of Cu on the Ca content in the stem was diminished. Addition of Cd decreased the accumulation of Ca in wood, especially the old wood, and Ca addition decreased the accumulation of Cd in roots, bark and new wood. By adding Ca in combination with Cd the Ca content was reduced in the bark, instead of in the old wood.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arduini, I., Godbold, D.L., Onnis, A., Stefani, A.: Heavy metals influence mineral nutrition of tree seedlings.-Chemosphere 36: 739–744, 1998.
Arvidsson, H., Lundkvist, H.: Effects of crushed wood ash on soil chemistry in young Norway spruce stands.-Forest Ecol. Manage. 176: 121–132, 2003.
Bell, C.W., Biddulph, O.: Translocation of calcium, Exchange versus mass flow.-Plant Physiol. 38: 610–614, 1963.
Bramryd, T., Fransman, B.: Silvicultural use of wood ashes-effects on the nutrient and heavy metal balance in a pine (Pinus sylvestris, L.) forest soil.-Water Air Soil Pollut. 85: 1039–1044, 1995.
Burton, K. W., Morgan, E., Roig, A.: Interactive effects of cadmium, copper and nickel on the growth of Sitka spruce and studies of metal uptake from nutrient solutions.-New Phytol. 103: 549–557, 1986.
Clarkson, D.T., Lüttge, U.: Mineral nutrition: divalent cations, transport and compartmentation.-Progress Bot. 51: 93–112, 1989.
Coughtrey, P.J., Martin, M.H.: Cadmium uptake and distribution in tolerant and nontolerant populations of Holcus lanatus grown in solution culture.-Oikos 30: 555–560, 1978.
Demarty, M., Morvan, C., Thellier, M.: Calcium and the cell wall.-Plant Cell Environ. 7: 441–448, 1984.
Demeyer, A., Voundi Nkana, J.C., Verloo, M.G.: Characteristics of wood ash and influence on soil properties and nutrient uptake: an overview.-Bioresource Technol. 77: 287–295, 2001.
Drašić, G., Mihailović, N., Stojanović, Z.: Cadmium toxicity: the effect on macro-and micro-nutrient contents in soybean seedlings.-Biol. Plant. 48: 605–607, 2004.
Eriksson, H.M.: Short-term effects of granulated wood ash on forest soil chemistry in SW and NE Sweden.-Scand. J. Forest Res. 2(Suppl.): 43–55, 1998.
Ernst, W.H.O., Verkleij, J.A.C., Schat, H.: Metal tolerance in plants.-Acta bot. neerl. 41: 229–248, 1992.
Ferguson, I.B., Bollard, E.G.: The movement of calcium in woody stems.-Ann. Bot. 40: 1057–1065, 1976.
Fernandes, J.C., Henriques, F.S.: Biochemical, physiological, and structural effects of excess copper in plants.-Bot. Rev. 57: 246–273, 1991.
Greger, M., Brammer, E., Lindberg, S., Larsson, G., Idestam-Almquist, J.: Uptake and physiological effects of cadmium in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris) related to mineral provision.-J. exp. Bot. 42: 729–737, 1991.
Gussarsson, M.: Cadmium-induced alterations in nutrient composition and growth of Betula pendula seedlings: the significance of fine roots as a primary target for cadmium toxicity.-J. Plant Nutr. 17: 2151–2163, 1994.
Hagemeyer, H.: Ecophysiology of plant growth under heavy metal stress.-In: Prasad, M.N.V., Hagemeyer, J. (ed.): Heavy Metal Stress in Plants from Molecules to Ecosystem. Pp. 157–181. Springer-Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg 1999.
Ingestad, T.: Mineral nutrient requirements of Pinus sylvestris and Picea abies seedlings.-Physiol. Plant. 45: 373–380, 1979.
Jarvis, S.C., Jones, L.H.P., Hopper, M.J.: Cadmium uptake from solution by plants and its transport from roots to shoots.-Plant Soil 44: 179–191, 1976.
Jones, R.G.W., Lunt, O.R.: The function of Ca in plants.-Bot. Rev. 33: 407–426, 1967.
Kawasaki, T., Moritsugu, M.: Effects of calcium on the absorption and translocation of heavy metals in excised barley roots: Multi-compartment transport box experiment.-Plant Soil 100: 21–34, 1987.
Kim, C.-G., Bell, J.N.B., Power, S.A.: Effects of soil cadmium on Pinus sylvestris L. seedlings.-Plant Soil 257: 443–449, 2003.
Kuhn, A.J., Schröder, W.H., Bauch, J.: On the distribution and transport of mineral elements in xylem, cambium and phloem of spruce (Picea abies [L.] Karst.).-Holzforschung 51: 487–496, 1997.
Landberg, T., Greger, M.: Differences in uptake and tolerance to heavy metals in Salix from unpolluted and polluted areas.-Appl. Geochem. 11: 175–180, 1996.
Liu, D., Jiang, W., Gao, X.: Effects of cadmium on root growth, cell division and nucleoli in root tip cells of garlic.-Biol. Plant. 47: 79–83, 2003.
Marschner, H. (ed.): Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants. 2nd Ed.-Academic Press, London 1995.
McLaughlin, S.B., Wimmer, R.: Tansley Review No. 104. Calcium physiology and terrestrial ecosystem processes.-New Phytol. 142: 373–417, 1999.
Österås, A.H., Ekvall, L., Greger, M.: Sensitivity to, and accumulation of, cadmium in Betula pendula, Picea abies, and Pinus sylvestris seedlings from different regions in Sweden.-Can. J. Bot. 78: 1440–1449, 2000.
Österås, A.H., Greger, M.: Accumulation of, and interactions between, calcium and heavy metals in wood and bark of Picea abies.-J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 166: 246–253, 2003.
Ouzounidou, G.: Copper-induced changes on growth, metal content and photosynthetic function of Alyssum montanum L. plants.-Environ. exp. Bot. 34: 165–172, 1994.
Piñeros, M., Tester, M.: Calcium channels in plant cells: selectivity, regulation and pharmacology.-J. exp. Bot., Special issue 48: 551–557, 1997.
Rumpf, S., Ludwig, B., Mindrup, M.: Effect of wood ash on soil chemistry of a pine stand in Northern Germany.-J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 164: 569–575, 2001.
Saleh, A.A.H., El-Meleigy, S.A., Ebad, F.A., Helmy, M.A., Jentschke, G. Godbold D.L.: Base cations ameliorate Zn toxicity but not Cu toxicity in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris).-J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 162: 275–279, 1999.
Sattelmacher, B.: The apoplast and its significance for plant mineral nutrition.-New Phytol. 149: 167–192, 2001.
Shear, C.B., Faust, M.: Calcium transport in apple trees.-Plant Physiol. 45: 670–674, 1970.
Thornton, B., Macklon, A.E.S.: Copper uptake by ryegrass seedlings; contribution of cell wall adsorption.-J. exp. Bot. 40: 1105–1111, 1989.
Tyler, L.D., McBride, M.B.: Influence of Ca, pH and humic acid on Cd uptake.-Plant Soil 64: 259–262, 1982.
Van Cutsem, P., Gillet, C.: Activity coefficients and selectivity values of Cu++, Zn++ and Ca++ ions adsorbed in the Nitella flexilis L. cell wall during triangular ion exchanges.-J. exp. Bot. 33: 847–853, 1982.
Wallace, A., Romney, E.M., Mueller, R.T., Alexander, G.V.: Calcium-trace metal interactions in soybean plants.-J. Plant Nutr. 2: 79–86, 1980.
White, P.J.: Calcium channels in the plasma membrane of roots cells.-Ann. Bot. 81: 173–183, 1998.
Wolterbeek, H.Th.: Cation exchange in isolated xylem cell walls of tomato. I. Cd2+ and Rb2+ exchange in adsorption experiments.-Plant Cell Environ. 10: 39–44, 1987.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Österås, A.H., Greger, M. Interactions between calcium and copper or cadmium in Norway spruce. Biol Plant 50, 647–652 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-006-0101-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-006-0101-6