Abstract
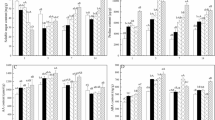
Ionomics and transcriptomics were applied to demonstrate response of rice to arsenite [As(III)] stress in the current study. Rice plants were cultured in nutrient solutions treated with 0, 100 and 500 μg/L As(III) coded as CK, As1 and As5, respectively. The rice ionomes exhibited discriminatory response to environmental disturbances. Solid evidence of the effects of As(III) stress on binding, transport or metabolism of P, K, Ca, Zn and Cu was obtained in this work. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the shoots were identified in three datasets: As1 vs CK, As5 vs CK and As5 vs As1. DEGs identified simultaneously in two or three datasets were selected for subsequent interaction and enrichment analyses. Upregulation of genes involved in protein kinase activity, phosphorus metabolic process and phosphorylation were detected in the rice treated with As(III), resulting in the maintenance of P homeostasis in the shoots. Zn and Ca binding genes were up-regulated since excess As inhibited the translocation of Zn and Ca from roots to shoots. Increased expression of responsive genes including HMA, WRKY, NAC and PUB genes conferred As tolerance in the rice plants to cope with external As(III) stress. The results suggested that As(III) stress could disturb the uptake and translocation of macro and essential elements by rice. Plants could regulate the expression of corresponding genes to maintain mineral nutrient homeostasis for essential metabolic processes.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Banerjee A, Singh A, Sudarshan M, Roychoudhury A (2021) Silicon nanoparticle-pulsing mitigates fluoride stress in rice by fine-tuning the ionomic and metabolomic balance and refining agronomic traits. Chemosphere 262:127826
Baxter I (2015) Should we treat the ionome as a combination of individual elements, or should we be deriving novel combined traits? J Exp Bot 66(8):2127–2131
Baxter I, Dilkes BP (2012) Elemental profiles reflect plant adaptations to the environment. Science 336(6089):1661–1663
Baxter IR, Vitek O, Lahner B, Muthukumar B, Borghi M, Morrissey J, Guerinot ML, Salt DE (2008) The leaf ionome as a multivariable system to detect a plant’s physiological status. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(33):12081–12086
Cao Y, Sun D, Ai H, Mei H, Liu X, Sun S, Xu G, Liu Y, Chen Y, Ma LQ (2017) Knocking out OsPT4 gene decreases arsenate uptake by rice plants and inorganic arsenic accumulation in rice grains. Environ Sci Technol 51(21):12131–12138
Chakrabarty D, Trivedi PK, Misra P, Tiwari M, Shri M, Shukla D, Kumar S, Rai A, Pandey A, Nigam D, Tripathi RD, Tuli R (2009) Comparative transcriptome analysis of arsenate and arsenite stresses in rice seedlings. Chemosphere 74(5):688–702
Chen H, Liang X, Gong X, Reinfelder JR, Chen H, Sun C, Liu X, Zhang S, Li F, Liu C, Zhao J, Yi J (2021) Comparative physiological and transcriptomic analyses illuminate common mechanisms by which silicon alleviates cadmium and arsenic toxicity in rice seedlings. J Environ Sci 109:88–101
Chutia R, Abel S, Ziegler J (2019) Iron and phosphate deficiency regulators concertedly control coumarin profiles in Arabidopsis thaliana roots during iron, phosphate, and combined deficiencies. Front Plant Sci 10:113
Cong W, Miao Y, Xu L, Zhang Y, Yuan C, Wang J, Zhuang T, Lin X, Jiang L, Wang N, Ma J, Sanguinet KA, Liu B, Rustgi S, Ou X (2019) Transgenerational memory of gene expression changes induced by heavy metal stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.). BMC Plant Biol 19(1):282
Cubadda F, Jackson BP, Cottingham KL, Van Horne YO, Kurzius-Spencer M (2017) Human exposure to dietary inorganic arsenic and other arsenic species: state of knowledge, gaps and uncertainties. Sci Total Environ 579:1228–1239
Deng F, Yamaji N, Xia J, Ma JF (2013) A member of the heavy metal P-type ATPase OsHMA5 is involved in xylem loading of copper in rice. Plant Physiol 163(3):1353–1362
Di X, Zheng F, Norton GJ, Beesley L, Zhang Z, Lin H, Zhi S, Liu X, Ding Y (2021) Physiological responses and transcriptome analyses of upland rice following exposure to arsenite and arsenate. Environ Exp Bot 183:104366
Du F, Yang Z, Liu P, Wang L (2018) Accumulation, translocation, and assessment of heavy metals in the soil-rice systems near a mine-impacted region. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(32):32221–32230
Du F, Liu P, Wang K, Yang Z, Wang L (2019) Influence of different arsenic species on uptake, speciation and efflux of arsenic in hydroponic rice plants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 186:109791
Du F, Liu P, Wang K, Yang Z, Wang L (2020) Ionomic responses of rice plants to the stresses of different arsenic species in hydroponics. Chemosphere 243:125398
Gindri RG, Navarro BB, da Cruz Dias PV, Tarouco CP, Nicoloso FT, Brunetto G, Berghetti ÁLP, da Silva LOS, Fett JP, Menguer PK, Ricachenevsky FK (2020) Physiological responses of rice (Oryza sativa L.) oszip7 loss-of-function plants exposed to varying Zn concentrations. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 26(7):1349–1359
Gu M, Zhang J, Li H, Meng D, Li R, Dai X, Wang S, Liu W, Qu H, Xu G (2017) Maintenance of phosphate homeostasis and root development are coordinately regulated by MYB1, an R2R3-type MYB transcription factor in rice. J Exp Bot 68(13):3603–3615
Guan S, Xu Q, Ma D, Zhang W, Xu Z, Zhao M, Guo Z (2019) Transcriptomics profiling in response to cold stress in cultivated rice and weedy rice. Gene 685:96–105
Hussain MM, Bibi I, Niazi NK, Shahid M, Iqbal J, Shakoor MB, Ahmad A, Shah NS, Bhattacharya P, Mao K, Bundschuh J, Ok YS, Zhang H (2021) Arsenic biogeochemical cycling in paddy soil-rice system: interaction with various factors, amendments and mineral nutrients. Sci Total Environ 773:145040
Jeyasingh PD, Goos JM, Thompson SK, Godwin CM, Cotner JB (2017) Ecological stoichiometry beyond redfield : an ionomic perspective on elemental homeostasis. Front Microbiol 8:722
Jeyasri R, Muthuramalingam P, Satish L, Adarshan S, Lakshmi MA, Pandian SK, Chen J-T, Ahmar S, Wang X, Mora-Poblete F, Ramesh M (2021) The role of OsWRKY genes in rice when faced with single and multiple abiotic stresses. Agronomy 11(7):1301
Kalita J, Pradhan AK, Shandilya ZM, Tanti B (2018) Arsenic stress responses and tolerance in rice: physiological cellular and molecular approaches rice. Science 25(5):235–249
Karley AJ, White PJ (2009) Moving cationic minerals to edible tissues: potassium, magnesium, calcium. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12(3):291–298
Khan E, Gupta M (2018) Arsenic–silicon priming of rice (Oryza sativa L.) seeds influence mineral nutrient uptake and biochemical responses through modulation of Lsi-1, Lsi-2, Lsi-6 and nutrient transporter genes. Sci Rep 8(1):10301
Kim M-S, Kang K-K, Cho Y-G (2021) Molecular and functional analysis of U-box E3 ubiquitin ligase gene family in rice (Oryza sativa). Int J Mol Sci 22(21):12088
Kumari P, Rastogi A, Shukla A, Srivastava S, Yadav S (2018) Prospects of genetic engineering utilizing potential genes for regulating arsenic accumulation in plants. Chemosphere 211:397–406
Li N, Liu H, Sun J, Zheng H, Wang J, Yang L, Zhao H, Zou D (2018) Transcriptome analysis of two contrasting rice cultivars during alkaline stress. Sci Rep 8:1–16
Li J, Zhang M, Sun J, Mao X, Wang J, Liu H, Zheng H, Li X, Zhao H, Zou D (2020) Heavy metal stress-associated proteins in rice and arabidopsis: genome-wide identification, phylogenetics, duplication, and expression profiles analysis. Front Genet 11:477
Lin G, He X, Zeng J, Yang Z, Wang L (2023) Ionome profiling and arsenic speciation provide evidence of arsenite detoxification in rice by phosphate and arsenite-oxidizing bacteria. J Environ Sci 128:129–138
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Love MI, Huber W, Anders S (2014) Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 15(12):1–21
Lv Y, Yang M, Hu D, Yang Z, Ma S, Li X, Xiong L (2017) The OsMYB30 transcription factor suppresses cold tolerance by interacting with a JAZ protein and suppressing β-amylase expression. Plant Physiol 173(2):1475–1491
Ma JF, Yamaji N, Mitani N, Xu X-Y, Su Y-H, McGrath SP, Zhao F-J (2008) Transporters of arsenite in rice and their role in arsenic accumulation in rice grain. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105(29):9931–9935
Mukhopadhyay A, Vij S, Tyagi AK (2004) Overexpression of a zinc-finger protein gene from rice confers tolerance to cold, dehydration, and salt stress in transgenic tobacco. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101(16):6309–6314
Musavizadeh Z, Najafi-Zarrini H, Kazemitabar SK, Hashemi SH, Faraji S, Barcaccia G, Heidari P (2021) Genome-wide analysis of Potassium channel genes in rice: expression of the OsAKT and OsKAT genes under salt stress. Genes 12(5):784
Nocito FF, Lancilli C, Dendena B, Lucchini G, Sacchi GA (2011) Cadmium retention in rice roots is influenced by cadmium availability, chelation and translocation. Plant Cell Environ 34(6):994–1008
Oono Y, Yazawa T, Kanamori H, Sasaki H, Mori S, Matsumoto T (2017) Genome-wide analysis of rice cis-natural antisense transcription under cadmium exposure using strand-specific RNA-Seq. BMC Genomics 18(1):761
Panchal P, Miller AJ, Giri J (2021) Organic acids: versatile stress-response roles in plants. J Exp Bot 72(11):4038–4052
Shaibur MR, Sera K, Kawai S (2016) Effect of arsenic on concentrations and translocations of mineral elements in the xylem of rice. J Plant Nutr 39(3):365–376
Sharma R, Cao P, Jung K-H, Sharma M, Ronald P (2013) Construction of a rice glycoside hydrolase phylogenomic database and identification of targets for biofuel research. Front Plant Sci 4:330
Singh S, Koyama H, Bhati KK, Alok A (2021) The biotechnological importance of the plant-specific NAC transcription factor family in crop improvement. J Plant Res 134(3):475–495
Stone R (2008) Food safety—arsenic and paddy rice: a neglected cancer risk? Science 321(5886):184–185
Sun J, Sun Y, Ahmed RI, Ren A, Xie M (2019) Research progress on plant RING-finger proteins. Genes 10(12):973
Vannini C, Locatelli F, Bracale M, Magnani E, Marsoni M, Osnato M, Mattana M, Baldoni E, Coraggio I (2004) Overexpression of the rice Osmyb4 gene increases chilling and freezing tolerance of Arabidopsis thaliana plants. Plant J 37(1):115–127
Vij S, Giri J, Dansana PK, Kapoor S, Tyagi AK (2008) The receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase (OsRLCK) gene family in rice: organization, phylogenetic relationship, and expression during development and stress. Mol Plant 1(5):732–750
Wickham H (2011) ggplot2. Wires Comput Stat 3(2):180–185
Wu C, Zou Q, Xue SG, Pan WS, Huang L, Hartley W, Mo JY, Wong MH (2016) The effect of silicon on iron plaque formation and arsenic accumulation in rice genotypes with different radial oxygen loss (ROL). Environ Pollut 212:27–33
Xiao W, Liu P, Wang K, Yang Z, Wang L (2021) Relationship between ionomics and transcriptomics of rice plant in response to arsenite stress. Environ Exp Bot 189:104565
Xu H, Watanabe KA, Zhang L, Shen QJ (2016) WRKY transcription factor genes in wild rice Oryza nivara. DNA Res 23(4):311–323
Yu L-j, Luo Y-f, Liao B, Xie L-j, Chen L, Xiao S, Li J-t, Hu S-n, Shu W-s (2012) Comparative transcriptome analysis of transporters, phytohormone and lipid metabolism pathways in response to arsenic stress in rice (Oryza sativa). New Phytol 195(1):97–112
Zhao R, Xie C-T, Xu Y, Ji D-H, Chen C-S, Ye J, Xue X-M, Wang W-L (2020) The response of Pyropia haitanensis to inorganic arsenic under laboratory culture. Chemosphere 261:128160
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41977351) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China (No. 2021JJ31094).
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41977351) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China (No. 2021JJ31094).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GL: Methodology, Investigation, Visualization, Writing- Original draft preparation. LM: Investigation, Visualization. XH: Investigation. JT: Methodology, Writing—Review & Editing, Resources. LW: Supervision, Writing- Original draft preparation, Writing—Review & Editing, Funding acquisition.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, G., Ma, L., He, X. et al. Gene regulation and ionome homeostasis in rice plants in response to arsenite stress: potential connection between transcriptomics and ionomics. Biometals 36, 1157–1169 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-023-00510-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-023-00510-z