Abstract
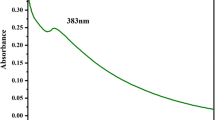
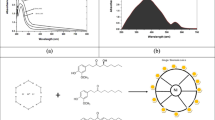
The interest of many has been attracted by plant-mediated synthesizing procedures for nanoparticles since they provide certain qualities including being cost-effective, quick, and compatible with the environment. In this regard, this work introduces the production of selenium-nanoparticles (Se-NPs) in a biological manner utilizing aqueous extracts of Rosmarinus officinalis (R. officinalis). Production of Se-NPs was confirmed using UV–visible (UV–Vis) spectrophotometry. Also, dynamic light scattering (DLS) analysis was used for determination particle size distribution, while we distinguished the identification of crystalline construction of nanoparticles through the means of X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern, DLS, and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) examination indicated that Se-NPs are often spherical with a size about 20 to 40 nm. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of the synthesized Se-NPs by R. officinalis extract against Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis), Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), Streptococcus mutans (S. mutans), Escherichia coli (E. coli), and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) was 256, 16, 32, 128, and 64 µg/mL, respectively. The synthesized Se-NPs had no significant effect on Mycobacterium simiae (M. simiae) and had exhibited a strong antimicrobial functionality towards the gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria and can stand as a potent antibacterial agent.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Na2SeO3 :
-
Sodium selenite
- Se-NPs:
-
Selenium-nanoparticles
- REMA:
-
Resazurin microtiter assay
- NA:
-
Nutrient agar
- MIC:
-
Minimum inhibitory concentration
- TSB:
-
Trypticase soy broth
- OADC:
-
Oleic acid, albumin, dextrose, and catalase
- UV–Vis:
-
Ultraviolet–visible
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscopy
- FT-IR:
-
Fourier transform infrared
- DLS:
-
Dynamic light scattering
- R. officinalis :
-
Rosmarinus officinalis
- M. tuberculosis :
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- S. aureus :
-
Staphylococcus aureus
- S. mutans :
-
Streptococcus mutans
- E. coli :
-
Escherichia coli
- P. aeruginosa :
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
References
Ali AM, Najmy R (2013) Structural, optical and photocatalytic properties of NiO–SiO2 nanocomposites prepared by sol–gel technique. Catal Today 208:2–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2012.09.016
Anu K, Singaravelu G, Murugan K, Benelli G (2016) Green-synthesis of selenium nanoparticles using garlic cloves (Allium sativum): biophysical characterization and cytotoxicity on Vero cells. J Clust Sci 28(1):551–563. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-016-1123-7
Anu K, Singaravelu G, Murugan K, Benelli G (2017) Green-synthesis of selenium nanoparticles using garlic cloves (Allium sativum): biophysical characterization and cytotoxicity on Vero cells. J Clust Sci 28(1):551–563
Bharathi S, Kumaran S, Suresh G, Ramesh M, Thangamani V, Pugazhvendan S, Sathiyamurthy K (2020) Extracellular synthesis of nano selenium from fresh water bacteria Bacillus sp., and its validation of antibacterial and cytotoxic potential. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 27:101655
Chellapa LR, Shanmugam R, Indiran MA, Samuel SR (2020) Biogenic nano selenium synthesis, its antimicrobial, antioxidant activity, and toxicity. Bioinspired Biomim Nanobiomater 9(3):184–189
Chen H, Yoo J-B, Liu Y, Zhao G (2011) Green synthesis and characterization of the nanoparticles and nanorods. Electron Mater Lett 7(4):333–336
Cittrarasu V, Balasubramanian B, Kaliannan D, Park S, Maluventhan V, Kaul T, Liu WC, Arumugam M (2019) Biological mediated Ag nanoparticles from Barleria longiflora for antimicrobial activity and photocatalytic degradation using methylene blue. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 47(1):2424–2430. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2019.1626407
Cittrarasu V, Kaliannan D, Dharman K, Maluventhen V, Easwaran M, Liu WC, Balasubramanian B, Arumugam M (2021) Green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles mediated from Ceropegia bulbosa Roxb extract and its cytotoxicity, antimicrobial, mosquitocidal and photocatalytic activities. Sci Rep 11(1):1–15
Cremonini E, Zonaro E, Donini M, Lampis S, Boaretti M, Dusi S, Melotti P, Lleo MM, Vallini G (2016) Biogenic selenium nanoparticles: characterization, antimicrobial activity, and effects on human dendritic cells and fibroblasts. Microb Biotechnol 9(6):758–771
Dawood MA, Basuini MFE, Yilmaz S, Abdel-Latif HM, Kari ZA, Abdul Razab MKA, Ahmed HA, Alagawany M, Gewaily MS (2021) Selenium nanoparticles as a natural antioxidant and metabolic regulator in aquaculture: a review. Antioxidants 10(9):1364
El-Batal AI, Mosallam FM, Ghorab M, Hanora A, Gobara M, Baraka A, Elsayed MA, Pal K, Fathy RM, Abd Elkodous M (2020) Factorial design-optimized and gamma irradiation-assisted fabrication of selenium nanoparticles by chitosan and Pleurotus ostreatus fermented fenugreek for a vigorous in vitro effect against carcinoma cells. Int J Biol Macromol 156:1584–1599
El-Batal AI, Ragab YM, Amin MA, El-Roubi GM, Mosallam FM (2021) Investigating the antimicrobial, antioxidant, and cytotoxic activities of the biologically synthesized glutathione selenium nano-incorporation. Biometals 34(4):1–15
Estevez H, Palacios A, Gil D, Anguita J, Vallet-Regi M, Gonzalez B, Prados-Rosales R, Luque-Garcia JL (2020) Antimycobacterial effect of selenium nanoparticles on Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Front Microbiol 11:800. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.00800
Fardsadegh B, Vaghari H, Mohammad-Jafari R, Najian Y, Jafarizadeh-Malmiri H (2019) Biosynthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activities assessment of fabricated selenium nanoparticles using Pelargonium zonale leaf extract. Green Process Synth 8(1):191–198
Ghaedi M, Yousefinejad M, Safarpoor M, Khafri HZ, Purkait MK (2015) Rosmarinus officinalis leaf extract mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and investigation of its antimicrobial properties. J Ind Eng Chem 31:167–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2015.06.020
Gunti L, Dass RS, Kalagatur NK (2019) Phytofabrication of selenium nanoparticles from Emblica officinalis fruit extract and exploring its biopotential applications: antioxidant, antimicrobial, and biocompatibility. Front Microbiol 10:931. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00931
Hassanien R, Abed-Elmageed AA, Husein DZ (2019) Eco-friendly approach to synthesize selenium nanoparticles: photocatalytic degradation of sunset yellow azo dye and anticancer activity. ChemistrySelect 4(31):9018–9026
Jain R, Gonzalez-Gil G, Singh V, Van Hullebusch E, Farges F, Lens P (2014) Biogenic selenium nanoparticles: production, characterization, and challenges. In: Nanobiotechnology. Studium Press LLC, Houston, pp 361–390
Jamkhande PG, Ghule NW, Bamer AH, Kalaskar MG (2019) Metal nanoparticles synthesis: an overview on methods of preparation, advantages, and disadvantages, and applications. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 53:101174
Jay V, Shafkat R (2018) Synthesis of selenium nanoparticles using Allium sativum extract and analysis of their antimicrobial property against gram-positive bacteria. Pharma Innov 7(9):262–266
Kalishwaralal K, Jeyabharathi S, Sundar K, Muthukumaran A (2016) A novel one-pot green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles and evaluation of its toxicity in zebrafish embryos. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 44(2):471–477
Kokila K, Elavarasan N, Sujatha V (2017) Diospyros montana leaf extract-mediated synthesis of selenium nanoparticles and their biological applications. N J Chem 41(15):7481–7490
Meenambigai K, Kokila R, Chandhirasekar K, Thendralmanikandan A, Kaliannan D, Ibrahim KS, Kumar S, Liu W, Balasubramanian B, Nareshkumar A (2021) Green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles mediated by Nilgirianthus ciliates leaf extracts for antimicrobial activity on foodborne pathogenic microbes and pesticidal activity against Aedes aegypti with molecular docking. Biol Trace Elem Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02868-y
Mosalam M, Marzouk F (2013) Effect of gamma radiation on the microbial synthesis of metal nanoparticles. MSc Thesis
Mosallam FM, Helmy EA, Bendary MM, El-Batal AI (2021) Potency of a novel synthesized Ag–eugenol nanoemulsion for treating some bacterial and fungal pathogens. J Mater Res 36:1–14
Ramamurthy C, Sampath KS, Arunkumar P, Kumar MS, Sujatha V, Premkumar K, Thirunavukkarasu C (2013) Green synthesis and characterization of selenium nanoparticles and its augmented cytotoxicity with doxorubicin on cancer cells. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 36(8):1131–1139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-012-0867-1
Salem SS, Fouda MMG, Fouda A, Awad MA, Al-Olayan EM, Allam AA, Shaheen TI (2020) Antibacterial, cytotoxicity and larvicidal activity of green synthesized selenium nanoparticles using Penicillium corylophilum. J Clust Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-020-01794-8
Shakibaie M, Forootanfar H, Golkari Y, Mohammadi-Khorsand T, Shakibaie MR (2015) Anti-biofilm activity of biogenic selenium nanoparticles and selenium dioxide against clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Proteus mirabilis. J Trace Elem Med Biol 29:235–241
Sharma G, Sharma AR, Bhavesh R, Park J, Ganbold B, Nam J-S, Lee S-S (2014) Biomolecule-mediated synthesis of selenium nanoparticles using dried Vitis vinifera (raisin) extract. Molecules 19(3):2761–2770
Shoeibi S, Mozdziak P, Golkar-Narenji A (2017) Biogenesis of selenium nanoparticles using green chemistry. Top Curr Chem 375(6):88
Singh N, Saha P, Rajkumar K, Abraham J (2014) Biosynthesis of silver and selenium nanoparticles by Bacillus sp. JAPSK2 and evaluation of the antimicrobial activity. Der Pharm Lett 6(6):175–181
Sowndarya P, Ramkumar G, Shivakumar M (2017) Green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles conjugated Clausena dentata plant leaf extract and their insecticidal potential against mosquito vectors. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 45(8):1490–1495
Srivastava N, Mukhopadhyay M (2015) Green synthesis and structural characterization of selenium nanoparticles and assessment of their antimicrobial property. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 38(9):1723–1730. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-015-1413-8
Tran PA, Webster TJ (2011) Selenium nanoparticles inhibit Staphylococcus aureus growth. Int J Nanomed 6:1553
Velgosova O, Veselovský L (2019) Synthesis of Ag nanoparticle using R. officinalis, U. dioica, and V. vitis-idea extracts. Mater Lett 248:150–152
Vellingiri MM, Ashwin JKM, Soundari AJPG, Sathiskumar S, Priyadharshini U, Paramasivam D, Liu W-C, Balasubramanian B (2021) Mycofabrication of AgONPs derived from Aspergillus terreus FC36AY1 and its potent antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anti-angiogenesis activities. Mol Biol Rep 48(12):1–14
Vikneshan M, Saravanakumar R, Mangaiyarkarasi R, Rajeshkumar S, Samuel S, Suganya M, Baskar G (2020) Algal biomass as a source for the novel oral nano-antimicrobial agent. Saudi J Biol Sci 27(12):3753–3758
Vyas J, Rana S (2017) Antioxidant activity and green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles using Allium sativum extract. Int J Phytomed 9:634
Wang Y, Shu X, Hou J, Lu W, Zhao W, Huang S, Wu L (2018) Selenium nanoparticle synthesized by Proteus mirabilis YC801: an efficacious pathway for selenite biotransformation and detoxification. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123809
Yang F, Tang Q, Zhong X, Bai Y, Chen T, Zhang Y, Li Y, Zheng W (2012) Surface decoration by Spirulina polysaccharide enhances the cellular uptake and anticancer efficacy of selenium nanoparticles. Int J Nanomed 7:835
Zare B, Babaie S, Setayesh N, Shahverdi AR (2013) Isolation and characterization of a fungus for extracellular synthesis of small selenium nanoparticles. Nanomed J 1(1):13–19
Zeebaree SYS, Zeebaree AYS, Zebari OIH (2020) Diagnosis of the multiple effects of selenium nanoparticles decorated by Asteriscus graveolens components in inhibiting HepG2 cell proliferation. Sustain Chem Pharm 15:100210
Zhang W, Chen Z, Liu H, Zhang L, Gao P, Li D (2011) Biosynthesis and structural characteristics of selenium nanoparticles by Pseudomonas alcaliphila. Colloids Surf B 88(1):196–201
Acknowledgements
The technical support of this work was provided by Mashhad University of Medical Sciences based on the MSc Thesis of Ms. F. Adibian.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adibian, F., Ghaderi, R.S., Sabouri, Z. et al. Green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles using Rosmarinus officinalis and investigated their antimicrobial activity. Biometals 35, 147–158 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-021-00356-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-021-00356-3