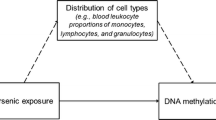
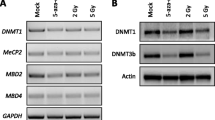
Abstract
Global methylation pattern regulates the normal functioning of a cell. Research have shown arsenic alter these methylation landscapes within the genome leading to aberrant gene expression and inducts various pathophysiological outcomes. Long interspersed nuclear elements (LINE-1) normally remains inert due to heavy methylation of it’s promoters, time and various environmental insults, they lose these methylation signatures and begin retro-transposition that has been associated with genomic instability and cancerous outcomes. Of the various high throughput technologies available to detect global methylation profile, development of LINE-1 methylation index shall provide a cost effect-screening tool to detect epimutagenic events in the wake of toxic exposure in a large number of individuals. In the present review, we tried to discuss the state of research and whether LINE-1 methylation can be considered as a potent epigenetic signature for arsenic toxicity.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahsan H, Steinmaus C (2013) Invited commentary: use of arsenical skin lesions to predict risk of internal cancer: implications for prevention and future research. Am J Epidemiol 177:213–216. doi:10.1093/aje/kws366
Alegria-Torres JA, Carrizales-Yanez L, Diaz-Barriga F, Rosso-Camacho F, Motta V, Tarantini L, Bollati V (2016) DNA methylation changes in Mexican children exposed to arsenic from two historic mining areas in San Luis potosi. Environ Mol Mutagen 57:717–723. doi:10.1002/em.22062
Ambatipudi S et al (2016) Tobacco smoking-associated genome-wide DNA methylation changes in the EPIC study. Epigenomics 8:599–618. doi:10.2217/epi-2016-0001
Bandyopadhyay AK, Paul S, Adak S, Giri AK (2016) Reduced LINE-1 methylation is associated with arsenic-induced genotoxic stress in children. Biometals 29:731–741. doi:10.1007/s10534-016-9950-4
Banerjee M et al (2010) Evaluation of the serum catalase and myeloperoxidase activities in chronic arsenic-exposed individuals and concomitant cytogenetic damage. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 249:47–54. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2010.08.013
Banerjee M et al (2013) High arsenic in rice is associated with elevated genotoxic effects in humans. Scie Rep 3:2195. doi:10.1038/srep02195
Bhattacharjee P, Paul S, Bhattacharjee P (2016) Risk of occupational exposure to asbestos, silicon and arsenic on pulmonary disorders: understanding the genetic-epigenetic interplay and future prospects. Environ Res 147:425–434. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2016.02.038
Brouha B, Schustak J, Badge RM, Lutz-Prigge S, Farley AH, Moran JV, Kazazian HH Jr (2003) Hot L1s account for the bulk of retrotransposition in the human population. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:5280–5285. doi:10.1073/pnas.0831042100
Bustaffa E, Stoccoro A, Bianchi F, Migliore L (2014) Genotoxic and epigenetic mechanisms in arsenic carcinogenicity. Arch Toxicol 88:1043–1067. doi:10.1007/s00204-014-1233-7
Chakraborti D, Rahman MM, Ahamed S, Dutta RN, Pati S, Mukherjee SC (2016) Arsenic groundwater contamination and its health effects in Patna district (capital of Bihar) in the middle Ganga plain, India. Chemosphere 152:520–529. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.02.119
Chatterjee D et al (2015) Arsenic exposure through drinking water leads to senescence and alteration of telomere length in humans: a case-control study in West Bengal, India. Mol Carcinog 54:800–809. doi:10.1002/mc.22150
Chen H, Li S, Liu J, Diwan BA, Barrett JC, Waalkes MP (2004) Chronic inorganic arsenic exposure induces hepatic global and individual gene hypomethylation: implications for arsenic hepatocarcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 25:1779–1786. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgh161
Cheng PS, Weng SF, Chiang CH, Lai FJ (2016) Relationship between arsenic-containing drinking water and skin cancers in the arseniasis endemic areas in Taiwan. J Dermatol 43:181–186. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.13058
Choudhury SR et al (2016) Optogenetic regulation of site-specific subtelomeric DNA methylation. Oncotarget 7:50380–50391. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.10394
Chowdhury R, Chatterjee R, Giri AK, Mandal C, Chaudhuri K (2010) Arsenic-induced cell proliferation is associated with enhanced ROS generation, Erk signaling and CyclinA expression. Toxicol Lett 198:263–271. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2010.07.006
Das N et al (2012) Arsenic exposure through drinking water increases the risk of liver and cardiovascular diseases in the population of West Bengal, India. BMC Public Health 12:639. doi:10.1186/1471-2458-12-639
Das N, Giri A, Chakraborty S, Bhattacharjee P (2016) Association of single nucleotide polymorphism with arsenic-induced skin lesions and genetic damage in exposed population of West Bengal, India. Mutat Res 809:50–56. doi:10.1016/j.mrgentox.2016.09.006
Dastgiri S, Mosaferi M, Fizi MA, Olfati N, Zolali S, Pouladi N, Azarfam P (2010) Arsenic exposure, dermatological lesions, hypertension, and chromosomal abnormalities among people in a rural community of northwest Iran. J Health Popul Nutr 28:14–22
Eckersley L (2002) Role of the Schwann cell in diabetic neuropathy. Int Rev Neurobiol 50:293–321
Faulk C, Kim JH, Jones TR, McEachin RC, Nahar MS, Dolinoy DC, Sartor MA (2015) Bisphenol A-associated alterations in genome-wide DNA methylation and gene expression patterns reveal sequence-dependent and non-monotonic effects in human fetal liver. Environ Epigenetics. doi:10.1093/eep/dvv006
Feng H et al (2013) Biomarkers of renal toxicity caused by exposure to arsenic in drinking water. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 35:495–501. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2013.02.010
Footitt EJ, Heales SJ, Mills PB, Allen GF, Oppenheim M, Clayton PT (2011) Pyridoxal 5′-phosphate in cerebrospinal fluid; factors affecting concentration. J Inherit Metab Dis 34:529–538. doi:10.1007/s10545-011-9279-7
Gagnon F, Lampron-Goulet E, Normandin L, Langlois MF (2016) Measurements of arsenic in the urine and nails of individuals exposed to low concentrations of arsenic in drinking water from private wells in a rural region of Quebec. Can J Environ Health 78:76–83
Gainetdinov IV et al (2016) Hypomethylation of human-specific family of LINE-1 retrotransposons in circulating DNA of lung cancer patients. Lung Cancer 99:127–130. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2016.07.005
Garry MR, Santamaria AB, Williams AL, DeSesso JM (2015) In utero arsenic exposure in mice and early life susceptibility to cancer. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 73:378–390. doi:10.1016/j.yrtph.2015.07.023
Ghosh P et al (2006) Cytogenetic damage and genetic variants in the individuals susceptible to arsenic-induced cancer through drinking water. Int J Cancer 118:2470–2478. doi:10.1002/ijc.21640
Ghosh P et al (2007) Comparison of health effects between individuals with and without skin lesions in the population exposed to arsenic through drinking water in West Bengal, India. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 17:215–223. doi:10.1038/sj.jes.7500510
Guz J et al (2008) The relationship between 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2′-deoxyguanosine level and extent of cytosine methylation in leukocytes DNA of healthy subjects and in patients with colon adenomas and carcinomas. Mutat Res 640:170–173. doi:10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2007.12.013
Hancks DC, Kazazian HH Jr (2016) Roles for retrotransposon insertions in human disease. Mob DNA 7:9. doi:10.1186/s13100-016-0065-9
Harada K et al (2015) LINE-1 methylation level and patient prognosis in a database of 208 hepatocellular carcinomas. Ann Surg Oncol 22:1280–1287. doi:10.1245/s10434-014-4134-3
Hossain MB, Vahter M, Concha G, Broberg K (2012) Low-level environmental cadmium exposure is associated with DNA hypomethylation in Argentinean women. Environ Health Perspect 120:879–884. doi:10.1289/ehp.1104600
Hossain K et al (2017) Chronic exposure to arsenic, LINE-1 hypomethylation, and blood pressure: a cross-sectional study in Bangladesh. Environ Health 16:20. doi:10.1186/s12940-017-0231-7
Huang CY, Pu YS, Shiue HS, Chen WJ, Lin YC, Hsueh YM (2016) Polymorphisms of human 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase 1 and 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine increase susceptibility to arsenic methylation capacity-related urothelial carcinoma. Arch Toxicol 90:1917–1927. doi:10.1007/s00204-015-1590-x
Intarasunanont P, Navasumrit P, Waraprasit S, Chaisatra K, Suk WA, Mahidol C, Ruchirawat M (2012) Effects of arsenic exposure on DNA methylation in cord blood samples from newborn babies and in a human lymphoblast cell line. Environ Health 11:31. doi:10.1186/1476-069X-11-31
Jaffe AE, Irizarry RA (2014) Accounting for cellular heterogeneity is critical in epigenome-wide association studies. Genome Biol 15:R31. doi:10.1186/gb-2014-15-2-r31
Jomova K et al (2011) Arsenic: toxicity, oxidative stress and human disease. J Appl Toxicol 31:95–107. doi:10.1002/jat.1649
Jones PL et al (1998) Methylated DNA and MeCP2 recruit histone deacetylase to repress transcription. Nat Genet 19:187–191. doi:10.1038/561
Karimi A, Madjd Z, Habibi L, Akrami SM (2014) Exposure of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to low-level As(2)O(3) causes an extra toxicity pathway via L1 retrotransposition induction. Toxicol Lett 229:111–117. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2014.05.025
Kile ML et al (2012) Prenatal arsenic exposure and DNA methylation in maternal and umbilical cord blood leukocytes. Environ Health Perspect 120:1061–1066. doi:10.1289/ehp.1104173
Kim EJ, Chung WC, Kim DB, Kim YJ, Lee JM, Jung JH, Lee YK (2016) Long interspersed nuclear element (LINE)-1 methylation level as a molecular marker of early gastric cancer. Dig Liver Dis 48:1093–1097. doi:10.1016/j.dld.2016.06.002
Kumar S, Yedjou CG, Tchounwou PB (2014) Arsenic trioxide induces oxidative stress, DNA damage, and mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis in human leukemia (HL-60) cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 33:42. doi:10.1186/1756-9966-33-42
Kumar R, Trivedi V, Murti K, Dey A, Singh JK, Nath A, Das P (2015) Arsenic exposure and haematological derangement in cervical cancer cases in India. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 16:6397–6400
Kundu M et al (2011) Precancerous and non-cancer disease endpoints of chronic arsenic exposure: the level of chromosomal damage and XRCC3 T241M polymorphism. Mutat Res 706:7–12. doi:10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2010.10.004
Laget S, Miotto B, Chin HG, Esteve PO, Roberts RJ, Pradhan S, Defossez PA (2014) MBD4 cooperates with DNMT1 to mediate methyl-DNA repression and protects mammalian cells from oxidative stress. Epigenetics 9:546–556. doi:10.4161/epi.27695
Lambrou A et al (2012) Arsenic exposure and DNA methylation among elderly men. Epidemiology 23:668–676. doi:10.1097/EDE.0b013e31825afb0b
Lehmann HC, Hoke A (2010) Schwann cells as a therapeutic target for peripheral neuropathies. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 9:801–806
Lertkhachonsuk R, Paiwattananupant K, Tantbirojn P, Rattanatanyong P, Mutirangura A (2015) LINE-1 methylation patterns as a predictor of postmolar gestational trophoblastic neoplasia. Biomed Res Int 2015:421747. doi:10.1155/2015/421747
Li J et al (2014) The prognostic value of global DNA hypomethylation in cancer: a meta-analysis. PLoS One 9:e106290. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0106290
Liu-Mares W, Mackinnon JA, Sherman R, Fleming LE, Rocha-Lima C, Hu JJ, Lee DJ (2013) Pancreatic cancer clusters and arsenic-contaminated drinking water wells in Florida. BMC Cancer 13:111. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-13-111
Ma Y et al (2015) Folic acid protects against arsenic-mediated embryo toxicity by up-regulating the expression of Dvr1. Sci Rep 5:16093. doi:10.1038/srep16093
Mass MJ, Wang L (1997) Arsenic alters cytosine methylation patterns of the promoter of the tumor suppressor gene p53 in human lung cells: a model for a mechanism of carcinogenesis. Mutat Res 386:263–277
Mathew L, Vale A, Adcock JE (2010) Arsenical peripheral neuropathy. Pract Neurol 10:34–38. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2009.201830
Mima K et al (2016) Tumor LINE-1 methylation level and colorectal cancer location in relation to patient survival. Oncotarget 7:55098–55109. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.10398
Miousse IR, Koturbash I (2015) The fine LINE: methylation drawing the cancer landscape. BioMed Res Int 2015:131547. doi:10.1155/2015/131547
Moat SJ, Doshi SN, Lang D, McDowell IF, Lewis MJ, Goodfellow J (2004) Treatment of coronary heart disease with folic acid: is there a future? Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 287:H1–H7. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00952.2003
Montoya-Durango DE, Ramos KA, Bojang P, Ruiz L, Ramos IN, Ramos KS (2016) LINE-1 silencing by retinoblastoma proteins is effected through the nucleosomal and remodeling deacetylase multiprotein complex. BMC Cancer 16:38. doi:10.1186/s12885-016-2068-9
Moore LE, Smith AH, Hopenhayn-Rich C, Biggs ML, Kalman DA, Smith MT (1997) Micronuclei in exfoliated bladder cells among individuals chronically exposed to arsenic in drinking water. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 6:31–36
Mostafa MG, Cherry N (2015) Arsenic in drinking water, transition cell cancer and chronic cystitis in rural Bangladesh. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12:13739–13749. doi:10.3390/ijerph121113739
Ohno K, Yanase T, Matsuo Y, Kimura T, Rahman MH, Magara Y, Matsui Y (2007) Arsenic intake via water and food by a population living in an arsenic-affected area of Bangladesh. Sci Total Environ 381:68–76. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.03.019
Ovchinnikov I, Rubin A, Swergold GD (2002) Tracing the LINEs of human evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:10522–10527. doi:10.1073/pnas.152346799
Paul S et al (2013a) Human urothelial micronucleus assay to assess genotoxic recovery by reduction of arsenic in drinking water: a cohort study in West Bengal, India. Biometals 26:855–862. doi:10.1007/s10534-013-9652-0
Paul S et al (2013b) Arsenic-induced toxicity and carcinogenicity: a two-wave cross-sectional study in arsenicosis individuals in West Bengal, India. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 23:156–162. doi:10.1038/jes.2012.91
Paul S et al (2014) Arsenic-induced promoter hypomethylation and over-expression of ERCC2 reduces DNA repair capacity in humans by non-disjunction of the ERCC2-Cdk7 complex. Metallomics 6:864–873. doi:10.1039/c3mt00328k
Paul S, Bhattacharjee P (2015) Epigenetics and arsenic toxicity. In: States JC (ed) Arsenic: exposure sources, health risks, and mechanisms of toxicity, vol 1. Wiley, New York, pp 421–436
Paul S, Giri AK (2015) Epimutagenesis: a prospective mechanism to remediate arsenic-induced toxicity. Environ Int 81:8–17. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2015.04.002
Paul S, Majumdar S, Giri AK (2015) Genetic susceptibility to arsenic-induced skin lesions and health effects: a review. Genes Environ 37:23. doi:10.1186/s41021-015-0023-7
Panieri E, Santoro MM (2016) ROS homeostasis and metabolism: a dangerous liason in cancer cells. Cell Death Dis 7:e2253. doi:10.1038/cddis.2016.105
Pilsner JR et al (2012) Influence of prenatal arsenic exposure and newborn sex on global methylation of cord blood DNA. PloS One 7:e37147. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0037147
Pizarro I, Gomez-Gomez M, Leon J, Roman D, Palacios MA (2016) Bioaccessibility and arsenic speciation in carrots, beets and quinoa from a contaminated area of Chile. Sci Total Environ 565:557–563. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.04.199
Puttipanyalears C, Kitkumthorn N, Buranapraditkun S, Keelawat S, Mutirangura A (2016) Breast cancer upregulating genes in stromal cells by LINE-1 hypermethylation and micrometastatic detection. Epigenomics 8:475–486. doi:10.2217/epi-2015-0007
Rhee YY et al (2015) Prognostic significance of promoter CpG island hypermethylation and repetitive DNA hypomethylation in stage I lung adenocarcinoma. Virchows Arch 466:675–683. doi:10.1007/s00428-015-1749-0
Sen A et al (2015) Multigenerational epigenetic inheritance in humans: DNA methylation changes associated with maternal exposure to lead can be transmitted to the grandchildren. Sci Rep 5:14466. doi:10.1038/srep14466
Shakoor MB et al (2015) Unraveling health risk and speciation of arsenic from groundwater in rural areas of Punjab, Pakistan. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12:12371–12390. doi:10.3390/ijerph121012371
Sigalotti L et al (2011) Methylation levels of the “long interspersed nucleotide element-1″ repetitive sequences predict survival of melanoma patients. J Transl Med 9:78. doi:10.1186/1479-5876-9-78
Sinczuk-Walczak H, Janasik BM, Trzcinka-Ochocka M, Stanislawska M, Szymczak M, Halatek T, Walusiak-Skorupa J (2014) Neurological and neurophysiological examinations of workers exposed to arsenic levels exceeding hygiene standards. Int J Occup Med Environ Health 27:1013–1025. doi:10.2478/s13382-014-0316-2
Tajuddin SM et al (2013) Genetic and non-genetic predictors of LINE-1 methylation in leukocyte DNA. Environ Health Perspect 121:650–656. doi:10.1289/ehp.1206068
Tellez-Plaza M et al (2014) Association of global DNA methylation and global DNA hydroxymethylation with metals and other exposures in human blood DNA samples. Environ Health Perspect 122:946–954. doi:10.1289/ehp.1306674
Terry MB, Delgado-Cruzata L, Vin-Raviv N, Wu HC, Santella RM (2011) DNA methylation in white blood cells: association with risk factors in epidemiologic studies. Epigenetics 6:828–837
Tong D, Ortega J, Kim C, Huang J, Gu L, Li GM (2015) Arsenic inhibits DNA mismatch repair by promoting EGFR expression and PCNA phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 290:14536–14541. doi:10.1074/jbc.M115.641399
Uthus EO, Davis C (2005) Dietary arsenic affects dimethylhydrazine-induced aberrant crypt formation and hepatic global DNA methylation and DNA methyltransferase activity in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 103:133–145. doi:10.1385/BTER:103:2:133
van Eijk KR et al (2012) Genetic analysis of DNA methylation and gene expression levels in whole blood of healthy human subjects. BMC Genom 13:636. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-13-636
Virani S, Rentschler KM, Nishijo M, Ruangyuttikarn W, Swaddiwudhipong W, Basu N, Rozek LS (2016) DNA methylation is differentially associated with environmental cadmium exposure based on sex and smoking status. Chemosphere 145:284–290. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.10.123
Wilhelm CS et al (2010) Implications of LINE1 methylation for bladder cancer risk in women. Clin Cancer Res 16:1682–1689. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2983
Wu MM et al (2006) Effect of plasma homocysteine level and urinary monomethylarsonic acid on the risk of arsenic-associated carotid atherosclerosis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 216:168–175. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2006.05.005
Wu LM et al (2016) Zeb2 recruits HDAC-NuRD to inhibit Notch and controls Schwann cell differentiation and remyelination. Nat Neurosci 19:1060–1072. doi:10.1038/nn.4322
Xiong Z, Laird PW (1997) COBRA: a sensitive and quantitative DNA methylation assay. Nucleic Acids Res 25:2532–2534
Xu M et al (2016) MeCP2 suppresses LIN28A expression via binding to its methylated-CpG islands in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncotarget 7:14476–14485. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.7507
Yamaguchi Y et al (2016) Arsenic acid inhibits proliferation of skin fibroblasts, and increases cellular senescence through ROS mediated MST1-FOXO signaling pathway. J Toxicol Sci 41:105–113. doi:10.2131/jts.41.105
Yu F, Zingler N, Schumann G, Stratling WH (2001) Methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 represses LINE-1 expression and retrotransposition but not Alu transcription. Nucleic Acids Res 29:4493–4501
Yu W et al (2011) Global analysis of DNA methylation by methyl-capture sequencing reveals epigenetic control of cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer cell. PLoS one 6:e29450. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0029450
Zabihi S, Eriksson UJ, Wentzel P (2007) Folic acid supplementation affects ROS scavenging enzymes, enhances Vegf-A, and diminishes apoptotic state in yolk sacs of embryos of diabetic rats. Reprod Toxicol 23:486–498. doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2007.03.007
Zhang H et al (2015) Interactive effects of N6AMT1 and As3MT in arsenic biomethylation. Toxicol Sci 146:354–362. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfv101
Zhang W, Tian F, Zheng J, Li S, Qiang M (2016) Chronic administration of benzo(a)pyrene induces memory impairment and anxiety-like behavior and increases of NR2B DNA methylation. PLoS One 11:e0149574. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0149574
Zhao CQ, Young MR, Diwan BA, Coogan TP, Waalkes MP (1997) Association of arsenic-induced malignant transformation with DNA hypomethylation and aberrant gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:10907–10912
Zhao MT, Whyte JJ, Hopkins GM, Kirk MD, Prather RS (2014) Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation and high-throughput sequencing (MeDIP-seq) using low amounts of genomic DNA. Cell Reprogr 16:175–184. doi:10.1089/cell.2014.0002
Zolot J (2016) Arsenic levels in drinking water linked to bladder cancer in New England. Am J Nurs 116:16. doi:10.1097/01.NAJ.0000490158.36747.67
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR, India) to provide SRF to SP; University Grants Commission (UGC, India) to provide JRF to P.B and Department of Science and Technology (DST-SERB, India, Grant #2620/2013) to provide grant to Dr. P.B. The authors are also thankful to Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi, India for providing Emeritus Project Grant #. 21(0885)/12/EMR-II to AKG.
Author contribution
SP, PB conducted literature survey. SP made the illustrations. AKG and Dr.PB helped in formulation of the table. All the authors contributed in scripting the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declares that they have no competing interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paul, S., Bhattacharjee, P., Giri, A.K. et al. Arsenic toxicity and epimutagenecity: the new LINEage. Biometals 30, 505–515 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-017-0021-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-017-0021-2