Abstract
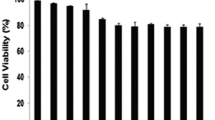
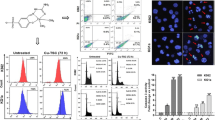
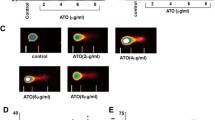
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a hematologic disorder characterized by the constitutive expression of BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase. Although successful implementation of tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of CML remain a traditional choice for molecularly targeted therapy, some patients present primary or secondary resistance to such therapy. Therefore, alternative therapeutic strategies are required to treat resistant CML cells. Accordingly, new anti-proliferative and/or pro-apoptotic compounds would be needed for clinical treatment. In the present investigation, we demonstrate that TPEN (e.g. 3 μM), a lipid-soluble metal chelator, induces apoptosis in K562 cells via a molecular cascade involving H2O2 ≫ JNK, NF-κB > c-JUN, P73 > PUMA, BAX > loss of ΔΨm > CASPASE-3 > nuclei/DNA fragmentation. Fragmentation of the nuclei and DNA are indicative of cell death by apoptosis. Remarkably, the antioxidant N-acetyl-cysteine, and inhibitors of the transcription factors CASPASE 3 and (JNK) kinase, decreased oxidative stress (OS) and cell death in these cells. This is evidenced by fluorescence microscopy, flow cytometry and immunocytochemistry for OS markers (e.g. generation of H2O2 and DJ 1 oxidation) and nuclear expression of apoptotic markers (e.g. activated caspase 3 and JNK kinase). In addition, TPEN causes no detectable damage in human peripheral blood lymphocyte cells (hPBLCs). We conclude that TPEN selectively induces apoptosis in K562 cells via an OS-mechanism. Our findings may provide insight into more effective CML anticancer therapies.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avila-Gomez IC, Velez-Pardo C, Jimenez-Del-Rio M (2010) Effects of insulin-like growth factor-1 on rotenone-induced apoptosis in lymphocyte cells. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 106(1): 53–61
Cao J, Lou S, Ying M, Xie N, Lin G, Dong R, Zhang J, Yan H, Yang X, He Q, Yang B (2014) The oxidations states of DJ-1 dictate the cells fate in response to oxidative stress triggered by 4-HPR: autophagy or apoptosis? Antioxid Redox Signal 21(10):1443–1459
Chen Y, Peng C, Li D, Li S (2010) Molecular and cellular bases of chronic myeloid leukemia. Protein Cell 1(2):124–132
Daniel AG, Peterson EJ, Farrell NP (2014) The bioinorganic chemistry of apoptosis: potential inhibitory zincbinding sites in caspase-3. Angew Chem Int Ed 53:4098–4101
Datta K, Babbar P, Srivastava T, Sinha S, Chattopadhyay P (2002) p53 dependent apoptosis in glioma cell lines in response to hydrogen peroxide induced oxidative stress. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 34(2):148–157
Davidson W, Ren Q, Kari G, Kashi O, Dicker AP, Rodeck U (2008) Inhibition of p73 function by Pifithrin-α as revealed by studies in zebrafish embryos. Cell Cycle 7(9):1224–1230
Durland-Busbice S, Reisman D (2002) Lack of p53 expression in human myeloid leukemias is not due to mutations in transcriptional regulatory regions of the gene. Leukemia 16(10):2165–2167
Fatfat M, Merhi RA, Rahal O, Stoyanovsky DA, Zaki A, Haidar H, Kagan VE, Gali-Muhtasib H, Machaca K (2014) Copper chelation selectively kills colon cancer cells through redox cycling and generation of reactive oxygen species. BMC Cancer 14:527
Fujioka S, Schmidt C, Sclabas GM, Li Z, Pelicano H, Peng B, Yao A, Niu J, Zhang W, Evans DB, Abbruzzese JL, Huang P, Chiao PJ (2004) Stabilization of p53 is a novel mechanism for proapoptotic function of NF-kappaB. J Biol Chem 279(26):27549–27559
Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Trojel-Hansen C, Kroemer G (2012a) Mitochondrial control of cellular life, stress, and death. Circ Res 111(9):1198–1207
Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Abrams JM, Alnemri ES, Baehrecke EH, Blagosklonny MV et al (2012b) Molecular definitions of cell death subroutines: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death. Cell Death Differ 19:107–120
Gambacorti-Passerini C, Piazza R (2015) How I treat newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia in 2015. Am J Hematol 90(2):156–161
Gribble SM, Roberts I, Grace C, Andrews KM, Green AR, Nacheva EP (2000) Cytogenetics of the chronic myeloid leukemia-derived cell line K562: karyotype clarification by multicolor fluorescence in situ hybridization, comparative genomic hybridization, and locus-specific fluorescence in situ hybridization. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 118(1):1–8
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144(5):646–674
Holyoake TL, Helgason GV (2015) Do we need more drugs for chronic myeloid leukemia? Immunol Rev 263(1):106–123
Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, Miller D, Bishop K, Altekruse SF, Kosary CL, Yu M, Ruhl J, International Agency for research in Cancer (2012) Globocan 2012: estimated cancer incidence, mortality and prevalence worldwide in 2012. http://globocan.iarc.fr/Pages/fact_sheets_cancer.aspx. December, 2016
Huber KL, Hardy JA (2012) Mechanism of zinc-mediated inhibition of caspase-9. Protein Sci 21(7):1056–1065
Hwang JJ, Kim HN, Kim J, Cho DH, Kim MJ, Kim YS, Kim Y, Park SJ, Koh JY (2010) Zinc(II) ion mediates tamoxifen-induced autophagy and cell death in MCF-7 breast cancer cell line. Biometals 23(6):997–1013
Jänicke RU, Sprengart ML, Wati MR, Porter AG (1998) Caspase-3 is required for DNA fragmentation and morphological changes associated with apoptosis. J Biol Chem 273(16):9357–9360
Jimenez-Del-Rio M, Velez-Pardo C (2012) The bad, the good and the ugly about oxidative stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2012:1–13
Kim TD, Türkmen S, Schwarz M, Koca G, Nogai H, Bommer C, Dörken B, Daniel P, le Coutre P (2010) Impact of additional chromosomal aberrations and BCR-ABL kinase domain mutations on the response to nilotinib in Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 95(4):582–588
Kinumi T, Kimata J, Taira T, Ariga H, Niki E (2004) Cysteine-106 of DJ-1 is the most sensitive cysteine residue to hydrogen peroxide-mediated oxidation in vivo in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 317(3):722–728
Komarov PG, Komarova EA, Kondratov RV, Christov-Tselkov K, Coon JS, Chernov MV, Gudkov AV (1999) A chemical inhibitor of p53 that protects mice from the side effects of cancer therapy. Science 285(5434):1733–1737
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Vandenabeele P, Abrams J, Alnemri ES, Baehrecke EH et al (2009) Classification of cell death: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2009. Cell Death Differ 16:3–11
Law JC, Ritke MK, Yalowich JC, Leder GH, Ferrell RE (1993) Mutational inactivation of the p53 gene in the human erythroid leukemic K562 cell line. Leuk Res 17(12):1045–1050
Liang ZQ, Li YL, Zhao XL, Han R, Wang XX, Wang Y, Chase TN, Bennett MC, Qin ZH (2007) NF-kappaB contributes to 6-hydroxydopamine-induced apoptosis of nigral dopaminergic neurons through p53. Brain Res 1145:190–203
Lu H, Hou G, Zhang Y, Dai Y, Zhao H (2014) c-Jun transactivates Puma gene expression to promote osteoarthritis. Mol Med Rep 9(5):1606–1612
Luna-Vargas MP, Chipuk JE (2016) Physiological and pharmacological control of BAK, BAX, and beyond. Trends Cell Biol 26(12):906–917
Makhov P, Golovine K, Uzzo RG, Rothman J, Crispen PL, Shaw T, Scoll BJ, Kolenko VM (2008) Zinc chelation induces rapid depletion of the X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis and sensitizes prostate cancer cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 15(11):1745–1751
Marcé S, Zamora L, Cabezón M, Xicoy B, Boqué C, Fernández C, Grau J, Navarro JT, Fernández de Sevilla A, Ribera JM, Feliu E, Millá F, Grupo ICO de estudio de mutaciones de ABL en pacientes afectos de LMC (2013) Frequency of ABL gene mutations in chronic myeloid leukemia patients resistant to imatinib and results of treatment switch to second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Med Clin (Barc) 141(3):95–99
Marinho HS, Real C, Cyrne L, Soares H, Antunes F (2014) Hydrogen peroxide sensing, signaling and regulation of transcription factors. Redox Biol 2:535–562
Martin AG, Trama J, Crighton D, Ryan KM, Fearnhead HO (2009) Activation of p73 and induction of Noxa by DNA damage requires NF-kappa B. Aging (Albany NY) 1(3):335–349
Meggyesi N, Kozma A, Halm G, Nahajevszky S, Bátai A, Fekete S, Barta A, Ujj G, Lueff S, Sipos A, Adám E, Bors A, Reményi P, Masszi T, Tordai A, Andrikovics H (2012) Additional chromosome abnormalities, BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase domain mutations and clinical outcome in Hungarian tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistant chronic myelogenous leukemia patients. Acta Haematol 127(1):34–42
Melino G, Bernassola F, Ranalli M, Yee K, Zong WX, Corazzari M, Knight RA, Green DR, Thompson C, Vousden KH (2004) p73 induces apoptosis via PUMA transactivation and Bax mitochondrial translocation. J Biol Chem 279(9):8076–8083
Mendivil-Perez M, Velez-Pardo C, Jimenez-Del-Rio M (2012) TPEN induces apoptosis independently of zinc chelator activity in a model of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and ex vivo acute leukemia cells through oxidative stress and mitochondria caspase-3- and AIF-dependent pathways. Oxid Med Cell Longev 313275
Miyama A, Saito Y, Yamanaka K, Hayashi K, Hamakubo T, Noguchi N (2011) Oxidation of DJ-1 induced by 6-hydroxydopamine decreasing intracellular glutathione. PLoS ONE 6(11):e27883
Naumann S, Reutzel D, Speicher M, Decker HJ (2001) Complete karyotype characterization of the K562 cell line by combined application of G-banding, multiplex-fluorescence in situ hybridization, fluorescence in situ hybridization, and comparative genomic hybridization. Leuk Res 25(4):313–322
Perry DK, Smyth MJ, Stennicke HR, Salvesen GS, Duriez P, Poirier GG, Hannun YA (1997) Zinc is a potent inhibitor of the apoptotic protease, caspase-3. A novel target for zinc in the inhibition of apoptosis. J Biol Chem 272(30):18530–185303
Peters UR, Tschan MP, Kreuzer KA, Baskaynak G, Lass U, Tobler A, Fey MF, Schmidt CA (1999) Distinct expression patterns of the p53-homologue p73 in malignant and normal hematopoiesis assessed by a novel real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction assay and protein analysis. Cancer Res 59:4233–4236
Redza-Dutordoir M, Averill-Bates DA (2016) Activation of apoptosis signalling pathways by reactive oxygen species. Biochim Biophys Acta 1863(12):2977–2992
Ruiz-Moreno C, Jimenez-Del-Rio M, Sierra-Garcia L, Lopez-Osorio B, Velez-Pardo C (2016) Vitamin E synthetic derivate-TPGS-selectively induces apoptosis in jurkat t cells via oxidative stress signaling pathways: implications for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Apoptosis 21(9):1019–1032
Shi Y, Toms BB, Dixit N, Kumari N, Mishra L, Goodisman J, Dabrowiak JC (2010) Cytotoxicity of Cu(II) and Zn(II) 2,2′-bipyridyl complexes: dependence of IC50 on recovery time. Chem Res Toxicol 23(8):1417–1426
Siomek A (2012) NF-κB signaling pathway and free radical impact. Acta Biochim Pol 59(3):323–331
Stuart CH, Singh R, Smith TL, D’Agostino R Jr, Caudell D, Balaji KC, Gmeiner WH (2016) Prostate-specific membrane antigen-targeted liposomes specifically deliver the Zn(2+) chelator TPEN inducing oxidative stress in prostate cancer cells. Nanomedicine (Lond) 11(10):1207–1222
Taira T, Saito Y, Niki T, Iguchi-Ariga SM, Takahashi K, Ariga H (2004) DJ-1 has a role in antioxidative stress to prevent cell death. EMBO Rep 5(2):213–218
Tatalovich Z, Mariotto A, Lewis DR, Chen HS, Feuer EJ, Cronin KA (eds) (2016) SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2013, National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, MD. http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2013/. (based on November 2015 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER web site, December 2016)
Xia Y, Shen S, Verma IM (2014) NF-κB, an active player in human cancers. Cancer Immunol Res 2(9):823–830
Yoon MK, Ha JH, Lee MS, Chi SW (2015) Structure and apoptotic function of p73. BMB Rep 48(2):81–90
Zubair H, Khan HY, Sohail A, Azim S, Ullah MF, Ahmad A, Sarkar FH, Hadi SM (2013) Redox cycling of endogenous copper by thymoquinone leads to ROS-mediated DNA breakage and consequent cell death: putative anticancer mechanism of antioxidants. Cell Death Dis 4:e660
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the “Committee for Development and Research [Comite para el Desarrollo y la Investigacion]-CODI”, UdeA, Grants #2013-2570 held by Marlene Jimenez-Del-Rio and Carlos Velez-Pardo. Luisa Rojas-Valencia is a master student from the Neurosciences program at the Basic Biomedical Sciences Academic Corporation, UdeA.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author contributions
MJ-Del-R and CV-P conceived and designed the experiments; LMRV performed the experiments; and LMR-V, CV-P, MJ-Del-R analyzed the data; MJ-Del-R contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; CV-P and MJ-Del-R wrote the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Carlos Velez-Pardo and Marlene Jimenez-Del-Rio share senior authorship.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rojas-Valencia, L., Velez-Pardo, C. & Jimenez-Del-Rio, M. Metal chelator TPEN selectively induces apoptosis in K562 cells through reactive oxygen species signaling mechanism: implications for chronic myeloid leukemia. Biometals 30, 405–421 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-017-0015-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-017-0015-0