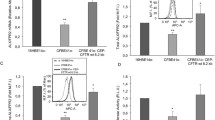
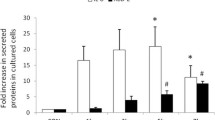
Abstract
Conflicting data are reported on pro- or anti-inflammatory activity of bovine lactoferrin (bLf) in different cell models as phagocytes or epithelial cell lines infected by bacteria. Here we evaluated the bLf effect on epithelial models mimicking two human pathologies characterized by inflammation and infection with specific bacterial species. Primary bronchial epithelium from a cystic fibrosis (CF) patient and differentiated intestinal epithelial cells were infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa LESB58 isolated from a CF patient and Adherent-Invasive Escherichia coli LF82 isolated from a Crohn’s disease patient. Surprisingly, bLf significantly reduced the intracellular bacterial survival, but differently modulated the inflammatory response. These data lead us to hypothesize that bLf differentially acts depending on the epithelial model and infecting pathogen. To verify this hypothesis, we explored whether bLf could modulate ferroportin (Fpn), the only known cellular iron exporter from cells, that, by lowering the intracellular iron level, determines a non permissive environment for intracellular pathogens. Here, for the first time, we describe the bLf ability to up-regulate Fpn protein in infected epithelial models. Our data suggest that the mechanism underlying the bLf modulating activity on inflammatory response in epithelial cells is complex and the bLf involvement in modulating cellular iron homeostasis should be taken into account.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alzoghaibi MA (2005) Neutrophil expression and infiltration into Crohn’s intestine. Saudi J Gastroenterol 11:63–72
Barnich N, Carvalho FA, Glasser AL, Darcha C, Jantscheff P, Allez M, Peeters H, Bommelaer G, Desreumaux P, Colombel JF, Darfeuille-Michaud A (2007) CEACAM6 acts as a receptor for adherent-invasive E. coli, supporting ileal mucosa colonization in Crohn disease. J Clin Investig 117:1566–1574. doi:10.1172/JCI30504
Berlutti F, Morea C, Battistoni A, Sarli S, Cipriani P, Superti F, Ammendolia MG, Valenti P (2005) Iron availability influences aggregation, biofilm, adhesion and invasion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Burkholderia cenocepacia. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 18:661–670
Berlutti F, Schippa S, Morea C, Sarli S, Perfetto B, Donnarumma G, Valenti P (2006) Lactoferrin downregulates pro-inflammatory cytokines upexpressed in intestinal epithelial cells infected with invasive or non invasive Escherichia coli strains. Biochem Cell Biol 84:351–357
Berlutti F, Superti F, Nicoletti M, Morea C, Frioni A, Ammendolia MG, Battistoni A, Valenti P (2008) Bovine lactoferrin inhibits the efficiency of invasion of respiratory A549 cells of different iron-regulated morphological forms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Burkholderia cenocepacia. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 21:51–59
Boucher RC (2002) An overview of the pathogenesis of cystic fibrosis lung disease. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 54:1359–1371. doi:10.1016/S0169-409X(02)00144-8
Cairo G, Recalcati S, Mantovani A, Locati M (2011) Iron trafficking and metabolism in macrophages: contribution to the polarized phenotype. Trends Immunol 32:241–247. doi:10.1016/j.it.2011.03.007
Cario E, Rosenberg IM, Brandwein SL, Beck PL, Reinecker HC, Podolsky DK (2000) Lipopolysaccharide activates distinct signaling pathways in intestinal epithelial cell lines expressing Toll-like receptors. J Immunol 164:966–972
Chassaing B, Koren O, Carvalho FA, Ley RE, Gewirtz AT (2013) AIEC pathobiont instigates chronic colitis in susceptible hosts by altering microbiota composition. Gut. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2013-304909
Cheng K, Smyth RL, Govan JR, Doherty C, Winstanley C, Denning N, Heaf DP, van Saene H, Hart CA (1996) Spread of beta-lactam-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a cystic fibrosis clinic. Lancet 348:639–642. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(96)05169-0
Cohen TS, Prince A (2012) Cystic fibrosis: a mucosal immunodeficiency syndrome. Nat Med 18:509–519. doi:10.1038/nm.2715
Cozens AL, Yezzi MJ, Kunzelmann K, Ohrui T, Chin L, Eng K, Finkbeiner WE, Widdicombe JH, Gruenert DC (1994) CFTR expression and chloride secretion in polarized immortal human bronchial epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 10:38–47. doi:10.1165/ajrcmb.10.1.7507342
Curran C, Demick KP, Mansfield JM (2006) Lactoferrin activates macrophages via TLR4-dependent and -independent signaling pathways. Cell Immunol 242:23–30. doi:10.1016/j.cellimm.2006.08.006
Darfeuille-Michaud A, Boudeau J, Bulois P, Neut C, Glasser AL, Barnich N, Bringer MA, Swidsinski A, Beaugerie L, Colombel JF (2004) High prevalence of adherent-invasive Escherichia coli associated with ileal mucosa in Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology 127:412–421. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2004.04.061
De Domenico I, Ward DM, Musci G, Kaplan J (2007) Evidence for the multimeric structure of ferroportin. Blood 109:2205–2209. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-06-032516
Ghio AJ, Piantadosi CA, Wang X, Dailey LA, Stonehuerner JD, Madden MC, Yang F, Dolan KG, Garrick MD, Garrick LM (2005) Divalent metal transporter-1 decreases metal-related injury in the lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 289:L460–L467. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00154.2005
Glasser AL, Boudeau J, Barnich N, Perruchot MH, Colombel JF, Darfeuille-Michaud A (2001) Adherent invasive Escherichia coli strains from patients with Crohn’s disease survive and replicate within macrophages without inducing host cell death. Infect Immunol 69:5529–5537. doi:10.1128/IAI.69.9.5529-5537.2001
Hayworth JL, Kasper KJ, Leon-Ponte M, Herfst CA, Yue D, Brintnell WC, Mazzuca DM, Heinrichs DE, Cairns E, Madrenas J, Hoskin DW, McCormick JK, Haeryfar SM (2009) Attenuation of massive cytokine response to the staphylococcal enterotoxin B superantigen by the innate immunomodulatory protein lactoferrin. Clin Exp Immunol 157:60–70. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2009.03963.x
Huebner C, Ding Y, Petermann I, Knapp C, Ferguson LR (2011) The probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 reduces pathogen invasion and modulates cytokine expression in Caco-2 cells infected with Crohn’s disease-associated E. coli LF82. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:2541–2544. doi:10.1128/AEM.01601-10
Kasvosve I (2013) Effect of ferroportin polymorphism on iron homeostasis and infection. Clin Chim Acta 1(416):20–25. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2012.11.013
Khan TZ, Wagener JS, Bost T, Martinez J, Accurso FJ, Riches DW (1995) Early pulmonary inflammation in infants with cystic fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 151:1075–1082. doi:10.1164/ajrccm.151.4.7697234
Kim CW, Lee TH, Park KH, Choi SY, Kim J (2012) Human lactoferrin suppresses TNF-α-induced intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression via competition with NF-κB in endothelial cells. FEBS Lett 586:229–234. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2011.12.011
Komatsu A, Satoh T, Wakabayashi H, Ikeda F (2013) Effects of bovine lactoferrin to oral Candida albicans and Candida glabrata isolates recovered from the saliva in elderly people. Odontology
Kukavica-Ibrulj I, Bragonzi A, Paroni M, Winstanley C, Sanschagrin F, O’Toole GA, Levesque RC (2008) In vivo growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains PAO1 and PA14 and the hypervirulent strain LESB58 in a rat model of chronic lung infection. J Bacteriol 190:2804–2813. doi:10.1128/JB.01572-07
Latorre D, Berlutti F, Valenti P, Gessani S, Puddu P (2012) LF immunomodulatory strategies: mastering bacterial endotoxin. Biochem Cell Biol 90:269–278. doi:10.1139/o11-059
Lee TW, Brownlee KG, Conway SP, Denton M, Littlewood JM (2003) Evaluation of a new definition for chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis patients. J Cyst Fibros 2:29–34. doi:10.1016/S1569-1993(02)00141-8
Legrand D (2012) Lactoferrin, a key molecule in immune and inflammatory processes. Biochem Cell Biol 90:252–268. doi:10.1139/o11-056
Lewis JD (2011) The utility of biomarkers in the diagnosis and therapy of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 140(6):1817–1826
Ludwiczek S, Aigner E, Theurl I, Weiss G (2003) Cytokine-mediated regulation of iron transport in human monocytic cells. Blood 101:4148–4154. doi:10.1182/blood-2002-08-2459
Martinez-Medina M, Aldeguer X, Lopez-Siles M, González-Huix F, Lopez-Oliu C, Dahbi G, Blanco JE, Blanco J, Garcia-Gil LJ, Darfeuille-Michaud A (2009) Molecular diversity of Escherichia coli in the human gut: new ecological evidence supporting the role of adherent-invasive E. coli (AIEC) in Crohn’s disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 15:872–882. doi:10.1002/ibd.20860
Moreau-Marquis S, Bomberger JM, Anderson GG, Swiatecka-Urban A, Ye S, O’Toole GA, Stanton BA (2008) The DeltaF508-CFTR mutation results in increased biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa by increasing iron availability. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 295:L25–L37. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00391
Nairz M, Schleicher U, Schroll A, Sonnweber T, Theurl I, Ludwiczek S, Talasz H, Brandacher G, Moser PL, Muckenthaler MU, Fang FC, Bogdan C, Weiss G (2013) Nitric oxide-mediated regulation of ferroportin-1 controls macrophage iron homeostasis and immune function in Salmonella infection. J Exp Med 210(5):855–873
Nichols D, Chmiel J, Berger M (2007) Chronic inflammation in the cystic fibrosis lung: alterations in inter- and intracellular signalling. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 34:146–162
O’Sullivan BP, Flume P (2009) The clinical approach to lung disease in patients with cystic fibrosis. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 30:505–513. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1238909
Paesano R, Pietropaoli M, Gessani S, Valenti P (2009) The influence of lactoferrin, orally administered, on systemic iron homeostasis in pregnant women suffering of iron deficiency and iron deficiency anemia. Biochimie 91:44–51. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2008.06.004
Paesano R, Berlutti F, Pietropaoli M, Goolsbee W, Pacifici E, Valenti P (2010) Lactoferrin efficacy versus ferrous sulfate in curing iron disorders in pregnant and non pregnant women. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 23:577–587
Pfefferkorn MD, Boone JH, Nguyen JT, Juliar BE, Davis MA, Parker KK (2010) Utility of fecal lactoferrin in identifying Crohn disease activity in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 51:425–428. doi:10.1097/MPG.0b013e3181d67e8f
Puddu P, Carollo MG, Belardelli F, Valenti P, Gessani S (2007) Role of endogenous interferon and LPS in the immunomodulatory effects of bovine lactoferrin in murine peritoneal macrophages. J Leukoc Biol 82:347–353. doi:10.1189/jlb.1106688
Puddu P, Latorre D, Carollo M, Catizone A, Ricci G, Valenti P, Gessani S (2011) Bovine lactoferrin counteracts Toll-like receptor mediated activation signals in antigen presenting cells. PLoS ONE 6:e22504. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0022504
Ranganathan SC, Parsons F, Gangell C, Brennan S, Stick SM, Sly PD (2011) Evolution of pulmonary inflammation and nutritional status in infants and young children with cystic fibrosis. Thorax 66:408–413. doi:10.1136/thx.2010.139493
Recalcati S, Locati M, Gammella E, Invernizzi P, Cairo G (2012) Iron levels in polarized macrophages: regulation of immunity and autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev 11:839–883. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2012.03.003
Reid DW, Lam QT, Schneider H, Walters EH (2004) Airway iron and iron-regulatory cytokines in cystic fibrosis. Eur Respir J 24:286–291. doi:10.1183/09031936.04.00104803
Reid DW, Carroll V, O’May C, Champion A, Kirov SM (2007) Increased airway iron as a potential factor in the persistence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis. Eur Respir J 30:286–292. doi:10.1183/09031936.00154006
Rolhion N, Darfeuille-Michaud A (2007) Adherent-invasive Escherichia coli in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 13:1277–1283
Ross SL, Tran L, Winters A, Lee KJ, Plewa C, Foltz I, King C, Miranda LP, Allen J, Beckman H, Cooke KS, Moody G, Sasu BJ, Nemeth E, Ganz T, Molineux G, Arvedson TL (2012) Molecular mechanism of hepcidin-mediated ferroportin internalization requires ferroportin lysines, not tyrosines or JAK-STAT. Cell Metab 15(6):905–917. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2012.03.017
Sagel SD, Sontag MK, Accurso FJ (2009) Relationship between antimicrobial proteins and airway inflammation and infection in cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol 44:402–409. doi:10.1002/ppul.21028
Sasaki M, Sitaraman SV, Babbin BA, Gerner-Smidt P, Ribot EM, Garrett N, Alpern JA, Akyildiz A, Theiss AL, Nusrat A, Klapproth JM (2007) Invasive Escherichia coli are a feature of Crohn’s disease. Lab Invest 87:1042–1054. doi:10.1038/labinvest.3700661
Siciliano R, Rega B, Marchetti M, Seganti L, Antonini G, Valenti P (1999) Bovine lactoferrin peptidic fragments involved in inhibition of herpes simplex virus type 1 infection. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 264:19–23. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1999.1318
Strober W, Fuss IJ (2011) Pro-inflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of IBD. Gastroenterology 140:1756–1767. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2011.02.016
Tirouvanziam R, Khazaal I, Peault B (2002) Primary inflammation in human cystic fibrosis small airways. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 283:L445–L451. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00419.2001
Tunney MM, Field TR, Moriarty TF, Patrick S, Doering G, Muhlebach MS, Wolfgang MC, Boucher R, Gilpin DF, McDowell A, Elborn JS (2008) Detection of anaerobic bacteria in high numbers in sputum from patients with cystic fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 177:995–1001. doi:10.1164/rccm.200708-1151OC
Valenti P, Catizone A, Pantanella F, Frioni A, Natalizi T, Tendini M, Berlutti F (2011) Lactoferrin decreases inflammatory response by cystic fibrosis bronchial cells invaded with Burkholderia cenocepacia iron-modulated biofilm. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 24:1057–1068
Vora P, Youdim A, Thomas LS, Fukata M, Tesfay SY, Lukasek K, Michelsen KS, Wada A, Hirayama T, Arditi M, Abreu MT (2004) Beta-defensin-2 expression is regulated by TLR signaling in intestinal epithelial cells. J Immunol 173:5398–5405
Wang G (2010) State-dependent regulation of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gating by a high affinity Fe3+ bridge between the regulatory domain and cytoplasmic loop 3. J Biol Chem 285:40438–40447. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.161497
Welsh KJ, Hwang SA, Boyd S, Kruzel ML, Hunter RL, Actor JK (2011) Influence of oral lactoferrin on Mycobacterium tuberculosis induced immunopathology. Tuberculosis 1:S105–S113. doi:10.1016/j.tube.2011.10.019
Wiesner J, Vilcinskas A (2010) Antimicrobial peptides: the ancient arm of the human immune system. Virulence 1:440–464. doi:10.4161/viru.1.5.12983
Yang F, Liu XB, Quinones M, Melby PC, Ghio A, Haile DJ (2002) Regulation of reticuloendothelial iron transporter MTP1 (Slc11a3) by inflammation. J Biol Chem 277:39786–39791
Acknowledgments
This work was granted by Italian Cystic Fibrosis Research Foundation (research project FFC#13/2013 adopted by Delegazione FFC di Palermo e di Vittoria Ragusa Catania 2) to FB and by Sapienza University of Rome to PV; thanks are due to Luigi Rosa for his enthusiastic technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper is dedicated to the memory of our colleague, Dr. Patriza Puddu who recently passed away.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frioni, A., Conte, M.P., Cutone, A. et al. Lactoferrin differently modulates the inflammatory response in epithelial models mimicking human inflammatory and infectious diseases. Biometals 27, 843–856 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-014-9740-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-014-9740-9