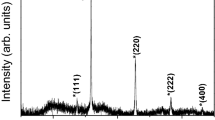
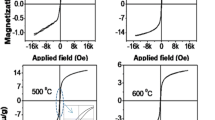
Abstract
Ferritin is not only important for iron storage and detoxification in living organisms, but a multifunctional size-constrained nanoplatform for biomimetic nanoparticles. In order to tailor the biomimetic nanoparticles for future applications, it is essential to investigate the effects of external factors such as temperature on the particle size and structure of reconstituted cores in ferritin. In this study, we systematically investigated the mineral composition, crystallinity, and particle size of human H-ferritin (HuHF) reconstituted at four different temperatures (25, 30, 37, and 42°C) by integrated magnetic and transmission electron microscopy analyses. Our results showed that the particle size of reconstituted ferrihydrite cores (~5 nm) in HuHF was temperature-independent. However, the significant changes of the induced magnetization at 5 T field (M5T) and remanent magnetization (Mr) at 5 K clearly showed that the crystallinity of reconstituted cores increased with increasing temperature, indicating that the reaction temperature deeply affects the structural order of reconstituted ferrihydrite cores rather than the particle size, and the reconstituted cores become more ordered at higher reaction temperatures. Our findings provide useful insights into biomineralization of ferritin under in vivo fever condition as well as in biomimetic synthesis of nanomaterials using ferritin. Furthermore, the rock magnetic methods should be very useful approaches for characterizing finite ferritin nanoparticles.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen PD, St Pierre TG, Street R (1998) Magnetic interactions in native horse spleen ferritin below the superparamagnetic blocking temperature. J Magn Magn Mater 177:1459–1460
Arosio P, Ingrassia R, Cavadini P (2009) Ferritins: a family of molecules for iron storage, antioxidation and more. Biochim Biophys Acta 1790:589–599
Berquo T, Erbs J, Lindquist A, Penn R, Banerjee S (2009) Effects of magnetic interactions in antiferromagnetic ferrihydrite particles. J Phys Condes Matter 21(17):176005
Bielig HJ, Bayer E (1955) Eisenaustausch Zwischen Proteiner-Modellversuche Zur Eisenresorption Und Speicherung Im Tierkorper. Naturwissenschaften 42(16):466
Cao CQ, Tian LX, Liu QS, Liu WF, Chen GJ, Pan YX (2010) Magnetic characterization of non-interacting, randomly oriented, nanometer-scale ferrimagnetic particles. J Geophys Res 115:B07103. doi:10.1029/2009JB006855
Chasteen ND, Harrison PM (1999) Mineralization in ferritin: an efficient means of iron storage. J Struct Biol 126:182–194
Chua-Anusorn W, Mun H-R, Webb J, Gorham NT, St. Pierre TG (2002) Effect of precipitation temperature and number of iron atoms per molecule on the structure of hydrated iron(III) oxyhydroxide ferritin cores synthesised in vitro. Hyperfine Interact 144(145):279–288
Cisowski S (1981) Interacting versus non-interacting single domain behavior in natural and synthetic samples. Phys Earth Planet Inter 26(1–2):56–62
Cushing BL, Kolesnichenko VL, O’Connor CJ (2004) Recent advances in the liquid-phase syntheses of inorganic nanoparticles. Chem Rev 104:3893–3946
Douglas T, Stark VT (2000) Nanophase cobalt oxyhydroxide mineral synthesized within the protein cage of ferritin. Inorg Chem 39(8):1828–1830
Douglas T, Dickson DPE, Betteridge S, Charnock J, Garner CD, Mann S (1995) Synthesis and structure of an iron(III) sulfide-ferritin bioinorganic nanocomposite. Science 269(5220):54–57
Dunlop DJ, Özdemir Ö (1997) Rock magnetism-fundamentals and frontiers. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Gilles C, Bonville P, Rakoto H, Broto JM, Wong KKW, Mann S (2002) Magnetic hysteresis and super antiferromagnetism in ferritin nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 241(2–3):430–440
Guyodo Y, Banerjee SK, Penn RL, Burleson D, Berquo TS, Seda T, Solheid P (2006) Magnetic properties of synthetic six-line ferrihydrite nanoparticles. Phys Earth Planet Inter 154:222–233
Harrison PM, Arosio P (1996) The ferritins: molecular properties, iron storage function and cellular regulation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1275:161–203
Harrison PM, Fischbach FA, Hoy TG, Haggis GH (1967) Ferric oxyhydroxide core of ferritin. Nature 216:1188–1190
Henkel O (1964) Remanenzverhalten und wechselwirkungen in hartmagnetischen teilchenkollektiven. Phys Status Solidi B 7(3):919–929
Kramer RM, Li C, Carter DC, Stone MO, Naik RR (2004) Engineered protein cages for nanomaterial synthesis. J Am Chem Soc 126(41):13282–13286
Macara IG, Hoy TG, Harrison PM (1972) The formation of ferritin from apoferritin. Biochem J 126:151–162
Meldrum FC, Cölfen H (2008) Controlling mineral morphologies and structures in biological and synthetic systems. Chem Rev 108(11):4332–4432
Meldrum FC, Wade VJ, Nimmo DL, Heywood BR, Mann S (1991) Synthesis of inorganic nanophase materials in supramolecular protein cages. Nature 349(21):684–687
Meldrum FC, Douglas T, Levi S, Arosio P, Mann S (1995) Reconstitution of manganese oxide cores in horse spleen and recombinant ferritins. J Inorg Biochem 58:59–68
Mørup S, Madsen DE, Frandsen C, Bahl CRH, Hansen MF (2007) Experimental and theoretical studies of nanoparticles of antiferromagnetic materials. J Phys Condes Matter 19:213202
Okuda M, Iwahori K, Yamashita I, Yoshimura H (2003) Fabrication of nickel and chromium nanoparticles using the protein cage of apoferritin. Biotechnol Bioeng 84(2):187–194
Papaefthymiou GC (2010) The Mössbauer and magnetic properties of ferritin cores. Biochim Biophys Acta 1800(8):886–897
Pâques EP, Pâques A, Crichton RR (1980) A study of the mechanism of ferritin formation-the effect of pH, ionic strength and temperature, inhibition by imidazole and kinetic analysis. Eur J Biochem 107:447–453
Pérez N, Guardia P, Roca AG, Morales MP, Serna CJ, Iglesias O, Bartolomé F, García LM, Batlle X, Labarta A (2008) Surface anisotropy broadening of the energy barrier distribution in magnetic nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 19:475704
Prené P, Tronc E, Jolivet JP, Livage J, Cherkaoui R, Noguès M, Dormann JL (1994) Mössbauer investigation of non-aggregated γ-Fe203 particles. Hyperfine Interact 93:1409–1414
Roberts AP, Cui Y, Verosub KL (1995) Wasp-waisted hysteresis loops: mineral magnetic characteristics and discrimination of components in mixed magnetic systems. J Geophys Res 100(B9):17909–17924
Rohrer JS, Islam QT, Watt GD, Sayers DE, Theil EC (1990) Iron environment in ferritin with large amounts of phosphate, from Azotobacter vinelandii and horse spleen, analyzed using extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS). Biochemistry 29:259–264
Santambrogio P, Cozzi A, Levi S, Rovida E, Magni F, Albertini A, Arosio P (2000) Functional and immunological analysis of recombinant mouse H- and L-ferritins from Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif 19(1):212–218
St Pierre TG, Chan P, Bauchspiess KR, Webb J, Betteridge S, Walton S, Dickson DPE (1996) Synthesis, structure and magnetic properties of ferritin cores with varying composition and degrees of structural order: models for iron oxide deposits in iron-overload diseases. Coord Chem Rev 151:125–143
Tartaj P (2009) Super paramagnetic composites: magnetism with no memory. Eur J Inorg Chem 2009(3):333–343
Tauxe L, Mullender TAT, Pick T (1996) Potbellies, wasp-waists, and super paramagnetism in magnetic hysteresis. J Geophys Res 101(B1):571–583
Tian LX, Cao CQ, Liu QS, Pan YX (2010) Low-temperature magnetic properties of horse spleen ferritin. Chin Sci Bull 55(27–28):3174–3180
Towe KM, Bradley WF (1967) Mineralogical constitution of colloidal “hydrous ferric oxides”. J Colloid Interface Sci 24(3):384–392
Tsukamoto R, Iwahori K, Muraoka M, Yamashita I (2005) Synthesis of Co3O4 nanoparticles using the cage-shaped protein, apoferritin. Bull Chem Soc Jpn 78(11):2075–2081
Ueno T, Suzuki M, Goto T, Matsumoto T, Nagayama K, Watanabe Y (2004) Size-selective olefin hydrogenation by a Pd nanocluster provided in an apo-ferritin cage. Angew Chem-Int Ed Engl 43(19):2527–2530
Wade VJ, Levi S, Arosio P, Treffry A, Harrison PM, Mann S (1991) Influence of site-directed modifications on the formation of iron cores in ferritin. J Mol Biol 221(4):1443–1452
Wade VJ, Treffry A, Laulhere JP, Bauminger ER, Cleton MI, Mann S, Briat JF, Harrison PM (1993) Structure and composition of ferritin cores from Pea Seed (Pisum-Sativum). Biochim Biophys Acta 1161(1):91–96
Warne B, Mayes EL (2003) Production of CoPt alloy grains within protein templates. Bioinspired nanoscale hybrid systems. Materials Research Society, Warrendale. pp 171–177
Wohlfarth EP (1955) The effect of particle interaction on the coercive force of ferromagnetic micropowders. Proc R Soc A Math Phys Eng Sci 232(1189):208–227
Yamashita I, Hayashi J, Hara M (2004) Bio-template synthesis of uniform CdSe nanoparticles using cage-shaped protein, apoferritin. Chem Lett 33(9):1158–1159
Yang XK, Barrett YC, Arosio P, Chasteen ND (1998) Reaction paths of iron oxidation and hydrolysis in horse spleen and recombinant human ferritins. Biochemistry 37(27):9743–9750
Zergenyi RS, Hirt AM, Zimmermann S, Dobson JP, Lowrie W (2000) Low-temperature magnetic behavior of ferrihydrite. J Geophys Res 105(B4):8297–8303
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 40821091 and 40904017), the CAS/SAFEA International Partnership Program for Creative Research Teams (KZCX2-YW-T10) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation. The authors are grateful to Paolo Arosio for providing us the vector pET12b-encoded cDNA of human H chain ferritin. The authors gratefully acknowledge the anonymous reviewers for very careful review and very constructive comments, Dr. Qingsong Liu and Jinhua Li for helping magnetic data analysis, and Dr. G.A. Paterson for improving the writing of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, L., Cao, C. & Pan, Y. The influence of reaction temperature on biomineralization of ferrihydrite cores in human H-ferritin. Biometals 25, 193–202 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-011-9497-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-011-9497-3