Abstract
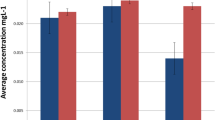
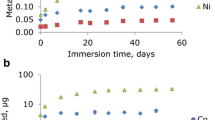
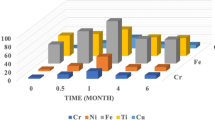
Although the metal devices used in orthodontic treatments are manufactured highly resistance to corrosion, they may still suffer some localized corrosion resulting from the oral cavity conditions. The corrosion causes the release of metals from the alloys used for their manufacture. In this report, we evaluated the in vivo metal ions release of three alloys (stainless steel, titanium and nickel-free) usually used in the orthodontics treatments and its genotoxicity. We applied to 15 patients, between 12 and 16 years, 4 tubes and 20 brackets. Samples from oral mucosa were taken before the treatment and 30 days later. The concentration of the titanium, chromium, manganese, cobalt, nickel, molybdenum and iron were detected using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). The genotoxicity was measured with a comet assay (Olive moment). The oral mucosa cells in contact with the stainless steel alloy displayed the greatest titanium and manganese concentrations and those in contact with the nickel-free alloy presented the greatest concentration of chromium and iron. Both alloys, stainless steel and nickel-free, induced a higher DNA damage in the oral mucosa cells than the titanium alloy, in which the Olive moment was similar to controls. Based on the results of our study, we can conclude that titanium brackets and tubes are the most biocompatible of the three alloys.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amini F, Borzabadi Farahani A, Jafari A, Rabbani M (2008) In vivo study of metal content of oral mucosa cells in patients with and without orthodontic appliances. Orthod Craniofac Res 11:51–56
Arvideon K, Cottler-Fox M, Friberg V (1986) Cytotoxic effects of Co–Cr alloys on fibroblast derived from human gingival. Scand J Dent Res 95:356–363
Besaratinia A, Van Straaten HW, Godschalk RW, Van Zandwijk N, Balm AJ, Kleinjans JC, Van Schooten FJ (2000) Immunoperoxidase detection of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-DNA adducts in mouth floor and buccal mucosa cells of smokers and nonsmokers. Environ Mol Mutagen 36:127–133
Danadevi K, Rozati R, Banu BS, Rao PH, Grover P (2003) DNA damage in workers exposed to lead using comet assay. Toxicology 187:183–193
Darabara MS, Bourithis LI, Zinelis S, Papadimitriou GD (2007) Metallurgical characterization, galvanic corrosion, and ionic release of orthodontic brackets coupled with Ni–Ti archwires. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 81:126–134
Faccioni F, Franceschetti P, Cepelloni M, Fracasso ME (2003) In vivo study on metal release fixed orthodontic appliances and DNA damage in oral mucosa cells. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop 124:687–694
Genelhu MCLS, Marigo M, Alves-Olivera LF, Malaquias LCC, Gómez RS (2005) Characterization of nickel-induced allergic contact stomatitis associated with fixed orthodontic appliances. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop 128:378–381
Geurtsen W (2002) Biocompatibility of dental casting alloys. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 13:71–84
Gursoy UK, Sokucu O, Uitto VJ, Aydin A, Demirer S, Toker H, Erdem O, Sayal A (2007) The role of nickel accumulation and epithelial cell proliferation in orthodontic treatment-induced gingival overgrowth. Eur J Orthod 29:555–558
House K, Sernetz F, Dymock D, Sandy J, Ireland A (2008) Corrosion of orthodontic appliances—should we care? Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop 133:584–592
Hwang CJ, Shin J-S, Cha J-Y (2001) Metal release from simulated fixed orthodontic appliances. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop 120:383–391
Iarmarcovai G, Sari Minodier I, Chaspoul F, Botta C, De Meo M, Orsiere T, Bergé-Lefranc JL, Gallice P, Botta A (2005) Risk assessment of welders using analysis of eight metals by ICP-MS in blood and urine and DNA damage evaluation by the comet and micronucleus assays; influence of XRCC1 and XRCC3 polymorphisms. Mutagenesis 20:425–432
Kang EH, Park SB, Kim HI, Kwon YH (2008) Corrosion-related changes on Ti-based orthodontic brackets in acetic NaF solutions: surface morphology, microhardness and element release. Dent Mater J 27:555–560
Kerosuo H, Moe G, Kleven E (1995) In vitro release of nickel and chromium from different types of simulated orthodontic appliances. Angle Orthod 65:111–116
Khan MA, Williams RL, Williams DF (1999) The corrosion behaviour of Ti–6Al-4 V, Ti-6Al-7Nb and Ti–13Nb-13Zr in protein solutions. Biomaterials 20:631–637
Kocadereli I, Atac A, Kale S, Ozer D (2000) Salivary nickel and chromium in patients with fixed orthodontic appliances. Angle Orthod 70:431–434
Laurent F, Grosgogeat B, Reclaru L, Dalard F, Lissac M (2001) Comparison of corrosion behaviour in presence of oral bacteria. Biomaterials 22:2273–2282
Lindsten R, Kurol J (1997) Orthodontic appliances in relation to nickel hypersensitivity: a review. J Orofac Orthop 58:100–108
Matos de Souza R, Macedo de Menezes L (2008) Nickel, chromium and iron levels in saliva of patients with simulated fixed orthodontic appliances. Angle Orthod 78:345–350
Mockers O, Deroze D, Camps J (2002) Cytotoxicity of orthodontic band, brackets and archwires in vitro. Dent Mater 18:311–317
Oh K-T, Kim K-M (2005) Iron release and cytotoxicity of stainless steel wires. Eur J Orthod 27:533–540
Oh KT, Choo SU, Kim KM, Kim KN (2005) A stainless steel bracket for orthodontic application. Eur J Orthod 27:237–244
Singh DP, Sehgal V, Pradhan KL, Chandna A, Gupta R (2008) Estimation of nickel and chromium in saliva of patients with fixed orthodontic appliances. World J Orthod 9:196–202
Starkjaer L, Menne T (1990) Nickel allergy and orthodontic treatment. Eur J Orthod 12:284–289
Summer B, Fink U, Zeller R, Rueff Maier S, Roider G, Thomas P (2007) Patch test reactivity to a cobalt-chromium-molybdenum alloy and stainless steel in metal-allergic patients in correlation to the metal ion release. Contact Dermatitis 57:35–39
Uthus EO, Seaborn CD (1996) Deliberations and evaluations of approaches, endpoints and paradigms for dietary recommendations of the other trace elements. J Nutr 126:2452S–2459S
Wataha JC, Lockwood PE, Khajotia SS, Turner R (1998) Effect of pH on element release from dental casting alloys. J Prosthet Dent 80:691–698
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by Seneca Foundation of the Region of Murcia (Spain) under a grant (n° 100260).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernández-Miñano, E., Ortiz, C., Vicente, A. et al. Metallic ion content and damage to the DNA in oral mucosa cells of children with fixed orthodontic appliances. Biometals 24, 935–941 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-011-9448-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-011-9448-z