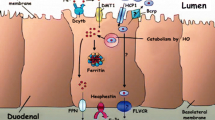
Abstract
Lactoferrin (Lf) is a mammalian exclusive protein widely distributed in milk and exocrine secretions exhibiting multifunctional properties. Many of the proven or proposed functions of Lf, apart from its iron binding activity, depend on its capacity to bind to other macromolecules. Lf can bind and sequester lipopolysaccharide (LPS), thus preventing pro-inflammatory pathway activation, sepsis and tissue damage. However, the interplay between Lf and LPS is complex, and may result in different outcomes, including both suppression of the inflammatory response and immune activation. These findings are critically relevant in the development of Lf-based therapeutic interventions in humans. Understanding the molecular basis and functional consequences of Lf-LPS interaction will provide insights for determining its role in health and disease.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcantara J, Padda JS, Schryvers AB (1992) The N-linked oligosaccharides of human lactoferrin are not required for binding to bacterial lactoferrin receptors. Can J Microbiol 38:1202–1205
Appelmelk BJ, An YQ, Geerts M, Thijs BG, de Boer HA, MacLaren DM, de Graaff J, Nuijens JH (1994) Lactoferrin is a lipid A-binding protein. Infect Immun 62:2628–2632
Artym J, Zimecki M, Kruzel ML (2004) Effects of lactoferrin on IL-6 production by peritoneal and alveolar cells in cyclophosphamide-treated mice. J Chemother 16:187–192
Ashida K, Sasaki H, Suzuki YA, Lonnerdal B (2004) Cellular internalization of lactoferrin in intestinal epithelial cells. Biometals 17:311–315
Baker EN, Baker HM (2005) Molecular structure, binding properties and dynamics of lactoferrin. Cell Mol Life Sci 62:2531–2539
Baker EN, Baker HM (2009) A structural framework for understanding the multifunctional character of lactoferrin. Biochimie 91:3–10
Baveye S, Elass E, Fernig DG, Blanquart C, Mazurier J, Legrand D (2000a) Human lactoferrin interacts with soluble CD14 and inhibits expression of endothelial adhesion molecules, E-selectin and ICAM-1, induced by the CD14-lipopolysaccharide complex. Infect Immun 68:6519–6525
Baveye S, Elass E, Mazurier J, Legrand D (2000b) Lactoferrin inhibits the binding of lipopolysaccharides to L-selectin and subsequent production of reactive oxygen species by neutrophils. FEBS Lett 469:5–8
Bellamy W, Takase M, Yamauchi K, Wakabayashi H, Kawase K, Tomita M (1992) Identification of the bactericidal domain of lactoferrin. Biochim Biophys Acta 1121:130–136
Beutler B, Rietschel ET (2003) Innate immune sensing and its roots: the story of endotoxin. Nat Rev Immunol 3:169–176
Brandenburg K, Kusumoto S, Seydel U (1997) Conformational studies of synthetic lipid A analogues and partial structures by infrared spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1329:183–201
Brandenburg K, Jurgens G, Muller M, Fukuoka S, Koch MH (2001) Biophysical characterization of lipopolysaccharide and lipid A inactivation by lactoferrin. Biol Chem 382:1215–1225
Britigan BE, Lewis TS, Waldschmidt M, McCormick ML, Krieg AM (2001) Lactoferrin binds CpG-containing oligonucleotides and inhibits their immunostimulatory effects on human B cells. J Immunol 167:2921–2928
Chapple DS, Mason DJ, Joannou CL, Odell EW, Gant V, Evans RW (1998) Structure-function relationship of antibacterial synthetic peptides homologous to a helical surface region on human lactoferrin against Escherichia coli serotype O111. Infect Immun 66:2434–2440
Chodaczek G, Zimecki M, Lukasiewicz J, Lugowski C (2006) A complex of lactoferrin with monophosphoryl lipid A is an efficient adjuvant of the humoral and cellular immune response in mice. Med Microbiol Immunol 195:207–216
Choe YH, Lee SW (1999) Effect of lactoferrin on the production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and nitric oxide. J Cell Biochem 76:30–36
Choi BK, Actor JK, Rios S, d’Anjou M, Stadheim TA, Warburton S, Giaccone E, Cukan M, Li H, Kull A, Sharkey N, Gollnick P, Kocieba M, Artym J, Zimecki M, Kruzel ML, Wildt S (2008) Recombinant human lactoferrin expressed in glycoengineered Pichia pastoris: effect of terminal N-acetylneuraminic acid on in vitro secondary humoral immune response. Glycoconj J 25:581–593
Chung MC, Wines BD, Baker H, Langley RJ, Baker EN, Fraser JD (2007) The crystal structure of staphylococcal superantigen-like protein 11 in complex with sialyl Lewis X reveals the mechanism for cell binding and immune inhibition. Mol Microbiol 66:1342–1355
Coddeville B, Strecker G, Wieruszeski JM, Vliegenthart JF, van Halbeek H, Peter-Katalinic J, Egge H, Spik G (1992) Heterogeneity of bovine lactotransferrin glycans. Characterization of alpha-D-Galp-(1–>3)-beta-D-Gal- and alpha-NeuAc-(2–>6)-beta-D-GalpNAc-(1–>4)-beta-D-GlcNAc-substituted N-linked glycans. Carbohydr Res 236:145–164
Cohen MS, Mao J, Rasmussen GT, Serody JS, Britigan BE (1992) Interaction of lactoferrin and lipopolysaccharide (LPS): effects on the antioxidant property of lactoferrin and the ability of LPS to prime human neutrophils for enhanced superoxide formation. J Infect Dis 166:1375–1378
Crouch SP, Slater KJ, Fletcher J (1992) Regulation of cytokine release from mononuclear cells by the iron-binding protein lactoferrin. Blood 80:235–240
Curran CS, Demick KP, Mansfield JM (2006) Lactoferrin activates macrophages via TLR4-dependent and -independent signaling pathways. Cell Immunol 242:23–30
Decoteau E, Yurchak AM, Partridge RE, Tomasi TB Jr (1972) Lactoferrin in synovial fluid of patients with inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 15:324–325
Derisbourg P, Wieruszeski JM, Montreuil J, Spik G (1990) Primary structure of glycans isolated from human leucocyte lactotransferrin. Absence of fucose residues questions the proposed mechanism of hyposideraemia. Biochem J 269:821–825
Dixon DR, Darveau RP (2005) Lipopolysaccharide heterogeneity: innate host responses to bacterial modification of lipid a structure. J Dent Res 84:584–595
Elass E, Masson M, Mazurier J, Legrand D (2002) Lactoferrin inhibits the lipopolysaccharide-induced expression and proteoglycan-binding ability of interleukin-8 in human endothelial cells. Infect Immun 70:1860–1866
Elass-Rochard E, Roseanu A, Legrand D, Trif M, Salmon V, Motas C, Montreuil J, Spik G (1995) Lactoferrin-lipopolysaccharide interaction: involvement of the 28–34 loop region of human lactoferrin in the high-affinity binding to Escherichia coli 055B5 lipopolysaccharide. Biochem J 312(Pt 3):839–845
Elass-Rochard E, Legrand D, Salmon V, Roseanu A, Trif M, Tobias PS, Mazurier J, Spik G (1998) Lactoferrin inhibits the endotoxin interaction with CD14 by competition with the lipopolysaccharide-binding protein. Infect Immun 66:486–491
Geijtenbeek TB, Van Vliet SJ, Koppel EA, Sanchez-Hernandez M, Vandenbroucke-Grauls CM, Appelmelk B, Van Kooyk Y (2003) Mycobacteria target DC-SIGN to suppress dendritic cell function. J Exp Med 197:7–17
Gifford JL, Hunter HN, Vogel HJ (2005) Lactoferricin: a lactoferrin-derived peptide with antimicrobial, antiviral, antitumor and immunological properties. Cell Mol Life Sci 62:2588–2598
Gringhuis SI, den Dunnen J, Litjens M, van Het Hof B, van Kooyk Y, Geijtenbeek TB (2007) C-type lectin DC-SIGN modulates Toll-like receptor signaling via Raf-1 kinase-dependent acetylation of transcription factor NF-kappaB. Immunity 26:605–616
Groot F, Geijtenbeek TB, Sanders RW, Baldwin CE, Sanchez-Hernandez M, Floris R, van Kooyk Y, de Jong EC, Berkhout B (2005) Lactoferrin prevents dendritic cell-mediated human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transmission by blocking the DC-SIGN–gp120 interaction. J Virol 79:3009–3015
Haridas M, Anderson BF, Baker EN (1995) Structure of human diferric lactoferrin refined at 2.2 A resolution. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 51:629–646
Haversen L, Ohlsson BG, Hahn-Zoric M, Hanson LA, Mattsby-Baltzer I (2002) Lactoferrin down-regulates the LPS-induced cytokine production in monocytic cells via NF-kappa B. Cell Immunol 220:83–95
Hayashida K, Kaneko T, Takeuchi T, Shimizu H, Ando K, Harada E (2004) Oral administration of lactoferrin inhibits inflammation and nociception in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis. J Vet Med Sci 66:149–154
Kawakami H, Lonnerdal B (1991) Isolation and function of a receptor for human lactoferrin in human fetal intestinal brush-border membranes. Am J Physiol 261:G841–G846
Kawamata T, Tooyama I, Yamada T, Walker DG, McGeer PL (1993) Lactotransferrin immunocytochemistry in Alzheimer and normal human brain. Am J Pathol 142:1574–1585
Kocieba M, Zimecki M, Kruzel M, Actor J (2002) The adjuvant activity of lactoferrin in the generation of DTH to ovalbumin can be inhibited by bovine serum albumin bearing alpha-D-mannopyranosyl residues. Cell Mol Biol Lett 7:1131–1136
Kruzel ML, Harari Y, Chen CY, Castro GA (2000) Lactoferrin protects gut mucosal integrity during endotoxemia induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice. Inflammation 24:33–44
Kruzel ML, Harari Y, Mailman D, Actor JK, Zimecki M (2002) Differential effects of prophylactic, concurrent and therapeutic lactoferrin treatment on LPS-induced inflammatory responses in mice. Clin Exp Immunol 130:25–31
Kruzel ML, Actor JK, Radak Z, Bacsi A, Saavedra-Molina A, Boldogh I (2009) Lactoferrin decreases LPS-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in cultured cells and in animal endotoxemia model. Innate Immun. doi:10.1177/1753425909105317
Kuwata H, Yip TT, Tomita M, Hutchens TW (1998) Direct evidence of the generation in human stomach of an antimicrobial peptide domain (lactoferricin) from ingested lactoferrin. Biochim Biophys Acta 1429:129–141
Lee WJ, Farmer JL, Hilty M, Kim YB (1998) The protective effects of lactoferrin feeding against endotoxin lethal shock in germfree piglets. Infect Immun 66:1421–1426
Legrand D, Salmon V, Coddeville B, Benaissa M, Plancke Y, Spik G (1995) Structural determination of two N-linked glycans isolated from recombinant human lactoferrin expressed in BHK cells. FEBS Lett 365:57–60
Legrand D, Elass E, Carpentier M, Mazurier J (2005) Lactoferrin: a modulator of immune and inflammatory responses. Cell Mol Life Sci 62:2549–2559
Legrand D, Pierce A, Elass E, Carpentier M, Mariller C, Mazurier J (2008) Lactoferrin structure and functions. Adv Exp Med Biol 606:163–194
Lu YC, Yeh WC, Ohashi PS (2008) LPS/TLR4 signal transduction pathway. Cytokine 42:145–151
Machnicki M, Zimecki M, Zagulski T (1993) Lactoferrin regulates the release of tumour necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 6 in vivo. Int J Exp Pathol 74:433–439
Mann DM, Romm E, Migliorini M (1994) Delineation of the glycosaminoglycan-binding site in the human inflammatory response protein lactoferrin. J Biol Chem 269:23661–23667
Mattsby-Baltzer I, Roseanu A, Motas C, Elverfors J, Engberg I, Hanson LA (1996) Lactoferrin or a fragment thereof inhibits the endotoxin-induced interleukin-6 response in human monocytic cells. Pediatr Res 40:257–262
Mitsuhashi Y, Otsuki K, Yoda A, Shimizu Y, Saito H, Yanaihara T (2000) Effect of lactoferrin on lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induced preterm delivery in mice. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 79:355–358
Miyazawa K, Mantel C, Lu L, Morrison DC, Broxmeyer HE (1991) Lactoferrin-lipopolysaccharide interactions. Effect on lactoferrin binding to monocyte/macrophage-differentiated HL-60 cells. J Immunol 146:723–729
Moore SA, Anderson BF, Groom CR, Haridas M, Baker EN (1997) Three-dimensional structure of diferric bovine lactoferrin at 2.8 A resolution. J Mol Biol 274:222–236
Munford RS (2005) Detoxifying endotoxin: time, place and person. J Endotoxin Res 11:69–84
Na YJ, Han SB, Kang JS, Yoon YD, Park SK, Kim HM, Yang KH, Joe CO (2004) Lactoferrin works as a new LPS-binding protein in inflammatory activation of macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol 4:1187–1199
Nigou J, Zelle-Rieser C, Gilleron M, Thurnher M, Puzo G (2001) Mannosylated lipoarabinomannans inhibit IL-12 production by human dendritic cells: evidence for a negative signal delivered through the mannose receptor. J Immunol 166:7477–7485
Otsuki K, Yakuwa K, Sawada M, Hasegawa A, Sasaki Y, Mitsukawa K, Chiba H, Nagatsuka M, Saito H, Okai T (2005) Recombinant human lactoferrin has preventive effects on lipopolysaccharide-induced preterm delivery and production of inflammatory cytokines in mice. J Perinat Med 33:320–323
Pathak SK, Basu S, Bhattacharyya A, Pathak S, Kundu M, Basu J (2005) Mycobacterium tuberculosis lipoarabinomannan-mediated IRAK-M induction negatively regulates Toll-like receptor-dependent interleukin-12 p40 production in macrophages. J Biol Chem 280:42794–42800
Puddu P, Carollo MG, Belardelli F, Valenti P, Gessani S (2007) Role of endogenous interferon and LPS in the immunomodulatory effects of bovine lactoferrin in murine peritoneal macrophages. J Leukoc Biol 82:347–353
Pugin J, Ulevitch RJ, Tobias PS (1993) A critical role for monocytes and CD14 in endotoxin-induced endothelial cell activation. J Exp Med 178:2193–2200
Raetz CR, Whitfield C (2002) Lipopolysaccharide endotoxins. Annu Rev Biochem 71:635–700
Samyn-Petit B, Wajda Dubos JP, Chirat F, Coddeville B, Demaizieres G, Farrer S, Slomianny MC, Theisen M, Delannoy P (2003) Comparative analysis of the site-specific N-glycosylation of human lactoferrin produced in maize and tobacco plants. Eur J Biochem 270:3235–3242
Sasaki Y, Otsuki K, Hasegawa A, Sawada M, Chiba H, Negishi M, Nagatsuka M, Okai T (2004) Preventive effect of recombinant human lactoferrin on lipopolysaccharide-induced preterm delivery in mice. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 83:1035–1038
Schromm AB, Brandenburg K, Loppnow H, Moran AP, Koch MH, Rietschel ET, Seydel U (2000) Biological activities of lipopolysaccharides are determined by the shape of their lipid A portion. Eur J Biochem 267:2008–2013
Schumann RR, Leong SR, Flaggs GW, Gray PW, Wright SD, Mathison JC, Tobias PS, Ulevitch RJ (1990) Structure and function of lipopolysaccharide binding protein. Science 249:1429–1431
Senkovich O, Cook WJ, Mirza S, Hollingshead SK, Protasevich II, Briles DE, Chattopadhyay D (2007) Structure of a complex of human lactoferrin N-lobe with pneumococcal surface protein a provides insight into microbial defense mechanism. J Mol Biol 370:701–713
Spik G, Strecker G, Fournet B, Bouquelet S, Montreuil J, Dorland L, van Halbeek H, Vliegenthart JF (1982) Primary structure of the glycans from human lactotransferrin. Eur J Biochem 121:413–419
Spik G, Coddeville B, Montreuil J (1988) Comparative study of the primary structures of sero-, lacto- and ovotransferrin glycans from different species. Biochimie 70:1459–1469
Talukder MJ, Harada E (2007) Bovine lactoferrin protects lipopolysaccharide-induced diarrhea modulating nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2 in mice. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 85:200–208
Uchida K, Matsuse R, Tomita S, Sugi K, Saitoh O, Ohshiba S (1994) Immunochemical detection of human lactoferrin in feces as a new marker for inflammatory gastrointestinal disorders and colon cancer. Clin Biochem 27:259–264
Ulvatne H, Samuelsen O, Haukland HH, Kramer M, Vorland LH (2004) Lactoferricin B inhibits bacterial macromolecular synthesis in Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 237:377–384
Valenti P, Antonini G (2005) Lactoferrin: an important host defence against microbial and viral attack. Cell Mol Life Sci 62:2576–2587
van Berkel PH, Geerts ME, van Veen HA, Kooiman PM, Pieper FR, de Boer HA, Nuijens JH (1995) Glycosylated and unglycosylated human lactoferrins both bind iron and show identical affinities towards human lysozyme and bacterial lipopolysaccharide, but differ in their susceptibilities towards tryptic proteolysis. Biochem J 312(Pt 1):107–114
van Berkel PH, van Veen HA, Geerts ME, de Boer HA, Nuijens JH (1996) Heterogeneity in utilization of N-glycosylation sites Asn624 and Asn138 in human lactoferrin: a study with glycosylation-site mutants. Biochem J 319(Pt 1):117–122
van Berkel PH, Geerts ME, van Veen HA, Mericskay M, de Boer HA, Nuijens JH (1997) N-terminal stretch Arg2, Arg3, Arg4 and Arg5 of human lactoferrin is essential for binding to heparin, bacterial lipopolysaccharide, human lysozyme and DNA. Biochem J 328(Pt 1):145–151
van de Graaf EA, Out TA, Kobesen A, Jansen HM (1991) Lactoferrin and secretory IgA in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from patients with a stable asthma. Lung 169:275–283
Vorland LH, Ulvatne H, Rekdal O, Svendsen JS (1999) Initial binding sites of antimicrobial peptides in Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Scand J Infect Dis 31:467–473
Wang D, Pabst KM, Aida Y, Pabst MJ (1995) Lipopolysaccharide-inactivating activity of neutrophils is due to lactoferrin. J Leukoc Biol 57:865–874
Ward PP, Uribe-Luna S, Conneely OM (2002) Lactoferrin and host defense. Biochem Cell Biol 80:95–102
Wei Z, Nishimura T, Yoshida S (2001) Characterization of glycans in a lactoferrin isoform, lactoferrin-a. J Dairy Sci 84:2584–2590
Weis WI, Taylor ME, Drickamer K (1998) The C-type lectin superfamily in the immune system. Immunol Rev 163:19–34
Westphal O, Luderitz O, Rietschel ET, Galanos C (1981) Bacterial lipopolysaccharide and its lipid A component: some historical and some current aspects. Biochem Soc Trans 9:191–195
Wright SD (1995) CD14 and innate recognition of bacteria. J Immunol 155:6–8
Wright SD, Ramos RA, Tobias PS, Ulevitch RJ, Mathison JC (1990) CD14, a receptor for complexes of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS binding protein. Science 249:1431–1433
Wu HF, Monroe DM, Church FC (1995) Characterization of the glycosaminoglycan-binding region of lactoferrin. Arch Biochem Biophys 317:85–92
Yajima M, Yajima T, Kuwata T (2005) Intraperitoneal injection of lactoferrin ameliorates severe albumin extravasation and neutrophilia in LPS-induced inflammation in neonatal rats. Biomed Res 26:249–255
Yamaguchi M, Matsuura M, Kobayashi K, Sasaki H, Yajima T, Kuwata T (2001) Lactoferrin protects against development of hepatitis caused by sensitization of Kupffer cells by lipopolysaccharide. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 8:1234–1239
Yamauchi K, Tomita M, Giehl TJ, Ellison RT III (1993) Antibacterial activity of lactoferrin and a pepsin-derived lactoferrin peptide fragment. Infect Immun 61:719–728
Yoshida S, Wei Z, Shinmura Y, Fukunaga N (2000) Separation of lactoferrin-a and -b from bovine colostrum. J Dairy Sci 83:2211–2215
Zagulski T, Lipinski P, Zagulska A, Broniek S, Jarzabek Z (1989) Lactoferrin can protect mice against a lethal dose of Escherichia coli in experimental infection in vivo. Br J Exp Pathol 70:697–704
Zhang GH, Mann DM, Tsai CM (1999) Neutralization of endotoxin in vitro and in vivo by a human lactoferrin-derived peptide. Infect Immun 67:1353–1358
Zimecki M, Kocieba M, Kruzel M (2002) Immunoregulatory activities of lactoferrin in the delayed type hypersensitivity in mice are mediated by a receptor with affinity to mannose. Immunobiology 205:120–131
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Puddu, P., Latorre, D., Valenti, P. et al. Immunoregulatory role of lactoferrin-lipopolysaccharide interactions. Biometals 23, 387–397 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-010-9307-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-010-9307-3