Abstract
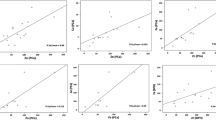
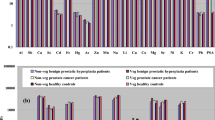
Pathophysiological changes in the prostate take the form of benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH) and prostate adenocarcinoma (PCa). In prostate, zinc is particularly important to its normal functioning, especially in terms of the consequences of hormone disturbance. The aim of this study was to assess the levels of Zn, Cu, Ca, Mg, and Se in the prostate dependent on the character of patological changes. Zinc, copper, magnesium and calcium were determined by AAS and selenium with spectrofluorometric method. Zn levels in BPH patients were over twofold higher than in controls. On the other hand, in the patients with PCa, the levels of Zn were found almost three times lower than in BPH patients and by almost 50% lower than in controls. In this study, significant changes in the levels of other essential elements were observed. The results apparently confirm the disturbed homeostasis of zinc and other essential elements in the etiology of BPH and PCa.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcaraz A, Hammerer P, Tubaro A, Schröder FH, Castro R (2009) Is there evidence of a relationship between benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer? findings of a literature review. Eur Urol 55:864–875
Anastassopoulou J, Theophanides T (2002) Magnesium-DNA interactions and the possible relation of magnesium to carcinogenesis irridation and free radicals. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 42(1):79–91
Arnold JT, Liu X, Allen JD, Le H, McFann KK, Blackman MR (2007) Androgen receptor or estrogen receptor-beta blockade alters DHEA-, DHT-, and E(2)-induced proliferation and PSA production in human prostate cancer cells. Prostate 67(11):1152–1162
Behne D, Kyriakopoulos A, Weiss-Nowak C, Kalckloesch M, Westphal C, Gessner H (1996) Newly found selenium-containing proteins in the tissues of the rat. Biol Trace Elem Res 55:99–100
Buschemeyer WCIII, Freedland SJ (2007) Obesity and prostate cancer: epidemiology and clinical implications. Eur Urol 52(2):331–343
Caffrey PB, Frenkel GD (1992) Selenite cytotoxicity in drug resistant and nonresistant human ovarian tumor cells. Cancer Res 52:4812–4816
Calle EE, Kaaks R (2004) Overweight, obesity and cancer: epidemiological evidence and proposed mechanisms. Nat Rev Cancer 4(8):579–591
Carson CIII, Rittmaster R (2003) The role of dihydrotestosterone in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology 61(4 Suppl 1):2–7
Costello LC, Franklin RB (2000) The intermediary metabolism of the prostate: a key to understanding the pathogenesis and progression of prostate malignancy. Oncology 59(4):269–282
Costello LC, Franklin RB (2006) The clinical relevance of the metabolism of prostate cancer; zinc and tumor suppression: connecting the dots. Mol Cancer 15:5–17
Costello LC, Franklin RB (2009) Prostatic fluid electrolyte composition for the screening of prostate cancer: a potential solution to a major problem. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 12(1):17–24
Costello LC, Franklin RB, Feng P (2005) Mitochondrial function, zinc, and intermediary metabolism relationships in normal prostate and prostate cancer. Mitochondrion 5(3):143–153
Daniel KG, Chen D, Orlu S, Cui QC, Miller FR, Dou QP (2005) Clioquinol and pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate complex with copper to form proteasome inhibitors and apoptosis inducers in human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res 7(6):897–908
Drake ENII, Sky-Peck HH (1989) Discriminant analysis of trace element distribution in normal and malignant human tissues. Cancer Res 49(15):4210–4215
El Bayoumy K (1994) Evaluation of chemopreventive agents against breast cancer and proposed strategies for future clinical intervention trials. Carcinogenesis 15:2395–2420
Erbersdobler A, Augustin H, Schlomm T, Henke RP (2004) Prostate cancers in the transition zone: Part 1; pathological aspects. BJU Int 94(9):1221–1225
Feng P, Li TL, Guan ZX, Franklin RB, Costello LC (2003) Effect of zinc on prostatic tumorigenicity in nude mice. Ann NY Acad Sci 1010:316–320
Franklin RB, Costello LC (2007) Zinc as an anti-tumor agent in prostate cancer and in other cancers. Arch Biochem Biophys 463(2):211–217
Friedman AE (2005) The Estradiol-Dihydrotestosterone model of prostate cancer. Theor Biol Med Model 2:10
Fuchs AG, de Lustig ES (1989) Localization of tissue copper in mouse mammary tumors. Oncology 46(3):183–187
Ghanter HE, Lawrence JR (1997) Chemical transformations of selenium in living organisms. Improved forms of selenium for cancer prevention. Tetrahedron 53:12229–12310
Gray MA, Centeno JA, Slaney DP, Ejnik JW, Todorov T, Nacey JN (2005) Environmental exposure to trace elements and prostate cancer in three New Zealand ethnic groups. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2(3–4):284–374
Griffin AC (1982) The chemo preventive role of selenium in car-cinogenesis. In: Amott MS, van Eys J, Wang YM (eds) Molecular interrelations of nutrition and cancer. Raven Press, New York, pp 401–408
Guess HA (2001) Benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer. Epidemio. Rev 23(1):152–158
Ip C, Lisk DJ (1994) Characterization of tissue profiles and anticarcinogenic responses in rats fed natural sources of selenium-rich products. Carcinogenesis 15:573–576
Jain M, Sharma K, Sharma VP (1994) Serum and tissue levels of zinc, copper, magnesium and retinol in prostatic neoplasms. Ind J Clin Biochem 9(2):106–108
Kumar V (2007) Basic pathology, 8th edn. Saunders/Elsevier, Philadelphia
Majumder S, Chatterjee S, Pal S, Biswas J, Efferth T, Choudhuri SK (2009) The role of copper in drug-resistant murine and human tumors. Biometals 22(2):377–384
Nano JL, Francois E, Rampal T (1990) In vivo and in vitro study of the role of selenium in colon carcinogenesis. In: Collery P, Poirier LA, Manfait M, Etienne JC (eds) Metal ions in biology and medicine. John Libbey Eurotext, Paris, pp 493–496
Quintero B, Planells E, del Carmen Cabeza M, Esquivias J, del Pilar Gutiérrez M, Sánchez C, Aranda P, Zarzuelo A, Llopis J (2006) Tumor-promoting activity of p-hydroxybenzenediazonium is accelerated in Mg-deficient rats. Chem Biol Interact 159(3):186–195
Ranade SS, Panday VK (1984) Transition metals in human cancer II. Sci Total Environ 40:245–257
Ronai Z, Tillotson JK, Traganos F, Darzynkiewicz Z, Conaway CC, Upadhyaya P, El-Bayoumy K (1995) Effects of organic and inorganic selenium compounds on rat mammary tumor cells. Int J Cancer 63:428–434
Salgueiro MJ, Weill R, Zubillaga M, Lysionek A, Caro R, Goldman C, Barrado D, Sarrasague MM, Ridolfi A, Boccio J (2004) Zinc deficiency and growth: current concepts in relationship to two important points: intellectual and sexual development. Biol Trace Elem Res 99(1–3):49–69
Salonen JT (1986) Selenium and human cancer. Ann Clin Res 18(1):18–21
Sarafanov AG, Todorov TI, Kajdacsy-Balla A, Gray MA, Macias V, Centeno JA (2008) Analysis of iron, zinc, selenium and cadmium in paraffin-embedded prostate tissue specimens using inductively coupled plasma mass-spectrometry. J Trace Elem Med Biol 22(4):305–314
Schatzl G, Madersbacher S, Thurridl T, Waldmüller J, Kramer G, Haitel A, Marberger M (2001) High-grade prostate cancer is associated with low serum testosterone levels. Prostate 47(1):52–58
Seltzer MH, Rosato FE, Fletcher MJ (1970) Serum and tissue calcium in human breast carcinoma. Cancer Res 30(3):615–616
Spallholz JA (1994) On the nature of selenium toxicity and carcinostatic activity. Free Rad Biol Med 17:45–64
Suzuki T, Yamanaka H, Tamura Y, Nakajima K, Kanatani K, Kimura M, Otaki N (1992) Metallothionein of prostatic tissues and fluids in rats and humans. Tohoku J Exp Med 166(2):251–257
Tapiero H, Townsend DM, Tew KD (2003) Trace elements in human physiology and pathology. Copper Biomed Pharmacother 57(9):386–398
Taylor RA, Cowin P, Couse JF, Korach KS, Risbridger GP (2006) 17beta-estradiol induces apoptosis in the developing rodent prostate independently of ERalpha or ERbeta. Endocrinology 147(1):191–200
Uauy R, Olivares M, Gonzalez M (1998) Essentiality of copper in humans. Am J Clin Nutr 67(5 Suppl):952S–959S
Voelker R (2000) Copper and cancer. JAMA 283:994
Waters DJ, Shen S, Glickman LT, Cooley DM, Bostwick DG, Qian J, Combs GF Jr, Morris JS (2005) Prostate cancer risk and DNA damage: translational significance of selenium supplementation in a canine model. Carcinogenesis 26(7):1256–1262
Wei H, Desouki MM, Lin S, Xiao D, Franklin RB, Feng P (2008) Differential expression of metallothioneins (MTs) 1, 2, and 3 in response to zinc treatment in human prostate normal and malignant cells and tissues. Mol Cancer 21:7
Willis MS, Wians FH (2003) The role of nutrition in preventing prostate cancer: a review of the proposed mechanism of action of various dietary substances. Clin Chim Acta 330(1–2):57–83
Wolf FI, Maier JA, Nasulewicz A, Feillet-Coudray C, Simonacci M, Mazur A, Cittadini A (2007) Magnesium and neoplasia: from carcinogenesis to tumor growth and progression or treatment. Arch Biochem Biophys 458(1):24–32
Yaman M, Atici D, Bakirdere S, Akdeniz I (2005) Comparison of trace metal concentrations in malign and benign human prostate. J Med Chem 48(2):630–634
Yan M, Song Y, Wong CP, Hardin K, Ho E (2008) Zinc deficiency alters DNA damage response genes in normal human prostate epithelial cells. J Nutr 138(4):667–673
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sapota, A., Daragó, A., Taczalski, J. et al. Disturbed homeostasis of zinc and other essential elements in the prostate gland dependent on the character of pathological lesions. Biometals 22, 1041–1049 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-009-9255-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-009-9255-y