Abstract
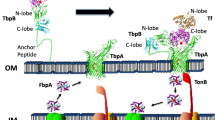
The transferrin iron acquisition system of Neisseria gonorrhoeae consists of two dissimilar transferrin binding proteins (Tbp) A and B. TbpA is a TonB dependent transporter while TbpB is a lipoprotein that makes iron acquisition from transferrin (Tf) more efficient. In an attempt to further define the individual roles of these receptors in the process of Tf-iron acquisition, the kinetics of the receptor proteins in regards to ligand association and dissociation were evaluated. Tf association with TbpB was rapid as compared to TbpA. Tf dissociation from the wild-type receptor occurred in a biphasic manner; an initial rapid release was followed by a slower dissociation over time. Both TbpA and TbpB demonstrated a two-phase release pattern; however, TbpA required both TonB and TbpB for efficient Tf dissociation from the cell surface. The roles of TbpA and TbpB in Tf dissociation were further examined, utilizing previously created HA fusion proteins. Using a Tf-utilization deficient TbpA-HA mutant, we concluded that the slower rate of ligand dissociation demonstrated by the wild-type transporter was a function of successful iron internalization. Insertion into the C-terminus of TbpB decreased the rate of Tf dissociation, while insertion into the N-terminus had no effect on this process. From these studies, we propose that TbpA and TbpB function synergistically during the process of Tf iron acquisition and that TbpB makes the process of Tf-iron acquisition more efficient at least in part by affecting association and dissociation of Tf from the cell surface.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcantara J, Schryvers AB (1996) Transferrin binding protein two interacts with both the N-lobe and C-lobe of ovotransferrin. Microb Pathog 20(2):73–85. doi:10.1006/mpat.1996.0007
Anderson JE, Sparling PF et al (1994) Gonococcal transferrin-binding protein 2 facilitates but is not essential for transferrin utilization. J Bacteriol 176(11):3162–3170
Bertani G (1951) Studies on lysogenesis I.: The mode of phage liberation by lysogenic Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 62(3):293–300
Bertani G (2004) Lysogeny at mid-twentieth century: P1, P2, and other experimental systems. J Bacteriol 186(3):595–600. doi:10.1128/JB.186.3.595-600.2004
Buchanan SK, Smith BS et al (1999) Crystal structure of the outer membrane active transporter FepA from Escherichia coli. Nat Struct Biol 6(1):56–63. doi:10.1038/4931
Bylund DB, Yamamura HI (1990) Methods for receptor binding. In: Yamamura HI (ed) Methods in neurotransmitter receptor analysis. Raven Press Ltd., New York
Cadieux N, Kadner RJ (1999) Site-directed disulfide bonding reveals an interaction site between energy-coupling protein TonB and BtuB, the outer membrane cobalamin transporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:10673–10678. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.19.10673
Cornelissen CN, Sparling PF (1996) Binding and surface exposure characteristics of the gonococcal transferrin receptor are dependent on both transferrin-binding proteins. J Bacteriol 178(5):1437–1444
Cornelissen CN, Biswas GD et al (1992) Gonococcal transferrin-binding protein 1 is required for transferrin utilization and is homologous to TonB-dependent outer membrane receptors. J Bacteriol 174(18):5788–5797
Cornelissen CN, Anderson JE et al (1997a) Characterization of the diversity and the transferrin-binding domain of gonococcal transferrin-binding protein 2. Infect Immun 65(2):822–828
Cornelissen CN, Anderson JE et al (1997b) Energy-dependent changes in the gonococcal transferrin receptor. Mol Microbiol 26(1):25–35. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.1997.5381914.x
DeRocco AJ, Cornelissen CN (2007) Identification of transferrin-binding domains in TbpB expressed by Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun 75(7):3220–3232. doi:10.1128/IAI.00072-07
Gudmundsdottir A, Bell PE et al (1989) Point mutations in a conserved region (TonB box) of Escherichia coli outer membrane protein BtuB affect vitamin B12 transport. J Bacteriol 171(12):6526–6533
Irwin SW, Averil N et al (1993) Preparation and analysis of isogenic mutants in the transferrin receptor protein genes, tbpA and tbpB, from Neisseria meningitidis. Mol Microbiol 8(6):1125–1133. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01657.x
Jian-Xin Wang HIY, Wang W (1992) The Use of the filtration technique in in vitro radioligand binding assays for membrane-bound and solubilized receptors. In: Hulme EC et al (eds) Receptor-ligand interactions a practical approach. Oxford University Press, New York
Jones SW (1982) Identification of receptors in vitro. In: Eckelman WC (ed) Receptor-binding radiotracers, vol 1. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 15–36
Kellogg DS Jr, Peacock WL Jr et al (1963) Neisseria gonorrhoeae. I. Virulence genetically linked to clonal variation. J Bacteriol 85:1274–1279
Kenney CD, Cornelissen CN (2002) Demonstration and characterization of a specific interaction between gonococcal transferrin binding protein A and TonB. J Bacteriol 184(22):6138–6145. doi:10.1128/JB.184.22.6138-6145.2002
Klug CS, Eaton SS et al (1998) Ligand-induced conformational change in the ferric enterobactin receptor FepA as studied by site-directed spin labeling and time-domain ESR. Biochemistry 37:9016–9023. doi:10.1021/bi980144e
Krell T, Renauld-Mongenie G et al (2003) Insight into the structure and function of the transferrin receptor from Neisseria meningitidis using microcalorimetric techniques. J Biol Chem 278(17):14712–14722. doi:10.1074/jbc.M204461200
Larsen RA, Foster-Hartnett D et al (1997) Regions of Escherichia coli TonB and FepA proteins essential for in vivo physical interactions. J Bacteriol 179(10):3213–3221
Lewis LA, Dyer DW (1995) Identification of an iron-regulated outer membrane protein of Neisseria meningitidis involved in the utilization of hemoglobin complexed to haptoglobin. J Bacteriol 177(5):1299–1306
Lissolo L, Maitre-Wilmotte G et al (1995) Evaluation of transferrin-binding protein 2 within the transferrin-binding complex as a potential antigen for future meningococcal vaccines. Infect Immun 63(3):884–890
Mazarin V, Rokbi B et al (1995) Diversity of the transferrin-binding protein Tbp2 of Neisseria meningitidis. Gene 158:145–146. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(95)00151-U
Mickelsen PA, Sparling PF (1981) Ability of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, and commensal Neisseria species to obtain iron from transferrin and iron compounds. Infect Immun 33(2):555–564
Mickelsen PA, Blackman E et al (1982) Ability of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, and commensal Neisseria species to obtain iron from lactoferrin. Infect Immun 35(3):915–920
Noto JM, Cornelissen CN (2008) Identification of TbpA residues required for transferrin-iron utilization by Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun 76(5):1960–1969. doi:10.1128/IAI.00020-08
Renauld-Mongenie G, Poncet D et al (1997) Identification of human transferrin-binding sites within meningococcal transferrin-binding protein B. J Bacteriol 179(20):6400–6407
Retzer MD, Yu RH et al (1998) Discrimination between apo and iron-loaded forms of transferrin by transferrin binding protein B and its N-terminal subfragment. Microb Pathog 25:175–180. doi:10.1006/mpat.1998.0226
Retzer MD, Yu RH et al (1999) Identification of sequences in human transferrin that bind to the bacterial receptor protein, transferrin-binding protein B. Mol Microbiol 32(1):111–121. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01331.x
Rohde KH, Dyer DW (2004) Analysis of haptoglobin and hemoglobin-haptoglobin interactions with the Neisseria meningitidis TonB-dependent receptor HpuAB by flow cytometry. Infect Immun 72(5):2494–2506. doi:10.1128/IAI.72.5.2494-2506.2004
Schryvers AB, Morris LJ (1988) Identification and characterization of the human lactoferrin-binding protein from Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun 56(5):1144–1149
Scott DC, Newton SMC et al (2002) Surface loop motion in FepA. J Bacteriol 184(17):4906–4911. doi:10.1128/JB.184.17.4906-4911.2002
Sims KL, Schryvers AB (2003) Peptide-peptide interactions between human transferrin and transferrin-binding protein B from Moraxella catarrhalis. J Bacteriol 185(8):2603–2610. doi:10.1128/JB.185.8.2603-2610.2003
Vonder Haar RA, Legrain M et al (1994) Characterization of a highly structured domain in Tbp2 from Neisseria meningitidis involved in binding to human transferrin. J Bacteriol 176(20):6207–6213
West SE, Sparling PF (1987) Aerobactin utilization by Neisseria gonorrhoeae and cloning of a genomic DNA fragment that complements Escherichia coli fhuB mutations. J Bacteriol 169(8):3414–3421
Yost-Daljev MK, Cornelissen CN (2004) Determination of surface-exposed, functional domains of gonococcal transferrin-binding protein A. Infect Immun 72(3):1775–1785. doi:10.1128/IAI.72.3.1775-1785.2004
Acknowledgments
Funding for this work was provided by Public Health Service grant R01 AI47141 from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health. We gratefully acknowledge Dr. Darrell Peterson, VCU Department of Biochemistry, for useful discussions regarding analysis of ligand dissociation data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DeRocco, A.J., Yost-Daljev, M.K., Kenney, C.D. et al. Kinetic analysis of ligand interaction with the gonococcal transferrin-iron acquisition system. Biometals 22, 439–451 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-008-9179-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-008-9179-y