Abstract
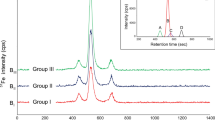
Subcellular distribution of metal-containing proteins of Fe, Cu, Zn and Cd were determined in the liver samples of iron overload mice by size exclusion high performance liquid chromatography with on-line coupling to UV and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Collision cell techniques was used to remove polyatomic interferences for some elements, such as Fe. Comparative molecular weight (MW) information of the elemental fraction was obtained within a retention time of 40 min. Fe was present only in high-MW (HMW) protein; Cu, Zn and Cd were found in different MW proteins. It was also observed that these four elements studied showed predominant association with HMW fractions. Moreover, compared with the normal group, we found that the contents of these elements except Cu significantly increased and the distribution of some elements like Cd changed in iron overload mouse liver. It means that excessive iron accumulation in vivo may affect the metabolism of other element such as Zn and Cd.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chery CC, Günther D, Cornelis R, Vanhaecke F, Moens L (2003) Detection of metals in proteins by means of polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry: application to selenium. Electrophoresis 24:3305–3313
De Smet H, De Wachter B, Lobinski R, Blust R (2001) Dynamics of (Cd, Zn)-metallothioneins in gills, liver and kidney of common carp Cyprinus carpio during cadmium exposure. Aquat Toxicol 52:269–281
Faa G, Terlizzo M, Gerosa C, Conqiu T, Anqelucci E (2002) Patterns of iron distribution in liver cells in β-thalassemia studied by X-ray microanalysis. Haematologica 87:479–484
Ferrarello CN, Fernandez de la Campa MR, Sanz-Medel A (2002) Multielement trace-element speciation in metal-biomolecules by chromatography coupled with ICP-MS. Anal Bioanal Chem 373:412–421
Fleet JC, Andrews GK, McCormick CC (1990) Iron-induced metallothionein in chick liver: a rapid, route-dependent effect independent of zinc status. J Nutr 120:1214–1222
Jurczuk M, Brzoska MM, Galazyn-Sidorczuk M (1997) Distribution of the 59Fe radioisotope in the organism of a rat after a subacute exposure to cadmium. Pol J Environ Stud 6:74–76
Kannamkumarath SS, Wrobel K, B’Hymer C, Caruso JA (2002) Capillary electrophoresis-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: an attractive complementary technique for elemental speciation analysis. J Chromatogr A 975:245–266
Leber A, Hemmens B, Klosch B, GoesslerW Raber G, Mayer B, Schmidt K (1999) Characterization of recombinant human endothelial nitric-oxide synthase purified from the yeast Pichia pastoris. J Biol Chem 274:37658–37664
Liuzzi JP, Avdemir F, Nam H, Knutson MD, Cousins RJ (2006) Zip14 (Slc39a14) mediates non-transferrin-bound iron uptake into cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:13612–13617
Lobiński R, Schaumlöffel D, Szpunar J (2006) Mass spectrometry in bioinorganic analytical chemistry. Mass Spectrom Rev 25:255–289
Nordberg M (1998) Metallothioneins: historical review and state of knowledge. Talanta 46:243–254
Martino FAR, Sánchez MLF, Medel AS (2002) Multi-elemental fractionation in milk whey by size exclusion chromatography coupled on line to ICP-MS. J Anal At Spectrom 17:1271
McCormick CC (1984) The tissue-specific accumulation of hepatic zinc metallothionein following parenteral iron loading. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 176:393–402
Miyazaki I, Asanuma M, Higashi Y, Sogawa CA, Tanaka K, Ogawa N (2002) Age-related changes in expression of metallothionein-III in rat brain. Neurosci Res 43:323–333
Papanastasiou DA, Vayenas DV, Vassilopoulos A, Repanti M (2000) Concentration of iron and distribution of iron and transferrin after experimental iron overload in rat tissues in vivo: study of the liver, the spleen, the central nervous system and other organs. Pathol Res Pract 196:47–54
Parkes JG, Templeton DM (1994) Iron transport and subcellular distribution in Hep G2 hepatocarcinoma cells. Ann Clin Lab Sci 24:509–520
Peterson GL (1977) A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem 83:346–350
Raja KB, Jafri SE, Peters TJ, Simpson RJ (2006) Iron and cadmium uptake by duodenum of hypotransferrinaemic mice. Biometals 19:547–553
Richarz AN, Bratter P (2002) Speciation analysis of trace elements in the brains of individuals with Alzheimer’s disease with special emphasis on metallothioneins. Anal Bioanal Chem 372:412–417
Roberts HR (1981) Food safety. Wiley, New York
Sadi BB, Wrobel K, Wrobel K, Kannamkumarath SS, Castillo JR, Caruso JA (2002) SEC-ICP-MS studies for elements binding to different molecular weight fractions of humic substances in compost extract obtained from urban solid waste. J Environ Monit 4:1010–1016
Stuhne-Sekalec L, Xu SX, Parkes JG, Olivieri NF, Templeton DM (1992) Speciation of tissue and cellular iron with on-line detection by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Anal Biochem 205:278–284
Szpunar J (2000) Bio-inorganic speciation analysis by hyphenated techniques. Analyst 125:963–988
Szpunar J (2005) Advances in analytical methodology for bioinorganic speciation analysis: metallomics, metalloproteomics and heteroatom-tagged proteomics and metabolomics. Analyst 130:442–465
Szpunar J, Lobiński R (2002) Multidimensional approaches in biochemical speciation analysis. Anal Bioanal Chem 373:404–411
Tanaka M, Yanagi M, Shirota K, Une Y, Nomure Y, Masaoka Y, Akahori F (1995) Effect of cadmium in the zinc deficient rat. Vet Hum Toxicol 37:203–208
Wang J, Dreessen D, Wiederin DR, Houk RS (2001) Measurement of trace elements in proteins extracted from liver by size exclusion chromatography-ICP-MS with a magnetic sector mass spectrometer. Anal Biochem 288:89–96
Wind M, Lehmann WD (2004) Element and molecular mass spectrometry—an emerging analytical dream team in the life sciences. J Anal At Spectrom 19:20–25
Yeh CF, Jiang SJ (2002) Determination of monophosphate nucleotides by capillary electrophoresis ICP-MS. Analyst 127:1324–1327
Zaidi JH, Arif M, Fatima I, Qureshi IH (2002) Radiochemical neutron activation analysis for trace elements of basic ingredients of pan. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 253:459–464
Zhang Y, Li HL, Zhao YL, Gao ZH (2006) Dietary supplementation of baicalin and quercetin attenuates iron overload induced mouse liver injury. Eur J Pharmacol 535:263–269
Zhao YL, Li HL, Gao ZH, Xu HB (2005) Effects of dietary baicalin supplementation on iron overload induced mouse liver oxidative injury. Eur J Pharmacol 509:195–200
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 30670481, 10490180), Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. KJCX3.SYW.N3), the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (No. 2005ABB008), the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (No. NCET-05-0649), E-Institutes of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (No. E-04010), and the Joint Laboratory of Nuclear Analytical Techniques of Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. K-114).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Li, B., Chen, C. et al. Hepatic distribution of iron, copper, zinc and cadmium-containing proteins in normal and iron overload mice. Biometals 22, 251–259 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-008-9161-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-008-9161-8