Abstract
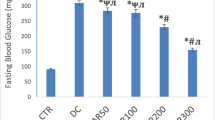
Iron, the prosthetic group of haemoglobin, was found to lower serum glucose levels of diabetic rats. Its regulative mechanism and effects on enzymatic activities of glucose metabolism are still unknown. In this study, the correlation between iron supply and enzymatic activities of glucose metabolism and respiratory chain were evaluated in liver and kidney tissues of alloxan induced-diabetic rats. After FeSO4 and metformin administration, serum samples were collected for serum glucose and fructosamine level measurements. Kidney and liver tissues were excised at the end of the study for assaying enzymatic activities of isocitrate dehydrogenase, succinate dehydrogenase, malate dehydrogenase, NADH-dehydrogenase and cytochrome-c-oxidase. Results showed significantly decreased serum glucose and fructosamine levels in treatment groups and enhanced enzymatic activities of several proteins as compared with the diabetic control group. Therefore, these data suggested that FeSO4 administration could increase the supply of oxygen, enhance enzymatic activities of glucose metabolism and the respiratory chain, accelerate glucose metabolism and consequently decrease serum glucose levels.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson RA (1997) Nutritional factors influencing the glucose/insulin system: chromium. J Am Coll Nutr 16:404–410
Bailey CJ, Turner RC (1996) Metformin. N Engl J Med 334(9):574–579. doi:10.1056/NEJM199602293340906
Becker DJ, Reul B, Ozcelikay AT et al (1996) Oral selenate improves glucose homeostasis and partly reverses abnormal expression of liver glycolytic and gluconeogenic enzymes in diabetic rats. Diabetologia 39(1):3–11. doi:10.1007/BF00400407
Brown IR, McBain AM, Chalmers J et al (1999) Sex difference in the relationship of calcium and magnesium excretion to glycaemic control in type-1 diabetes mellitus. Clin Chim Acta 283(1–2):119–128. doi:10.1016/S0009-8981(99)00040-6
Christiansen MP, Linfoot PA, Neese RA et al (1997) Metformin effects upon post absorptive intra hepatic carbohydrate fluxes. Diabetes 46(Suppl1):244A. doi:10.2337/diabetes.46.2.244
Christophe EM, Christel M, Ivo H et al (2000) Soluble transferrin receptor level: a new marker of iron deficiency anemia, a common manifestation of gastric autoimmunity in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 23(9):1384–1388. doi:10.2337/diacare.23.9.1384
Cui M, Sun JM, Sun HW (2007) Analysis of iron, zinc, magnesium in whole serum of the II diabetes mellitus. J Hebei University (Natural Sci. Ed.) 27(2):179–183
Cunningham JJ, Fu A, Mearkle PL, Brown RG (1994) Hyperzincurea in individuals with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: concurrent zinc status and the effect of high dose zinc supplementation. Metabolism 43(12):1558–1562. doi:10.1016/0026-0495(94)90016-7
Cusi K, DeFronzo RA (1998) Metformin: a review of its metabolic effects. Diabetes Res 6(1):98–131
Cusi K, Consoli A, DeFronzo RA (1996) Metabolic effect of metformin on glucose and lactate metebolism in non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81(11):4059–4067. doi:10.1210/jc.81.11.4059
Duncan DB (1957) Multiple range tests for correlated and heteroscedastic means. Biometrics 13:164–176. doi:10.2307/2527799
Facchini FS, Saylor KL (2003) A low-iron-available, polyphenol-enriched, carbohydrate-restricted diet to slow progression of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 52(5):1204–1209. doi:10.2337/diabetes.52.5.1204
Gurson CT, Saner G (1971) Effect of chromium on glucose utilization in marasmic protein-calorie malnutrition. Am J Clin Nutr 24(11):1313–1319
Howard RL, Buddington B, Alfrey AC (1991) Urinary albumin, transferrin and iron excretion in diabetic patients. Kidney Int 40(5):923–926. doi:10.1038/ki.1991.295
Jansson LT, Perkkio MV, Willis WT et al (1985) Red cell superoxide dismutase is increased in iron deficiency anemia. Acta Haematol 74(4):218–221
Jatoba CA, de Rezende AA, de Paiva Rodrigues SJ et al (2008) Liver iron overload induced by tamoxifen in diabetic and non-diabetic female Wistar rats. Biometals 21(2):171–178
Jiang R, Manson JE, Meigs JB et al (2004) Body iron stores in relation to risk of type 2 diabetes in apparently healthy women. J Am Med Assoc 291(6):711–717. doi:10.1001/jama.291.6.711
Johnson D, Lordy H (1967) Isolation of liver and kidney mitochondria. Methods Enzymol 10(1):94–96
Kimura K (1996) Role of essential trace elements in the disturbance of carbohydrate metabolism. Nippon Rinsho 54(1):79–84
King J (1965) The hydrolases—acid and alkaline phosphatase. In: Van D (ed) Practical clinical enzymology. Nortstand Company Limited, London, pp 191–208
Knutson MD, Walter PB, Ames BN et al (2000) Both iron deficiency and daily iron supplements increase lipid peroxidation in rats. J Nutr 130(5):621–628
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193(1):265–275
Malhotra A, Sanghi V (1997) Regulation of contractile proteins in diabetes. Cardiovasc Res 34(1):34–40. doi:10.1016/S0008-6363(97)00059-X
Masini A, Salvioli G, Cremonesi P et al (1994) Dietary iron deficiency in the rat. I. Abnormalities in energy metabolism of the hepatic tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta 1188(1–2):46–52. doi:10.1016/0005-2728(94)90020-5
Matthaei S, Hamann A, Klein HH et al (1991) Association of Metformin’s effect to increase insulin-stimulated glucose transport with potentiation of insulin-induced translocation of glucose transporters from intracellular pool to plasma membrane in rat adipocytes. Diabetes 40(7):850–857. doi:10.2337/diabetes.40.7.850
Mertz M (1969) Chromium occurrence and function in biological systems. Physiol Rev 49(2):163–169
Mertz W, Toepfer EW, Roginski EE (1974) Present knowledge of the role of chromium. Fed Proc 33(11):2275–2280
Minakami S, Ringer RL, Singer TJP (1962) Studies on respiratory chainlinked dihydrodiphosphopyridine nucleotide dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem 237(2):569–576
Nankivell BJ, Tay YC, Boadle RA et al (1994) Lysosomal iron accumulation in diabetic nephropathy. Ren Fail 16(3):367–381. doi:10.3109/08860229409044877
Nomura Y, Okamoto S, Sakamoto M et al (2005) Effect of cobalt on the liver glycogen content in the streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Mol Cell Biochem 277(1–2):127–130. doi:10.1007/s11010-005-5777-y
Peter AM (2000) Bioenergentics and the metabolism of carbohydrates and lipids. In: Robert KM, Daryl KG, Victor WR (eds) Harper’s biochemistry, 25th s. Science publishing company, Beijing, China, pp 182–208
Pierce G, Dhalla N (1985) Heart mitochondrial function in chronic experimental diabetes in rats. Can J Cardiol 1(1):48–54
Qian P, Guo J, Liu C et al (2003) Effect of iron on peroxidation and non-enzymatic glycation in diabetic rats. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu 32(5):446–448
Scott DA, Fischer AM (1938) The insulin and zinc content of normal and diabetic pancreas. J Clin Invest 17(6):725–728. doi:10.1172/JCI101000
Stanley W, Lopaschuk G, McCormack J (1997) Regulation of energy substrate metabolism in the diabetic heart. Cardiovasc Res 34(1):25–33. doi:10.1016/S0008-6363(97)00047-3
Stumvoll M, Nurjhan N, Periello G et al (1995) Metabolic effects of metformin in non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 333(9):550–554. doi:10.1056/NEJM199508313330903
Underwood EJ, Mertz W (1986) Trace elements in human and animal nutrition, vol 1. Academic Press, New York, p 255
Wharton C, Tzagoloff A (1967) Cytochrome oxidase from beef heart mitochondria. Methods Enzymol 10(2):245–250
Xu YJ, Wu XQ, Liu W et al (2002) A convenient assay of glycoserum by nitroblue tetrazolium with iodoacetamide. Clin Chim Acta 325(1–2):127–131. doi:10.1016/S0009-8981(02)00277-2
Zhou XJ, Laszik Z, Wang XQ et al (2000) Association of renal injury with increased oxygen free radical activity and altered nitric oxide metabolism in chronic experimental hemosiderosis. Lab Invest 80(12):1905–1914. doi:10.1038/labinvest.3780200
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by by a grant from National Science Fund for Creative Research Groups (Grant No.40721002), a grant from Research Foundation for Advanced Talents of Jiangsu University (1821360005) and Anhui biotechnological technology company.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Lian, B. & Cui, F. Effect of FeSO4 treatment on glucose metabolism in diabetic rats. Biometals 21, 685–691 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-008-9153-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-008-9153-8