Abstract
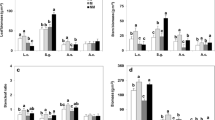
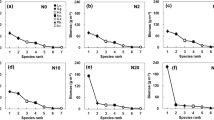
Litter chemical traits are one of the dominant controls on litter decomposition. Increasing atmospheric nitrogen (N) deposition is expected to alter litter chemical traits at the community level in both direct (altering intraspecific chemistry) and indirect ways (changing species abundance and composition). Compared to intraspecific changes, the role of changes in species composition in driving the responses of litter chemical traits to N enrichment has been seldom quantitatively addressed. We quantified the relative contribution of intraspecific changes versus changes in community composition on litter traits and how this would be influenced by the magnitude of N deposition by taking advantage of a long-term field N addition experiment in a semi-arid grassland with a wide range of N addition rates. Nitrogen deposition altered plant species abundance by facilitating the dominance of one species with a nutrient acquisitive strategy, producing higher quality litter and being more responsive to N addition at the intraspecific level. Overall, changes in species composition, intraspecific changes and their interaction all led to higher litter quality (higher N and lower lignin, cellulose and hemicellulose concentrations) under N deposition treatments. The relative contribution of species composition on the responses of litter chemical traits to N deposition also increased with N addition rate, ranging from 5 to 40% for litter N, and from 2 to ~ 30% for the three structural carbon components. Our results demonstrate the positive impacts of increasing N deposition on litter quality through changing intraspecific C and N chemistry and species turnover, which has potential consequences for litter decomposition and nutrient cycling in ecosystems. Further, we highlight the important contribution of shifts in species abundance to the plant-mediated biogeochemical responses to N deposition.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aerts R, de Caluwe H, Beltman B (2003) Plant community mediated vs. nutritional controls on litter decomposition rates in grasslands. Ecology 84(12):3198–3208
Albert CH, Grassein F, Schurr FM, Vieilledent G, Violle C (2011) When and how should intraspecific variability be considered in trait-based plant ecology? Perspect Plant Ecol 13(3):217–225
Bai Y, Wu J, Clark CM, Naeem S, Pan Q, Huang J, L Zhang, Han X (2010) Tradeoffs and thresholds in the effects of nitrogen addition on biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: evidence from inner Mongolia Grasslands. Glob Chang Biol 16(2):358–372
Bardgett RD (2017) Plant trait-based approaches for interrogating belowground function. Biol Environ 117B(1):1–13
Berg B (2014) Decomposition patterns for foliar litter—a theory for influencing factors. Soil Biol Biochem 78:222–232
Berg B, Matzner E (1997) Effect of N deposition on decomposition of plant litter and soil organic matter in forest systems. Environ Rev 5(1):1–25
Berg B, Davey MP, De Marco A, Emmett B, Faituri M, Hobbie SE, Johansson MB, Liu C, McClaugherty C, Norell L, Rutigliano FA, Vesterdal L, De Santo AV (2010) Factors influencing limit values for pine needle litter decomposition: a synthesis for boreal and temperate pine forest systems. Biogeochemistry 100(1–3):57–73
Bobbink R (1991) Effects of nutrient enrichment in Dutch Chalk grassland. J Appl Ecol 28(1):28–41
Booker FL, Anttonen S, Heagle AS (1996) Catechin proanthocyanidin and lignin contents of loblolly pine (Pinus taeda) needles after chronic exposure to ozone. New Phytol 132(3):483–492
Chapin FS III (1980) The mineral nutrition of wild plants. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 11:233–260
Chen SP, Bai YF, Zhang HX, Han XG (2005) Comparing physiological responses of two dominant grass species to nitrogen addition in Xilin River Basin of China. Environ Exp Bot 53(1):65–75
Clark CM, Tilman D (2008) Loss of plant species after chronic low-level nitrogen deposition to prairie grasslands. Nature 451:712–715
Conant RT, Ryan MG, Ågren GI, Birge HE, Davidson EA, Eliasson PE, Evans SE, Frey SD, Giardina CP, Hopkins FM, Hyvönen R, Kirschbaum MUF, Lavallee JM, Leifeld J, Parton WJ, Megan Steinweg J, Wallenstein MD, Martin Wetterstedt JA, Bradford MA (2011) Temperature and soil organic matter decomposition rates—synthesis of current knowledge and a way forward. Glob Chang Biol 17(11):3392–3404
Cornelissen JH, Van Bodegom PM, Aerts R, Callaghan TV, Van Logtestijn RS, Alatalo J, Chapin FS, Gerdol R, Gudmundsson J, Gwynn-Jones D, Hartley AE, Hik DS, Hofgaard A, Jónsdóttir IS, Karlsson S, Klein JA, Laundre J, Magnusson B, Michelsen A, Molau U, Onipchenko VG, Quested HM, Sandvik SM, Schmidt IK, Shaver GR, Solheim B, Soudzilovskaia NA, Stenström A, Tolvanen A, Totland Ø, Wada N, Welker JM, Zhao X, Team MOM (2007) Global negative vegetation feedback to climate warming responses of leaf litter decomposition rates in cold biomes. Ecol Lett 10(7):619–627
Cornwell WK, Cornelissen JH, Amatangelo K, Dorrepaal E, Eviner VT, Godoy O, Hobbie SE, Hoorens B, Kurokawa H, Pérez-Harguindeguy N, Quested HM, Santiago LS, Wardle DA, Wright IJ, Aerts R, Allison SD, Van Bodegom P, Brovkin V, Chatain A, Callaghan TV, Díaz S, Garnier E, Gurvich DE, Kazakou E, Klein JA, Read J, Reich PB, Soudzilovskaia NA, Victoria Vaieretti M, Westoby M (2008) Plant species traits are the predominant control on litter decomposition rates within biomes worldwide. Ecol Lett 11(10):1065–1071
Cotrufo MF, Inescon P (1996) Elevated CO2 reduces field decomposition rates of Betula pendula Roth leaf litter. Oecologia 106(4):525–530
De Long JR, Sundqvist MK, Gundale MJ, Giesler R, Wardle DA (2016) Effects of elevation and nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization on plant defence compounds in subarctic tundra heath vegetation. Funct Ecol 30(2):314–325
Dentener F, Drevet J, Lamarque JF, Bey I, Eickhout B, Fiore AM, Hauglustaine D, Horowitz LW, Krol M, Kulshrestha UC, Lawrence M, Galy-Lacaux C, Rast S, Shindell D, Stevenson D, Van Noije T, Atherton C, Bell N, Bergman D, Butler T, Cofala J, Collins B, Doherty R, Ellingsen K, Galloway J, Gauss M, Montanaro V, Müller JF, Pitari G, Rodriguez J, Sanderson M, Solmon F, Strahan S, Schultz M, Sudo K, Szopa S, Wild O (2006) Nitrogen and sulfur deposition on regional and global scales: a multimodel evaluation. Global Biogeochem Cycle 20(4):3
Duprè C, Stevens CJ, Ranke T, Bleeker A, Peppler-Lisbach C, Gowing DJG, Dise NB, Dorland E, Bobbink R, Diekmann M (2010) Changes in species richness and composition in European acidic grasslands over the past 70 years: the contribution of cumulative atmospheric nitrogen deposition. Glob Chang Biol 16(1):344–357
Fanin N, Hättenschwiler S, Barantal S, Schimann H, Fromin N (2011) Does variability in litter quality determine soil microbial respiration in an Amazonian rainforest? Soil Biol Biochem 43(5):1014–1022
Fioretto A, Di Nardo C, Papa S, Fuggi A (2005) Lignin and cellulose degradation and nitrogen dynamics during decomposition of three leaf litter species in a Mediterranean ecosystem. Soil Biol Biochem 37(6):1083–1091
Freschet GT, Aerts R, Cornelissen JHC (2012) Multiple mechanisms for trait effects on litter decomposition: moving beyond home-field advantage with a new hypothesis. J Ecol 100(3):619–630
Garnier E, Cortez J, Billès G, Navas M, Roumet C, Debussche M, Laurent G, Blanchard A, Aubry D, Bellmann A, Neill C, Toussaint J-P (2004) Plant functional markers capture ecosystem properties during secondary succession. Ecology 85(9):2630–2637
Grime JP (1998) Benefits of plant diversity to ecosystems: immediate filter and founder effects. J Ecol 86(6):902–910
Hättenschwiler S, Jørgensen HB (2010) Carbon quality rather than stoichiometry controls litter decomposition in a tropical rain forest. J Ecol 98(4):754–763
Hättenschwiler S, Vitousek PM (2000) The role of polyphenols in terrestrial ecosystem nutrient cycling. Trends Ecol Evol 15(6):238–243
Hector A, Beale AJ, Minns A, Otway SJ, Lawton JH (2000) Consequences of the reduction of plant diversity for litter decomposition: effects through litter quality and microenvironment. Oikos 90(2):357–371
Henry HA, Cleland EE, Field CB, Vitousek PM (2005) Interactive effects of elevated CO2, N deposition and climate change on plant litter quality in a California annual grassland. Oecologia 142(3):465–473
Hobbie SE (2000) Interactions between litter lignin and soil nitrogen availability during leaf litter decomposition in a Hawaiian montane forest. Ecosystems 3(5):484–494
Hobbie SE (2015) Plant species effects on nutrient cycling: revisiting litter feedbacks. Trends Ecol Evol 30(6):357–363
Jia Y, Yu G, He N, Zhan X, Fang H, Sheng W, Zuo Y, Zhang D, Wang Q (2014) Spatial and decadal variations in inorganic nitrogen wet deposition in China induced by human activity. Sci Rep 4:3763
Jones CG, Hartley SE (1999) A protein competition model of phenolic allocation. Oikos 86(1):27–44
Kichenin E, Wardle DA, Peltzer DA, Morse CW, Freschet GT, Kitajima K (2013) Contrasting effects of plant inter- and intraspecific variation on community-level trait measures along an environmental gradient. Funct Ecol 27(5):1254–1261
Knorr M, Frey SD, Curtis PS (2005) Nitrogen additions and litter decomposition—a meta-analysis. Ecology 86(12):3252–3257
Kobe RK, Lepcyk CA, Iyer M (2005) Resorption efficiency decreases with increasing green leaf nutrient in a global data set. Ecology 86(10):2780–2792
Li JZ, Lin S, Taube F, Pan QM, Dittert K (2011) Above and belowground net primary productivity of grassland influenced by supplemental water and nitrogen in Inner Mongolia. Plant Soil 340(1–2):253–264
Liu J, Wu N, Wang H, Sun J, Peng B, Jiang P, Bai E (2016) Nitrogen addition affects chemical composition of plant tissues litter and soil organic matter. Ecology 97(7):1796–1806
Lü XT, Freschet GT, Flynn DFB, Han XG (2012) Plasticity in leaf and stem nutrient resorption proficiency potentially reinforces plant-soil feedbacks and microscale heterogeneity in a semi-arid grassland. J Ecol 100(1):144–150
Melillo JM, Aber JD, Muratore JF (1982) Nitrogen and lignin control of hardwood leaf litter decomposition dynamics. Ecology 63(3):621–626
Schuster MJ, Smith NG, Dukes JS (2016) Responses of aboveground C and N pools to rainfall variability and nitrogen deposition are mediated by seasonal precipitation and plant community dynamics. Biogeochemistry 129(3):389–400
Siefert A, Violle C, Chalmandrier L, Albert CH, Taudiere A, Fajardo A, Aarssen LW, Baraloto C, Carlucci MB, Cianciaruso MV, Dantas VL, de Bello F, Duarte LDS, Fonseca CR, Freschet GT, Gaucherand S, Nicolas Gross N, Hikosaka K, Jackson B, Jung V, Kamiyama C, Katabuchi M, Kembel SW, Kichenin E, Kraft NJB, Lagerström A, Le Bagousse-Pinguet Y, Li Y, Mason N, Messier J, Nakashizuka T, Overton JM, Peltzer DA, Pérez-Ramos IM, Pillar VD, Prentice HC, Richardson S, Sasaki T, Schamp BS, Schöb C, Shipley B, Sundqvist M, Sykes MT, Vandewalle M, Wardle DA (2015) A global meta-analysis of the relative extent of intraspecific trait variation in plant communities. Ecol Lett 18(12):1406–1419
Sjöberg G, Nilsson SI, Persson T, Karlsson P (2004) Degradation of hemicellulose cellulose and lignin in decomposing spruce needle litter in relation to N. Soil Biol Biochem 36(11):1761–1768
Smith MD, Knapp AK, Collins SL (2009) A framework for assessing ecosystem dynamics in response to chronic resource alterations induced by global change. Ecology 90(12):3279–3289
Taylor KACC (1995) A modification of the phenol sulfuric-acid assay for total carbohydrates giving more comparable absorbances. Appl Biochem Biotech 53(3):207–214
Vergutz L, Manzoni S, Porporato A, Novais RF, Jackson RB (2012) Global resorption efficiencies and concentrations of carbon and nutrients in leaves of terrestrial plants. Ecol Monogr 82(2):205–220
Waldrop MP, Zak DR, Sinsabaugh RL, Gallo M, Lauber C (2004) Nitrogen deposition modifies soil carbon storage through changes in microbial enzymatic activity. Ecol Appl 14(4):1172–1177
Wright IJ, Westoby M (2003) Nutrient concentration resorption and life span: leaf traits of Australian sclerophyll species. Funct Ecol 17(1):10–19
Yang H, Li Y, Wu M, Zhang Z, Li L, Wan S (2011) Plant community responses to nitrogen addition and increased precipitation: the importance of water availability and species traits. Glob Chang Biol 17(9):2936–2944
Zhang Y, Han X, He N, Long M, Huang J, Zhang G, Wang Q, Han X (2014a) Increase in ammonia volatilization from soil in response to N deposition in Inner Mongolia grasslands. Atmos Environ 84:156–162
Zhang Y, Lu X, Isbell F, Stevens C, Han X, He N, Zhang G, Yu Q, Huang J, Han X (2014b) Rapid plant species loss at high rates and at low frequency of N addition in temperate steppe. Glob Chang Biol 20(11):3520–3529
Zhang W, Chao L, Yang Q, Wang Q, Fang Y, Wang S (2016) Litter quality mediated nitrogen effect on plant litter decomposition regardless of soil fauna presence. Ecology 97(10):2834–2843
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the staff of the Inner Mongolia Grassland Ecosystem Research Station (IMGERS) for supporting this study. We thank Chenxi Tian, Sihan Liu, Yi Wu, and Yue Sun for assistance with laboratory work. We appreciate comments and suggestions from Dr. Scott Bridgham and anonymous reviewers, which help us improve the quality of this work. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31770503 and 31470505), the National Basic Research Program of China (2016YFC0500601 and 2015CB150802), Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDB15010403), the Key Research Program from CAS (QYZDB-SSW-DQC006), and Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS (2014174). Authors declare no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XTL and XGH designed the research; SLH, JXY, YHZ, JXY, YYH, and HWW collected and analyzed the data; SLH, XTL, and GTF wrote the manuscript; all authors contributed critically to the drafts and gave final approval for publication.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Scott Bridgham.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, SL., Freschet, G.T., Yang, JJ. et al. Quantifying the indirect effects of nitrogen deposition on grassland litter chemical traits. Biogeochemistry 139, 261–273 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-018-0466-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-018-0466-6