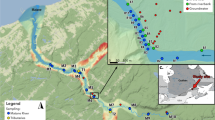
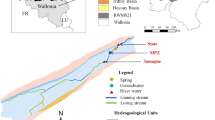
Abstract
The dissolved CO 2 concentration of stream waters is an important component of the terrestrial carbon cycle and an important pathway for release of CO2 to the atmosphere. This study uses data from the UK's largest groundwater monitoring network to estimate the importance of groundwater in contributing excess dissolved CO2 to the atmosphere. The study shows that:
-
(i)
the arithmetic mean concentration of excess dissolved CO2 in the groundwater was 4.99 mg C/I with a standard deviation of 2.53
-
(ii)
for the groundwater composition of excess dissolved CO2 analysis shows no statistical difference between years but does show a significant intra-annual effect and a significant difference between aquifers
-
(iii)
A weighted average of the estimate the areal export of excess dissolved CO2 from the groundwater of the catchment is between 1.4 and 2.9 t C/km2
-
(iv)
the flux of excess dissolved CO2 at the catchment outlet over the period between 1975 and 2002 averages 1.79 kt C/year.
If this were replicated across the UK then the flux of CO2 from rivers would be 0.65 Mt C/year.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Abril H. Etcheber A.V. Borges M. Frankignoulle (2000) ArticleTitleExcess atmospheric carbon dioxide transported by rivers into the Scheldt estuary C.R. Acad. Sci. Paris. Sciences de la Terre et des Plantes 330 761–768
J.A.C. Barth J. Veizer (1999) ArticleTitleCarbon cycle in St.Lawerence aquatic ecosystems at Cornall (Ontario), Canada: seasonal and spatial variations Chem. Geol. 159 107–128 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00036-4
N. Christophersen R.P. Hooper (1992) ArticleTitleMultivariate analysis of stream water chemical data: the use of principal component analysis for the end-member mixing problem Water Resour. Res. 28 99–107 Occurrence Handle10.1029/91WR02518
J.J. Cole N.F. Caraco G.W. Kling T.K. Kratz (1994) ArticleTitleCarbon dioxide supersaturation in the surface water of lakes Science 265 1568–1570
J.J. Cole N.F. Caraco (2001) ArticleTitleCarbon in catchmernts: connecting terrestrial carbon losses with aquatic metabolism Mar. Freshwater Res. 52 101–110 Occurrence Handle10.1071/MF00084
J.C. Dawson M.F. Billet C. Neal S. Hill (2002) ArticleTitleA comparison of particulatedissolved and gaseous carbon in two contrasting upland streams in the UK J. Hydrol. 257 226–246 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0022-1694(01)00545-5
A.M. Hartley W.A. House B.S.C. Leadbeater M.E. Callow (1996) ArticleTitleThe use of microelectrodes to study the precipitation of calcite upon algal biofilms J. Colloid Interface Sci. 183 498–505 Occurrence Handle10.1006/jcis.1996.0573
D. Hope M.F. Billett R. Milne T.A.W. Brown (1997) ArticleTitleExports of organic carbon in British rivers Hydrol. Process. 11 325–344 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1099-1085(19970315)11:3<325::AID-HYP476>3.0.CO;2-I
D. Hope S.M. Palmer M.F. Billet J.C. Dawson (2001) ArticleTitleCarbon dioxide and methane oxidation evasion from a temperate peatland stream Limnol. Oceanogr. 46 847–857 Occurrence Handle10.4319/lo.2001.46.4.0847
I.A. Janssens A. Freibauer P. Ciais P. Smith G-J. Nabuurs G. Folberth B. Schlamadinger R.W.A. Hutjes R. Ceulemans E.D. Schulze R. Valentini A.J. Dolman (2003) ArticleTitleEurope's terrestrial biosphere absorbs 7 to 12% of European anthropogenic CO2 emissions Science 300 1538–1542 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.1083592
H.P. Jarvie C. Neal D.V. Leach G.P. Ryland W.A. House A.J. Robson (1997) ArticleTitleMajor ion concentrations and the inorganic carbon chemistry of the Humber rivers Sci. Total Environ. 194/195 285–302
J.B. Jones P.J. Mulholland (1998) ArticleTitleCarbon dioxide variation in a hardwood forest stream: an integrative measure of whole catchment soil respiration Ecosystems 1 183–196
J.B. Jones E.H. Stanley P.J. Mulholland (2003) ArticleTitleLong-term decline in carbon dioxide supersaturation in rivers across the contiguous United States Geophys. Res. Lett. 30 IssueID10 1495 Occurrence Handle10.1029/2003GL017056
Kempe S. 1982. Long term records of CO2 pressure fluctuations in fresh waters. In: Degens E.T.(ed.), Transport of Carbon and Minerals in Major World Rivers, part 1.
G.W. Kling G.W. Kipphut M.C. Miller (1991) ArticleTitleArtic lakes and streams as conduits to the atmosphere: implications for tundra carbon budgets Science 251 298–301
I.G. Littlewood (1992) Estimating constituent loads in rivers: a review Institute of Hydrology, rep. 117. Institute of Hydrology Wallingford, UK
W. Ludwig J.L. Probst S. Kempe (1996) ArticleTitlePredicting the oceanic input of organic carbon from continental erosion Global Biogeochem. Cycles 10 23–41 Occurrence Handle10.1029/95GB02925
M. Meybeck (1993) ArticleTitleRiverine transport of atmospheric carbon : sources, global typology and budget Water soil and air pollution 70 443–464
C. Neal W.A. House K. Down (1998a) ArticleTitleAn assessment of excess carbon dioxide partial pressure in natural waters based on pH and alkalinity measurements Sci. Total Environ. 210/211 173–185
C. Neal M. Harrow R. Williams (1998b) ArticleTitleDissolved carbon dioxide and oxygen in the River Thames: spring-summer 1997 Sci. Total Environ. 210/211 205–217
R. Sempere B. Charriere F. Van Wambeke G. Cauwet (2001) ArticleTitleCarbon inputs of the Rhone River to the Mediterranean Sea: biogeochemical implications Global Biogeochem. Cycles 14 669–681
J. Siemans (2003) ArticleTitleThe European carbon budget: a gap Science 302 1681
InstitutionalAuthorNameSmithsonian Institute (1966) Smithsonian Miscellaneous Collections, 114 EditionNumber6 Smithsonian Institute Press Washington
Stumm W. and Morgan J.J. 1996. Aquatic Chemistry – Chemical Equilibria and Rates in Natural Waters. 3rd edn. Wiley Interscience, pp. 1022.
B.W. Webb Y. Zhang (1999) ArticleTitleWater temperatures and heat budgets in Dorset chalk water courses Hydrol. Process. 13 309–321 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1099-1085(19990228)13:3<309::AID-HYP740>3.0.CO;2-7
F. Worrall T.P. Burt (2005) ArticleTitleReconstructing long-term records of dissolved CO2 Hydrol. Process 19 1791–1806
F. Worrall R. Harriman C.D. Evans C. Watts J. Adamson C. Neal E. Tipping T.P. Burt I. Grieve D. Montieth P.S. Naden T. Nisbet B. Reynolds P. Stevens (2004) ArticleTitleTrends in dissolved organic carbon in UK rivers and lakes Biogeochemistry 70 369–402 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10533-004-8131-7
F. Worrall T.P. Burt J. Adamson (2005) ArticleTitleFluxes of dissolved carbon dioxide and inorganic carbon from an upland peat catchment: implications for soil respiration Biogeochemistry 73 515–539 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10533-004-1717-2
Worrall F., Swank W.T. and Burt T.P. 2005. Fluxes of inorganic carbon from forested catchments. Hydrol. Process. (in press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Worrall, F., Lancaster, A. The Release of CO2 from Riverwaters – the Contribution of Excess CO2 from Groundwater. Biogeochemistry 76, 299–317 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-005-6449-4
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-005-6449-4