Abstract.
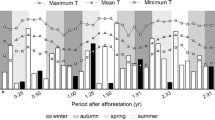
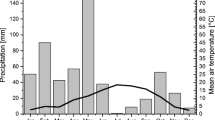
We measured soil surface CO2 efflux (Fs) in loblolly pine stands (Pinus taeda L.) located on the Virginia Piedmont (VA) and South Carolina Coastal Plain (SC) in efforts to assess the impact climate, productivity, and cultural practices have on Fs in the managed loblolly pine ecosystem. The effect of stand age on Fs was examined using a replicated chronosequence approach in which stands ranging from 1 to 25 years since planting were investigated. Soil CO2 efflux was measured on both VA and SC sites for over a year using a closed dynamic system. Multiple linear regression was used to evaluate Fs correlates and examine the relationship between candidate explanatory variables and Fs. Soil temperature (top 10 cm) was the major correlate with Fs on both locations. We observed a positive age effect on Fs in VA stands and no relationship between age and Fs in SC stands. Annual soil C efflux declined with stand age in SC due to both reductions in soil temperatures as crown closure occurs and a diminishing heterotrophic C substrate pool. Annual estimated efflux ranges from 16.7 to 13.2 Mg C ha−1 for 1 and 20-year-old stands, respectively. In contrast, annual soil C efflux increased with age in VA stands as a result of the positive relationship between stand age and Fs, which appears to be related to an increase in the contribution of root respiration to total Fs over time. In VA stands, efflux estimates range from 7.6 to 12.3 Mg C ha−1 for 1 and 20-year-old stands, respectively. These results demonstrate the need to further consider the impact forest management and within-region variability have on soil C efflux over time when estimating C budgets.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.E. Banfield J.S. Bhatti H. Jiang M.J. Apps (2002) ArticleTitleVariability in regional scale estimates of carbon stocks in boreal forest ecosystems: results from west-central Alberta Forest Ecol. Manage 169 15–27 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0378-1127(02)00292-X
N. Buchmann (2000) ArticleTitleBiotic and abiotic factors controlling soil respiration rates in Picea abies stands Soil Biol. Biochem 32 1625–1635 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXntFSlsro%3D
J.R. Butnor K.H. Johnsen R. Oren G.G. Katul (2003) ArticleTitleReduction of forest floor respiration by fertilization on both carbon dioxide-enriched and reference 17-year-old loblolly pine stands Global Change Biol 9 849–861 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2486.2003.00630.x
S.X. Chang C.M. Preston G.F. Weetman (1995) ArticleTitleSoil microbial biomass and microbial minerizable N in a clear-cut chronosequence on northern Vancouver IslandBritish Columbia Can. J. Forest Res 25 1595–1607
R.T. Conant J.M. Klopatek R.C. Malin C.C. Klopatek (1998) ArticleTitleCarbon pools and fluxes along an environmental gradient in northern Arizona Biogeochemistry 43 43–61 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1006004110637
N.T. Edwards B.M. Ross-Todd (1983) ArticleTitleSoil carbon dynamics in a mixed deciduous forest following clear-cutting with and without residue removal Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J 47 1014–1021 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3sXlvFersLk%3D
D.M. Eisenstat PrefixVan K.C.J. Rees (1994) ArticleTitleThe growth and function of pine roots Ecol. Bull 43 76–91
K.C. Ewel W.P. Cropper H.L. Gholz (1987a) ArticleTitleSoil CO2 evolution in Florida slash pine plantations I. Changes through time Can. J. Forest Res 17 325–329
K.C. Ewel W.P. Cropper H.L. Gholz (1987b) ArticleTitleSoil CO2 evolution in Florida slash pine plantations II. Importance of root respiration Can. J. Forest Res 17 330–333
InstitutionalAuthorNameFood and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) (2001) Global Forest Resources Assessment 2000 – Main Report FAO Rome
I.J. Fernandez Y. Son C.R. Kraske L.E. Rustad M.B. David (1993) ArticleTitleSoil carbon dioxide characteristics under different forest types and after harvest Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J 57 1115–1121 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXns1Ciug%3D%3D
C.B. Field I.Y. Fung (1999) ArticleTitleEnhanced: the not-so-big US carbon sink Science 285 544 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.285.5427.544 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXkvF2rsbY%3D
H. Fritze T. Pennanen J. Pietikäinen (1993) ArticleTitleRecovery of soil microbial biomass and activity from prescribed burning Can. J. Forest Res 23 1286–1290
A.M. Gordon R.E. Schlentner PrefixVan K. Cleve (1987) ArticleTitleSeasonal patterns in soil respiration and CO2 evolution following harvesting in the white spruce forests of interior Alaska Can. J. Forest Res 17 304–310
B.E. Haynes S.T. Gower (1995) ArticleTitleBelowground carbon allocation in unfertilized and fertilized red pine plantations in northern Wisconsin Tree Physiol 15 317–325 Occurrence Handle14965955
T. Hernandez C. Garcia I. Reinhardt (1997) ArticleTitleShort-term effect of wildfire on chemical, biochemical and microbiological properties of Mediterranean pine forest soils Biol. Fertil. Soils 25 109–116 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s003740050289 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXltVWksb0%3D
P. Hogberg A. Nordgren N. Buchmann A.F.S. Taylor A. Ekblad M.N. Hogberg G. Nyberg M. Ottosson-Lofvenius D.J. Read (2001) ArticleTitleLarge-scale forest girdling shows that current photosynthesis drives soil respiration Nature 411 789–792
J. Irvine B.E. Law (2002) ArticleTitleContrasting soil respiration in young and old-growth ponderosa pine forests Global Change Biol 8 1183–1194 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2486.2002.00544.x
E.G. Jobaggy R.B. Jackson (2000) ArticleTitleThe vertical distribution of soil organic carbon and its relation to climate and vegetation Ecol. Appl 10 423–436
J.M. Klopatek (2002) ArticleTitleBelowground carbon pools and processes in different ages stands of Douglas-fir Tree Physiol 22 197–204 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XitVCnsbY%3D Occurrence Handle11830416
B.E. Law M.G. Ryan P.M. Anthoni (1999) ArticleTitleSeasonal and annual respiration of a ponderosa pine ecosystem Global Change Biol 5 169–182 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2486.1999.00214.x
J. Lee I.K. Morrison J.D. Leblanc M.T. Dumas D.A. Cameron (2002) ArticleTitleCarbon sequestration in trees and regrowth vegetation as affected by clearcut and partial harvesting in a second-growth boreal mixedwood Forest Ecol. Manage 169 83–101 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0378-1127(02)00300-6
J. Liski D. Perruchoud T. Karjalainen (2002) ArticleTitleIncreasing carbon stocks in the forest soils of western Europe Forest Ecol. Manage 169 159–175 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0378-1127(02)00306-7
L.M. Litton M.G. Ryan D.H. Knight P.D. Stahl (2003) ArticleTitleSoil-surface carbon dioxide efflux and microbial biomass in relation to tree density 13 years after a stand replacing fire in a lodgepole pine ecosystem Global Change Biol 9 680–696 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2486.2003.00626.x
A.J. Londo M.G. Messina S.H. Schoenholtz (1999) ArticleTitleForest harvesting effects on soil temperaturemoistureand respiration in a bottomland hardwood forest Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J 63 637–644 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXks1ajur8%3D
D.E. Lytle C.S. Cronan (1998) ArticleTitleComparitive soil CO2 evolution, litter decay, and root dynamics in clearcut and uncut spruce–fir forest Forest Ecol. Manage 103 121–128 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0378-1127(97)00182-5
C.A. Maier L.W. Kress (2000) ArticleTitleSoil CO2 evolution and root respiration in 11 year-old loblolly pine (Pinus taeda) plantations as affected by moisture and nutrient availability Can. J. Forest Res 30 347–359 Occurrence Handle10.1139/cjfr-30-3-347
A.U. Mallik D. Hu (1997) ArticleTitleSoil respiration following site preparation treatments in boreal mixedwood forest Forest Ecol. Manage 97 265–275 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0378-1127(97)00067-4
B. Pajari (1995) ArticleTitleSoil respiration in a poor upland site of Scots pine stand subjected to elevated temperatures and atmospheric carbon concentration Plant Soil 168–169 563–570
R.E. Pangle J. Seiler (2002) ArticleTitleInfluence of seedling roots, environmental factors and soil characteristics on soil CO2 efflux rates in a 2 year old loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) plantation in the Virginia Piedmont Environ. Pollut 116 s85–s96 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0269-7491(01)00261-5 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XhsFer Occurrence Handle11833922
J. Pietikainen H. Fritze (1993) ArticleTitleMicrobial biomass and activity in the humus layer following burning: short-term effects of two different fires Can. J. Forest Res 23 1275–1285
J. Pietikäinen H. Fritze (1995) ArticleTitleClear-cutting and prescribed burning in coniferous forest: comparision of effects on soil fungal and total microbial biomass, respiration activity and nitrification Soil Biol. Biochem 27 101–109 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0038-0717(94)00125-K
R.A. Progar T.D. Schowalter C.M. Freitag J.J. Morrell (2000) ArticleTitleRespiration from coarse woody debris as affected by moisture and saprotroph functional diversity in Western Oregon Oecologica 124 426–431
T.G. Pypker A.L. Fredeen (2003) ArticleTitleBelow ground CO2 efflux from cut blocks of varying ages in sub-boreal British Columbia Forest Ecol. Manage 172 249–259 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0378-1127(01)00799-X
J.W. Raich W.H. Schlesinger (1992) ArticleTitleThe global carbon dioxide flux in soil respiration and its relationship to vegetation and climate Tellus 44 81–99 Occurrence Handle10.1034/j.1600-0889.1992.t01-1-00001.x
J.W. Raich A. Tufekcioglu (2000) ArticleTitleVegetation and soil respiration: correlations and controls Biogeochemistry 48 71–90 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXitVOjsro%3D
D.D. Richter D. Markewitz S.E. Trumbore C.G. Wells (1999) ArticleTitleRapid accumulation and turnover of soil carbon in a re-restablishing forest Nature 400 56–58 Occurrence Handle10.1038/21867 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXksFeisb0%3D
L.E. Rustad T.G. Huntington R.D. Boone (2000) ArticleTitleControls on soil respiration: implications for climate change Biogeochemistry 49 1–6 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1006255431298
J. Rotter K. Danish (2000) ArticleTitleForest carbon and the Kyoto Protocol’s clean development mechanism J. Forestry 98 38–47
O. Schabenberger F.J. Pierce (2002) Contemporary Statistical Models for the Plant and Soil Sciences CRC Press New York 185–189
W.H. Schlesinger J.A. Andrews (2000) ArticleTitleSoil respiration and the global carbon cycle Biogeochemistry 48 7–20 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1006247623877 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXitVOjsr8%3D
Southeast Regional Climate Center 2003, June 30. Southeastern Regional Climate Center. Retrieved July 9 from the World Wide Web: http://water.dnr.state.SC.us/water/climate/sercc/climateinfo/monthly/monthly.html
R.G. Striegl K.P. Wickland (1998) ArticleTitleEffects of a clear-cut harvest on soil respiration of a jack pine-lichen woodland Can. J. Forest Res 28 534–539 Occurrence Handle10.1139/cjfr-28-4-534
D.E. Toland D.R. Zak (1994) ArticleTitleSeasonal patterns of soil respiration in intact and clear-cut northern harwood forests Can. J. Forest Res 24 1711–1716
S.E. Trumbore O.A. Chadwick R. Amundson (1996) ArticleTitleRapid exchange between soil carbon and atmospheric carbon dioxide driven by temperature change Science 272 393–396 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XisVehu7g%3D
D.P. Turner G.J. Koerper M.E. Harmon J.J. Lee (1995) ArticleTitleA carbon budget for forests of the conterminous United States Ecol. Appl 5 421–436
H.T. Valentine (1999) ArticleTitleEstimation of the net primary productivity of even-age stands with a carbon-allocation model Ecol. Model 122 139–149 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0304-3800(99)00134-9 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXmtlehsLg%3D
R. Valentini G. Matteucci A.J. Dolman E.-D. Schulze C. Rebmann E.J. Moors A. Granier P. Gross N.O. Jensen K. Pilegaard A. Lindroth A. Grelle C. Bernhofer T. Grunwald M. Aubinet R. Ceulemans A.S. Kowalski T. Vesala U. Rannik P. Berbigier D. Loustau J. Guomundsson H. Thorgeirsson A. Ibrom K. Morgenstern R. Clement J. Moncrieff L. Montagnani S. Minerbi P.G. Jarvis (2000) ArticleTitleRespiration as the main determinant of carbon balance in European forests Nature 404 861–865
C. Wang B. Bond-Lamberty S.T. Gower (2002) ArticleTitleEnvironmental controls on carbon dioxide flux from black spruce coarse woody debris Oecologica 132 374–381 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00442-002-0987-4
Wear D.N. and Greis J.G. 2002. P. 299–328. Southern forest resource assessment. United States Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Technical Report GTR SRS-53, 53 pp.
Wiseman P.E. 2001. Soil CO2 efflux across four age classes of plantation pine (Pinus taeda L.) on the Virginia Piedmont. M.S. thesis, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, Virginia, 105 pp.
G.M. Woodwell J.E. Hobbie R.A. Houghton J.M. Melillo B. Moore B.J. Peterson G.R. Shaver (1983) ArticleTitleGlobal deforestation: contribution to atmospheric carbon dioxide Science 222 1081–1086
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gough, C.M., Seiler, J.R., Wiseman, .E. et al. Soil CO2 efflux in loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) plantations on the Virginia Piedmont and South Carolina Coastal Plain over a rotation-length chronosequence. Biogeochemistry 73, 127–147 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-004-0566-3
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-004-0566-3