Abstract
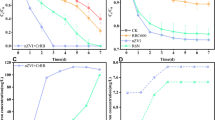
Bioreduction of Cr(VI) is cost-effective and environmentally friendly, however, the slow bioreduction rate limits its application. In this study, the potential synergistic enhancement of Cr(VI) bioreduction by shewanella oneidensis MR-1 (S. oneidensis) with goethite and riboflavin (RF) was investigated. The results showed that the S. oneidensis reaction system reduce 29.2% of 20 mg/L Cr(VI) after 42 h reaction, while the S. oneidensis/goethite/RF reaction system increased the Cr(VI) reduction rate to 87.74%. RF as an efficient electron shuttle and Fe(II) from goethite bioreduction were identified as the crucial components in Cr(VI) reduction. XPS analysis showed that the final precipitates of Cr(VI) reduction were Cr(CH3C(O)CHC(O)CH3)3 and Cr2O3 and adhered to the bacterial cell surface. In this process, the microbial surface functional groups such as hydroxyl and carboxyl groups participated in the adsorption and reduction of Cr(VI). Meanwhile, an increase in cytochrome c led to an increase in electron transfer system activity (ETSA), causing a significant enhancement in extracellular electron transfer efficiency. This study provides insight into the mechanism of Cr(VI) reduction in a complex environment where microorganisms, iron minerals and RF coexist, and the synergistic treatment method of Fe(III) minerals and RF has great potential application for Cr(VI) detoxification in aqueous environment.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen GC, Tucker PM (1976) Multiplet splitting of X-ray photoelectron lines of chromium complexes. the effect of covalency on the 2p core level spin-orbit separation. Inorg Chim Acta 16:41–45
Bae S, Lee Y, Kwon MJ et al (2014) Riboflavin-mediated RDX transformation in the presence of Shewanella putrefaciens CN32 and lepidocrocite. J Hazard Mater 274:24–31
Baltrusaitis J, Cwiertny DM, Grassian VH (2007) Adsorption of sulfur dioxide on hematite and goethite particle surfaces. Phys Chem Chem Phys 9(41):5542–5554
Bird LJ, Bonnefoy V, Newman DK (2011) Bioenergetic challenges of microbial iron metabolisms. Trends Microbiol 19(7):330–340
Bishop ME, Glasser P, Dong H et al (2014) Reduction and immobilization of hexavalent chromium by microbially reduced Fe-bearing clay minerals. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 133:186–203
Butler EC, Chen L, Hansel CM et al (2015) Biological versus mineralogical chromium reduction: potential for reoxidation by manganese oxide. Environ Sci-Process Impacts 17(11):1930–1940
Chen J, Strous M (2013) Denitrification and aerobic respiration, hybrid electron transport chains and co-evolution. Biochim Biophys Acta-Bioenerg 1827(2):136–144
Chon CM, Kim JG, Moon HS (2006) Kinetics of chromate reduction by pyrite and biotite under acidic conditions. Appl Geochem 21(9):1469–1481
Cutting RS, Coker VS, Fellowes JW et al (2009) Mineralogical and morphological constraints on the reduction of Fe (III) minerals by Geobacter sulfurreducens. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 73(14):4004–4022
Duhl KL, TerAvest MA (2019) Shewanella oneidensis NADH dehydrogenase mutants exhibit an amino acid synthesis defect. Front Energy Res 7:116
Gang H, Xiao C, Xiao Y et al (2019) Proteomic analysis of the reduction and resistance mechanisms of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 under long-term hexavalent chromium stress. Environ Int 127:94–102
Ge C, Huang M, Huang D et al (2022) Effect of metal cations on antimicrobial activity and compartmentalization of silver in Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 upon exposure to silver ions. Sci Total Environ 838:156401
Gui M, Chen Q, Ni J (2017) Effect of sulfamethoxazole on aerobic denitrification by strain Pseudomonas stutzeri PCN-1. Bioresour Technol 235:325–331
Gupta P, Diwan B (2017) Bacterial exopolysaccharide mediated heavy metal removal: a review on biosynthesis, mechanism and remediation strategies. Biotechnol Rep 13:58–71
Hansel CM, Benner SG, Nico P et al (2004) Structural constraints of ferric (hydr) oxides on dissimilatory iron reduction and the fate of Fe (II). Geochim Cosmochim Acta 68(15):3217–3229
He Y, Guo J, Song Y et al (2021) Acceleration mechanism of bioavailable Fe (III) on Te (IV) bioreduction of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1: promotion of electron generation, electron transfer and energy level. J Hazard Mater 403:123728
Hunting ER, Vijver MG, van der Geest HG et al (2015) Resource niche overlap promotes stability of bacterial community metabolism in experimental microcosms. Front Microbiol 6:105
Jaiswal A, Banerjee S, Mani R et al (2013) Synthesis, characterization and application of goethite mineral as an adsorbent. J Environ Chem Eng 1(3):281–289
Jiang Y, Shi M, Shi L (2019) Molecular underpinnings for microbial extracellular electron transfer during biogeochemical cycling of earth elements. Sci China-Life Sci 62(10):1275–1286
Jiang M, Zheng X, Chen Y (2020) Enhancement of denitrification performance with reduction of nitrite accumulation and N2O emission by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 in microbial denitrifying process. Water Res 169:115242
Jiang Z, Shi M, Shi L (2020) Degradation of organic contaminants and steel corrosion by the dissimilatory metal-reducing microorganisms Shewanella and Geobacter spp. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 147:104842
Jin Y, Li Z, Zhou E et al (2019) Sharing riboflavin as an electron shuttle enhances the corrosivity of a mixed consortium of Shewanella oneidensis and Bacillus licheniformis against 316L stainless steel. Electrochim Acta 316:93–104
Kantar C, Ari C, Keskin S (2015) Comparison of different chelating agents to enhance reductive cr (VI) removal by pyrite treatment procedure. Water Res 76:66–75
Kwak S, Yoo JC, Moon H et al (2018) Role of clay minerals on reduction of cr(VI). Geoderma 312(1):1–5
Li YS, Church JS, Woodhead AL (2012) Infrared and Raman spectroscopic studies on iron oxide magnetic nano-particles and their surface modifications. J Magn Magn Mater 324(8):1543–1550
Li Y, Ren C, Zhao Z et al (2019) Enhancing anaerobic degradation of phenol to methane via solubilizing Fe (III) oxides for dissimilatory iron reduction with organic chelates. Bioresour Technol 291:121858
Li H, Zhang L, Ye L et al (2022) Arsenic biotransformation in industrial wastewater treatment residue: Effect of co-existing Shewanella sp ANA-3 and MR-1. J Environ Sci 118:14–20
Liu X, Chu G, Du Y et al (2019) The role of electron shuttle enhances Fe (III)-mediated reduction of cr (VI) by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 35(4):1–8
Liu H, Li P, Wang H et al (2020) Arsenic mobilization affected by extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of the dissimilatory iron reducing bacteria isolated from high arsenic groundwater. Sci Total Environ 735:139501
Liu K, Li F, Pang Y et al (2022) Electron shuttle-induced oxidative transformation of arsenite on the surface of goethite and underlying mechanisms. J Hazard Mater 425:127780
Ma L, Du Y, Chen S et al (2021) Nanoscale zero-valent iron coupling with Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 for enhanced reduction/removal of aqueous cr (VI). Sep Purif Technol 277:119488
Ma L, Du Y, Chen S et al (2022) Highly efficient removal of cr (VI) from aqueous solution by pinecone biochar supported nanoscale zero-valent iron coupling with Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Chemosphere 287:132184
Malele CN, Ray J, Jones WE Jr (2010) Synthesis, characterization and spectroscopic study of riboflavin–molybdenum complex. Polyhedron 29(2):749–756
Martin CB, Wilfong E, Ruane P et al (2005) An action spectrum of the Riboflavin-photosensitized inactivation of lambda phage. Photochem Photobiol 81(2):474–480
Meng Y, Zhao Z, Burgos WD et al (2018) Iron (III) minerals and anthraquinone-2, 6-disulfonate (AQDS) synergistically enhance bioreduction of hexavalent chromium by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Sci Total Environ 640:591–598
Middleton SS, Latmani RB, Mackey MR et al (2003) Cometabolism of cr (VI) by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 produces cell‐associated reduced chromium and inhibits growth. Biotechnol Bioeng 83(6):627–637
Mohamed A, Yu L, Fang Y et al (2020) Iron mineral-humic acid complex enhanced cr (VI) reduction by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Chemosphere 247:125902
Mohamed A, Sun B, Yu C et al (2021) Size effect of hematite particles on the cr (VI) reduction by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. J Environ Chem Eng 9(2):105096
Possetto D, Reynoso A, Natera J et al (2021) Kinetics of the riboflavin-sensitized degradation of pyrethroid insecticides. J Photochem Photobiol A-Chem 418:113416
Radzevič A, Niaura G, Ignatjev I et al (2016) Electropolymerisation of the natural monomer riboflavin and its characterisation. Electrochim Acta 222:1818–1830
Ri C, Tang J, Liu F et al (2022) Enhanced microbial reduction of aqueous hexavalent chromium by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 with biochar as electron shuttle. J Environ Sci 113:12–25
Song X, Chen Z, Wang X et al (2017) Ligand effects on nitrate reduction by zero-valent iron: role of surface complexation. Water Res 114:218–227
Stern N, Mejia J, He S et al (2018) Dual role of humic substances as electron donor and shuttle for dissimilatory iron reduction. Environ Sci Technol 52(10):5691–5699
Tsugama D, Liu S, Takano T (2009) Evaluation of Fe (III) reduction by mitochondria induced with a respiratory substrate NADH or succinate, using a Fe (II)-specific chelator bathophenanthroline disulfonate in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biologia 64(5):877–880
Viamajala S, Peyton BM, Sani RK et al (2004) Toxic effects of chromium (VI) on anaerobic and aerobic growth of shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Biotechnol Prog 20(1):87–95
Wang G, Zhang B, Li S et al (2017) Simultaneous microbial reduction of vanadium (V) and chromium (VI) by Shewanella loihica PV-4. Bioresour Technol 227:353–358
Wang H, Zhao HP, Zhu L (2020) Structures of nitroaromatic compounds induce Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 to adopt different electron transport pathways to reduce the contaminants. J Hazard Mater 384:121495
Wang C, Liu H, Wang G et al (2022) Photocatalytic removal of metronidazole and cr (VI) by a novel Zn3In2S6/Bi2O3 S-scheme heterojunction: performance, mechanism insight and toxicity assessment. Chem Eng J 450:138167
Wang X, Chen T, Gao C et al (2022) Effect of extracellular polymeric substances removal and re-addition on the denitrification performance of activated sludge: carbon source metabolism, electron transfer and enzyme activity. J Environ Chem Eng 10:108069
Weber KA, Achenbach LA, Coates JD (2006) Microorganisms pumping iron: anaerobic microbial iron oxidation and reduction. Nat Rev Microbiol 4(10):752–764
White GF, Edwards MJ, Gomez-Perez L et al (2016) Mechanisms of bacterial extracellular electron exchange. Adv Microb Physiol 68:87–138
Wu C, An W, Liu Z et al (2020) The effects of biochar as the electron shuttle on the ferrihydrite reduction and related arsenic (as) fate. J Hazard Mater 390:121391
Xia ZC, Cheng YY, Kong WQ et al (2016) Electron shuttles alter selenite reduction pathway and redistribute formed Se(0) nanoparticles. Process Biochem 51(3):408–413
Yan W, Guo W, Wang L et al (2021) Extracellular polymeric substances from Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 biofilms mediate the transformation of ferrihydrite. Sci Total Environ 784:147245
Yang Y, Ding Y, Hu Y et al (2015) Enhancing bidirectional electron transfer of Shewanella oneidensis by a synthetic flavin pathway. ACS Synth Biol 4(7):815–823
Yi Y, Zhao T, Zang Y et al (2021) Different mechanisms for riboflavin to improve the outward and inward extracellular electron transfer of Shewanella loihica. Electrochem Commun 124:106966
Yu H, Liu G, Dong B et al (2021) Humic acids promote hydroxyl radical production during transformation of biogenic and abiogenic goethite under redox fluctuation. Chem Eng J 424(5):130359
Zhang P, Xu D, Li Y et al (2015) Electron mediators accelerate the microbiologically influenced corrosion of 304 stainless steel by the Desulfovibrio vulgaris biofilm. Bioelectrochemistry 101:14–21
Zhang F, Xu W, Zhang L et al (2022a) Riboflavin as a non-quinone redox mediator for enhanced cr (VI) removal by Shewanella putrefaciens. J Mol Liq 351:118622
Zhang Y, Zhao Q, Chen B (2022) Reduction and removal of cr(VI) in water using biosynthesized palladium nanoparticles loaded Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Sci Total Environ 805:150336
Zhao M, Zhang C, Yang X et al (2020) Preparation of highly-conductive pyrogenic carbon-supported zero-valent iron for enh anced Cr (VI) reduction. J Hazard Mater 396:122712
Zhao J, Li F, Cao Y et al (2021) Microbial extracellular electron transfer and strategies for engineering electroactive microorganisms. Biotechnol Adv 53:107682
Zhao C, Li Y, Li X et al (2022) Biological removal of sulfamethoxazole enhanced by S. Oneidensis MR-1 via promoting nadh generation and electron transfer and consumption. J Hazard Mater 426:127839
Zhou LY, Chen S, Li H et al (2018) EDDS enhanced Shewanella putrefaciens CN32 and α-FeOOH reductive dechlorination of carbon tetrachloride. Chemosphere 198:556–564
Zhou H, Ye M, Zhao Y et al (2022) Sodium citrate and biochar synergistic improvement of nanoscale zero-valent iron composite for the removal of chromium (VI) in aqueous solutions. J Environ Sci 115:227–239
Zhu Y, Li H, Zhang G et al (2018) Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution by different surface-modified biochars: acid washing, nanoscale zero-valent iron and ferric iron loading. Bioresour Technol 261:142–150
Zou D, Tong J, Feng C et al (2022) Synthesis of biochar@ α-Fe2O3@ Shewanella loihica complex for remediation of soil contaminated by hexavalent chromium: optimization of conditions and mechanism. Chemosphere 303:134858
Zuo H, Kukkadapu R, Zhu Z et al (2020) Role of clay-associated humic substances in catalyzing bioreduction of structural Fe (III) in nontronite by Shewanella putrefaciens CN32. Sci Total Environ 741:140213
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Key Technologies Research and Development Program [Grant Numbers 2019YFC1803804], the Fundamental Research Fund for the Central Universities [Grant Numbers N2001012].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YZ: Investigation, Methodology, Writing - original draft. HL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Validation, Visualization, Writing - review & editing. YY: Investigation, Methodology, Data curation. BW: Data curation, Formal analysis. XL: Investigation, Methodology, Resourses, Software. KW: Data curation, Resources. PW: Investigation, Methodology, Formal analysis. CZ: Data Curation, Validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Y., Li, H., Yang, Y. et al. Goethite and riboflavin synergistically enhance Cr(VI) reduction by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Biodegradation 34, 155–167 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-022-10010-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-022-10010-5