Abstract
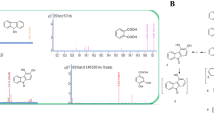
The pentafluorosulfanyl (SF5–) substituent conveys properties that are beneficial to drugs and agrochemicals. As synthetic methodologies improve the number of compounds containing this group will expand and these chemicals may be viewed as emerging pollutants. As many microorganisms can degrade aromatic xenobiotics, we investigated the catabolism of SF5-substituted aminophenols by bacteria and found that some Pseudomonas spp. can utilise these compounds as sole carbon and energy sources. GC–MS analysis of the culture supernatants from cultures grown in 5-(pentafluorosulfanyl) 2-aminophenol demonstrated the presence of the N-acetylated derivative of the starting substrate and 4-(pentafluorosulfanyl)catechol. Biotransformation experiments with re-suspended cells were also conducted and fluorine-19 NMR analyses of the organic extract and aqueous fraction from suspended cell experiments revealed new resonances of SF5-substituted intermediates. Supplementation of suspended cell cultures with yeast extract dramatically improved the degradation of the substrate as well as the release of fluoride ion. 4-(Pentafluorosulfanyl)catechol was shown to be a shunt metabolite and toxic to some of the bacteria. This is the first study to demonstrate that microorganisms can biodegrade SF5-substituted aromatic compounds releasing fluoride ion, and biotransform them generating a toxic metabolite.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altomonte S, Zanda M (2012) Synthetic chemistry and biological activity of pentafluorosulphanyl (SF5) organic molecules. J Fluorine Chem 143:57–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfluchem.2012.06.030
Arora PK, Srivastava A, Singh VP (2014) Novel degradation pathway of 4-chloro-2-aminophenol via 4-chlorocatechol in Burkholderia sp. RKJ 800. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(3):2298–2304. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2167-y
Beier P, Pastyrikova T (2011) Hydroxylation of nitro-(pentafluorosulfanyl)benzenes via vicarious nucleophilic substitution of hydrogen. Tetrahedron Lett 52(34):4392–4394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2011.06.011
Davis KJ, He Z, Somerville CC, Spain CJ (1999) Genetic and biochemical comparison of 2-aminophenol 1,6-dioxygenase of Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes JS45 to meta-cleavage dioxygenases: divergent evolution of 2-aminophenol meta-cleavage pathway. Arch Microbiol 172(5):330–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002030050787
Diaz E, Jimenez JI, Nogales J (2013) Aerobic degradation of aromatic compounds. Curr Opin Biotechnol 24:431–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2012.10.010
Gaillard M, Vallaeys T, Vorholter FJ, Minoia M, Werlen C, Sentchilo V, Puhler A, van der Meer JR (2006) The clc element of Pseudomonas sp strain B13, a genomic island with various catabolic properties. J Bacteriol 188(5):1999–2013. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.188.5.1999-2013.2006
Gillis EP, Eastman KJ, Hill MD, Donnelly DJ, Meanwell NA (2015) Applications of fluorine in medicinal chemistry. J Med Chem 58(21):8315–8359. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00258
Hendriks CMM, Penning TM, Zang TZ, Wiemuth D, Grunder S, Sanhueza IA, Schoenebeck F, Bolm C (2015) Pentafluorosulfanyl-containing flufenamic acid analogs: syntheses, properties and biological activities. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 25(20):4437–4440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.09.012
Hughes D, Clark BR, Murphy CD (2011) Biodegradation of polyfluorinated biphenyl in bacteria. Biodegradation 22:741–749. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-010-9411-7
Jackson DA, Mabury SA (2009) Environmental properties of pentafluorosulfanyl compounds: physical properties and photodegradation. Environ Toxicol Chem 28(9):1866–1873
Jeschke P (2010) The unique role of halogen substituents in the design of modern agrochemicals. Pest Manag Sci 66(1):10–27. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.1829
Kavanagh E, Winn M, Gabhann CN, O’Connor NK, Beier P, Murphy CD (2014) Microbial biotransformation of aryl sulfanylpentafluorides. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(1):753–758. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1985-2
Kiel M, Engesser KH (2015) The biodegradation vs. biotransformation of fluorosubstituted aromatics. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(18):7433–7464. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6817-5
Lim DS, Choi JS, Pak CS, Welch JT (2007) Synthesis and herbicidal activity of a pentafluorosulfanyl analog of trifluralin. J Pestic Sci 32(3):255–259. https://doi.org/10.1584/jpestics.G06-50
Murphy CD (2007) The application of F-19 nuclear magnetic resonance to investigate microbial biotransformations of organofluorine compounds. OMICS 11(3):314–324. https://doi.org/10.1089/omi.2007.0002
Murphy CD (2010) Biodegradation and biotransformation of organofluorine compounds. Biotechnol Lett 32(3):351–359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-009-0174-3
Murphy CD, Sandford G (2015) Recent advances in fluorination techniques and their anticipated impact on drug metabolism and toxicity. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 11(4):589–599. https://doi.org/10.1517/17425255.2015.1020295
Savoie PR, Welch JT (2015) Preparation and utility of organic pentafluorosulfanyl-containing compounds. Chem Rev 115(2):1130–1190. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr500336u
Takenaka S, Murakami S, Shinke R, Aoki K (1998) Metabolism of 2-aminophenol by Pseudomonas sp. AP-3: modified meta-cleavage pathway. Arch Microbiol 170(2):132–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002030050624
Takenaka S, Murakami S, Kim YJ, Aoki K (2000) Complete nucleotide sequence and functional analysis of the genes for 2-aminophenol metabolism from Pseudomonas sp AP-3. Arch Microbiol 174(4):265–272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002030000203
Vida N, Pastyrikova T, Klepetarova B, Beier P (2014) Synthesis of aliphatic sulfur pentafluorides by oxidation of SF5-containing anisole, phenols, and anilines. J Org Chem 79(18):8906–8911. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo501562z
Vida N, Vaclavik J, Beier P (2016) Synthesis and reactivity of aliphatic sulfur pentafluorides from substituted (pentafluorosulfanyl)benzenes. Beilstein J Org Chem 12:110–116. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjoc.12.12
Welch JT, Lim DS (2007) The synthesis and biological activity of pentafluorosulfanyl analogs of fluoxetine, fenfluramine, and norfenfluramine. Bioorg Med Chem 15(21):6659–6666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2007.08.012
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Initial Training Network, FLUOR21, funded by the FP7 Marie Curie Actions of the European Commission (FP7-PEOPLE-2013-ITN-607787). SH was supported by an Irish Research Council Government of Ireland Postdoctoral Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saccomanno, M., Hussain, S., O’Connor, N.K. et al. Biodegradation of pentafluorosulfanyl-substituted aminophenol in Pseudomonas spp.. Biodegradation 29, 259–270 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-018-9827-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-018-9827-z