Abstract
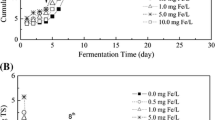
The effect of copper (added as CuCl2) on the anaerobic co-digestion of Phragmites straw and cow dung was studied in pilot experiments by investigating the biogas properties, process stability, substrate degradation and enzyme activities at different stages of mesophilic fermentation. The results showed that 30 and 100 mg/L Cu2+ addition increased the cumulative biogas yields by up to 43.62 and 20.77% respectively, and brought forward the daily biogas yield peak, while 500 mg/L Cu2+ addition inhibited biogas production. Meanwhile, the CH4 content in the 30 and 100 mg/L Cu2+-added groups was higher than that in the control group. Higher pH values (close to pH 7) and lower oxidation–reduction potential (ORP) values in the Cu2+-added groups after the 8th day indicated better process stability compared to the control group. In the presence of Cu2+, the degradation of volatile fatty acids (VFAs) and other organic molecules (represented by chemical oxygen demand, COD) generated from hydrolysis was enhanced, and the ammonia nitrogen (NH4 +-N) concentrations were more stable than in the control group. The contents of lignin and hemicellulose in the substrate declined in the Cu2+-added groups while the cellulose contents did not. Neither the cellulase nor the coenzyme F420 activities could determine the biogas producing efficiency. Taking the whole fermentation process into account, the promoting effect of Cu2+ addition on biogas yields was mainly attributable to better process stability, the enhanced degradation of lignin and hemicellulose, the transformation of intermediates into VFA, and the generation of CH4 from VFA.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez R, Lidén G (2009) Low temperature anaerobic digestion of mixtures of llama, cow and sheep manure for improved methane production. Biomass Bioenerg 33:527–533
Ashekuzzaman SM, Poulsen TG (2011) Optimizing feed composition for improved methane yield during anaerobic digestion of cow manure based waste mixtures. Bioresour Technol 102:2213–2218
Bayer EA, Lamed R, Himmel ME (2007) The potential of cellulases and cellulosomes for cellulosic waste management. Curr Opin Biotechnol 18:237–245
Ben Salem Z, Laffray X, Ashoour A et al (2014) Metal accumulation and distribution in the organs of Reeds and Cattails in a constructed treatment wetland (Etueffont, France). Ecol Eng 64:1–17
Bitton G (1994) Wastewater microbiology, 1st edn. Wiley-Liss, New York
Blanc FC, Molof AH (1973) Electrode potential monitoring and electrolytic control in anaerobic digestion. J Water Pollut Control Fed 45:655–667
Cao Z, Wang S, Wang T et al (2015) Using contaminated plants involved in phytoremediation for anaerobic digestion. Int J Phytoremediat 17:201–207
Chakraborty N, Chatterjee M, Sarkar GM, Lahiri SC (2010) Inhibitory effects of the divalent metal ions on biomethanation by isolated mesophilic methanogen in AC21 medium in presence or absence of juices from water hyacinth. BioEnergy Res 3:314–320
Chen Y, Cheng JJ, Creamer KS (2008) Inhibition of anaerobic digestion process: a review. Bioresour Technol 99:4044–4064
Cheng Y, Sang S, Huang H et al (2007) Variation of coenzyme F420 activity and methane yield in landfill simulation of organic waste. J China Univ Min Technol 17:403–408
Codina JC, Muñoz MA, Cazorla FM et al (1998) The inhibition of methanogenic activity from anaerobic domestic sludges as a simple toxicity bioassay. Water Res 32:1338–1342
Colussi I, Cortesi A, Della Vedova L et al (2009) Start-up procedures and analysis of heavy metals inhibition on methanogenic activity in EGSB reactor. Bioresour Technol 100:6290–6294
Gbogbo F, Otoo SD (2015) The concentrations of five heavy metals in components of an economically important urban coastal wetland in Ghana: public health and phytoremediation implications. Environ Monit Assess 187:655
Harper SR, Pohland FG (1986) Recent developments in hydrogen management during anaerobic biological wastewater treatment. Biotechnol Bioeng 28:585–602
Jain SK, Gujral GS, Jha NK, Vasudevan P (1992) Production of biogas from Azolla pinnata R. Br and Lemna minor L.: effect of heavy metal contamination. Bioresour Technol 41:273–277
Kabatapendias A (2011) Trace elements in soils and plants, 4th edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Karri S, Sierra-Alvarez R, Field JA (2006) Toxicity of copper to acetoclastic and hydrogenotrophic activities of methanogens and sulfate reducers in anaerobic sludge. Chemosphere 62:121–127
Khan AW, Trottier TM (1978) Effect of sulfur-containing compounds on anaerobic degradation of cellulose to methane by mixed cultures obtained from sewage sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol 35:1027–1034
Kraus LS (1948) Central states sewage works association 1948 operators’ breakfast forum. Sewage Work J 20:1092–1106
Kretsinger RH, Uversky VN, Permyakov EA (2013) Encyclopedia of metalloproteins, 1st edn. Springer, New York
Lawrence AW, McCarty PL (1965) The role of sulfide in preventing heavy metal toxicity in anaerobic treatment. J Water Pollut Control Fed 37:392–406
Lee SJ (2008) Relationship between oxidation reduction potential (ORP) and volatile fatty acid (VFA) production in the acid-phase anaerobic digestion process. University of Canterbury. Civil and Natural Resources Engineering
Lenártová V, Holovská K, Javorský P (1998) The influence of mercury on the antioxidant enzyme activity of rumen bacteria Streptococcus bovis and Selenomonas ruminantium. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 27:319–325
Leung HM, Duzgoren-Aydin NS, Au CK et al (2016) Monitoring and assessment of heavy metal contamination in a constructed wetland in Shaoguan (Guangdong Province, China): bioaccumulation of Pb, Zn, Cu and Cd in aquatic and terrestrial components. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(10):9079–9088
Lin CY, Chen CC (1999) Effect of heavy metals on the methanogenic UASB granule. Water Res 33:409–416
Liu A, Xu S, Lu C et al (2014) Anaerobic fermentation by aquatic product wastes and other auxiliary materials. Clean Technol Environ Policy 16:415–421
Lo HM, Lin KC, Liu MH et al (2009) Solubility of heavy metals added to MSW. J Hazard Mater 161:294–299
Manyiloh CE, Mamphweli SN, Meyer EL et al (2013) Microbial anaerobic digestion (bio-digesters) as an approach to the decontamination of animal wastes in pollution control and the generation of renewable energy. Int J Environ Res Public Heal 10:4390–4417
Moestedt J, Nordell E, Shakeri Yekta S et al (2016) Effects of trace element addition on process stability during anaerobic co-digestion of OFMSW and slaughterhouse waste. Waste Manag 47:11–20
Mori K, Hatsu M, Kimura R, Takamizawa K (2000) Effect of heavy metals on the growth of a methanogen in pure culture and coculture with a sulfate-reducing bacterium. J Biosci Bioeng 90:260–265
Mudhoo A, Kumar S (2013) Effects of heavy metals as stress factors on anaerobic digestion processes and biogas production from biomass. Int J Environ Sci Technol 10:1383–1398
Pilon M, Abdel-Ghany SE, Cohu CM et al (2006) Copper cofactor delivery in plant cells. Curr Opin Plant Biol 9:256–263
Pokój T, Bułkowska K, Gusiatin ZM et al (2015) Semi-continuous anaerobic digestion of different silage crops: VFAs formation, methane yield from fiber and non-fiber components and digestate composition. Bioresour Technol 190:201–210
Rezania S, Ponraj M, Talaiekhozani A et al (2015) Perspectives of phytoremediation using water hyacinth for removal of heavy metals, organic and inorganic pollutants in wastewater. J Environ Manage 163:125–133
Roongtanakiat N, Tangruangkiat S, Meesat R (2007) Utilization of Vetiver grass (Vetiveria zizanioides) for removal of heavy metals from industrial wastewaters. Scienceasia 33:397–403
Sawayama S, Tada C, Tsukahara K, Yagishita T (2004) Effect of ammonium addition on methanogenic community in a fluidized bed anaerobic digestion. J Biosci Bioeng 97:65–70
Seravalli J, Gu W, Tam A et al (2003) Functional copper at the acetyl-CoA synthase active site. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 100:3689–3694
Shakeri Yekta S, Lindmark A, Skyllberg U et al (2014) Importance of reduced sulfur for the equilibrium chemistry and kinetics of Fe(II), Co(II) and Ni(II) supplemented to semi-continuous stirred tank biogas reactors fed with stillage. J Hazard Mater 269:83–88
Shakeri Yekta S, Skyllberg U, Danielsson Å et al (2016) Chemical speciation of sulfur and metals in biogas reactors-Implications for cobalt and nickel bio-uptake processes. J Hazard Mater 324:110–116
Stoltz E, Greger M (2002) Accumulation properties of As, Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn by four wetland plant species growing on submerged mine tailings. Environ Exp Bot 47:271–280
Su Y (2011) Biogas fermentation detection technology. Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing
Tabatabaei M, Sulaiman A, Nikbakht AM et al (2011) Influential parameters on biomethane generation in anaerobic wastewater treatment plants. In: Manzanera M (ed) Alternative Fuel. INTECH Open Access Publisher, Rijeka. doi:10.5772/24681
Tian Y, Zhang H (2016) Producing biogas from agricultural residues generated during phytoremediation process: possibility, threshold, and challenges. Int J Green Energy 13:1556–1563
Tian Y, Zhang H, Chai Y et al (2016) Biogas properties and enzymatic analysis during anaerobic fermentation of Phragmites australis straw and cow dung: influence of nickel chloride supplement. Biodegradation 28:15–25
Tiecher TL, Ceretta CA, Ferreira PAA et al (2016) The potential of Zea mays L. in remediating copper and zinc contaminated soils for grapevine production. Geoderma 262:52–61
Verma VK, Singh YP, Rai JPN (2007) Biogas production from plant biomass used for phytoremediation of industrial wastes. Bioresour Technol 98:1664–1669
Wang M, Wang S, Pan X et al (2011) Supplementation of four different oils affects gas production and coenzyme F_(420) of ruminal microbe in vitro. Chin J Anim Nutr 23:1819–1825
Wei FS (2002) Monitoring and analysis methods of water and wastewater. Chinese Environmental Science Press, Beijing
Yue Z-B, Yu H-Q, Wang Z-L (2007) Anaerobic digestion of cattail with rumen culture in the presence of heavy metals. Bioresour Technol 98:781–786
Zandvoort MH, Van Hullebusch ED, Fermoso FG, Lens PNL (2006) Trace metals in anaerobic granular sludge reactors: bioavailability and dosing strategies. Eng Life Sci 6:293–301
Zayed G, Winter J (2000) Inhibition of methane production from whey by heavy metals—protective effect of sulfide. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 53:726–731
Zhang R, Wu F, Liu C et al (2008) Characteristics of organic phosphorus fractions in different trophic sediments of lakes from the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River region and Southwestern Plateau, China. Environ Pollut 152:366–372
Zhang H, Tian Y, Wang L et al (2016) Effect of ferrous chloride on biogas production and enzymatic activities during anaerobic fermentation of cow dung and Phragmites straw. Biodegradation 572(27):69–82
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the National Special Water Programs (Nos. 2009ZX07210-009, 2015ZX07203-011, 2015ZX07204-007, 2017ZX07101-003), Ecological Riverway Artificial Strengthen Key Technology Research and Demonstration Project of Shandong Province (2012–2014, No. SDHBPJ-ZB-08).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, H., Tian, Y., Zhang, H. et al. Copper stressed anaerobic fermentation: biogas properties, process stability, biodegradation and enzyme responses. Biodegradation 28, 369–381 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-017-9802-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-017-9802-0