Abstract
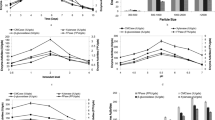
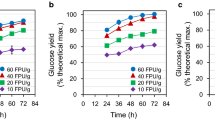
The poor management of solid wastes in Tanzania urban centers is a chronic problem that has increasingly become a source of environmental pollution. Bioconversion offers a cheap and safe method of not only disposing these wastes, but also it has the potential to convert lignocellulosic wastes into usable forms such as reducing sugars that could be used as food. This paper reports a preliminary study on the physical characteristics, acid pretreatment, saccharification by cellulase from Trichoderma reesei and fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae of the lignocellulosic component of the solid wastes collected from various dumping sites located in Kinondoni Municipality, Dar es Salaam city. The results showed that overall, the lignocellulosic component constitute about 50% of solid wastes dumped in the study areas. Maximum production of reducing sugars was obtained after 6 h of saccharification while highest concentrations of bioethanol were achieved after 48 h of fermentation. Microbial bioconversion of lignocellulose component yielded up to 21% bioethanol.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bruce E (1985) Annual Reports on Fermentation Process, Vol 8 (pp 299–323). Academic press Inc. Department of Agriculture and Chemical Engineering Colorado State University, USA
EB Cowling TK Kirk (1976) ArticleTitleProperties of cellulose and lignocellulosic materials as substrates for enzymatic conversion processes Biotechnol. Bioeng. Symp. 6 95–123 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE2sXnsVKlsg%3D%3D
LT Fan YH Lee (1980) ArticleTitleThe nature of lignocellulosics and their pretreatment for enzymatics hydrolysis Biotechnol. Bioeng. 22 177–186 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3cXntFOksA%3D%3D
LT Fan HL Young MM Gharpurai (1985) The Nature of Lignocellulosics and their Pretreatments for Enzymatic Hydrolysis Johm Wiley & SonsInc. New York, USA 156–157
D Kamely A Chakrabarty GS Omenn (1990) Biotechnology and Biodegradation. Adv. Biotechnol. Series 4 Gulf publishing Co. Tokyo
McMillan JD (1994) Conversion of hemicellulose hydrolyzates to ethanol. In: Enzymatic conversion of biomass for fuel production. ACS Symp. Ser. 566: 410–435
GL Miller (1959) ArticleTitleUse of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar Anal. Chem. 31 426–428 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaG1MXmtFKiuw%3D%3D
MA Millett AJ Baker LD Satter (1975) ArticleTitlePretreatment to enhance chemical, enzymatic and microbial attack of cellulose materials Biotechnol. Bioeng. Symp. 5 193–219 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE28XnsF2ltA%3D%3D
GYS Mtui (2000) Production of sugars & ethanol from steam exploded rice straw. Proc. scientific conference on research capacity profiles. Faculty of Science University of Dar es Salaam Tanzania
LP Ramos JN Saddler (1994) ArticleTitleBioconversion of wood residue: mechanisms involved in pretreating and hydrolyzing lignocellulosic materials ACS Symp. Ser. 566 325–341 Occurrence Handle10.1021/bk-1994-0566.ch016 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXit1Glur8%3D
PF Stanbury A Whitaker (1989) Principles of Fermentation Technology Pergamon Press Oxford, UK 255–256
Wayman M & Parekh S (1990) Biotechnology of Biomass Conversion: Fuels and Chemicals from Renewable Sources. In: Biotechnology Series, 30 Vol (pp 40–71). Open University Press, UK
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mtui, G., Nakamura, Y. Bioconversion of lignocellulosic waste from selected dumping sites in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. Biodegradation 16, 493–499 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-004-5826-3
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-004-5826-3