Abstract
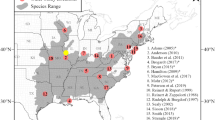
The use of surrogate species in conservation planning has been applied with disappointing results on relatively large sets of species. It could still prove useful for optimizing conservation efforts when considering a small set of species with similar ecological requirements, however few field tests of this nature have been carried out. The aim of this research is to compare the response of three arboreal rodent species—the fat dormouse (Glis glis), the hazel dormouse (Muscardinus avellanarius) and the red squirrel (Sciurus vulgaris)—to habitat loss and fragmentation, with the aim of identifying priorities for conservation and evaluating possible optimization of conservation efforts under different scenarios: habitat restoration and selection of focal patches. We studied the distribution of the three species in a sample of patches in a highly fragmented landscape in central Italy, using a patch-landscape scale approach. The distribution was studied by using hair tubes, nestboxes and nocturnal surveys. The three species showed analogous responses to increasing isolation and decreasing size of habitat patches; what differed however, was the magnitude of responses. Our results show possible application of surrogacy within this restricted group of species, however several caveats arise depending on the conservation strategy and available funding. If habitat restoration is the objective, then the fat dormouse should be the target species for guiding size and isolation of patches. On the other hand, the magnitude of the differences and patch requirements for this species, question the feasibility of these conservation actions. If selection of focal patches for conservation is the objective then selecting the fat dormouse as a focal/umbrella species would overlook areas suitable for the other two species. Feasible optimisation of conservation efforts may be possible only between the red squirrel and the hazel dormouse.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andelman SJ, Fagan WF (2000) Umbrellas and flagships: efficient conservation surrogates or expensive mistakes? Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:5954–5959. doi:10.1073/pnas.100126797
Arrigoni PV (1998) La vegetazione forestale foreste e macchie della Toscana. Edizioni regione Toscana, Firenze
Bennet AF, Radford JQ, Haslem A (2007) Properties of land mosaics: implications for nature conservation agricultural environments. Biol Conserv 133:250–264. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2006.06.008
Bright PW, Morris PA (1996) Why are Dormice rare? A case study in conservation biology. Mammal Rev 26(4):157–187. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2907.1996.tb00151.x
Bright PW, Mitchell P, Morris PA (1994) Dormouse distribution: survey techniques insular ecology and selection of sites for conservation. J Appl Ecol 31:329–339. doi:10.2307/2404547
Brooker L (2002) The application of focal species knowledge to landscape design in agricultural lands using the ecological neighbourhood as a template. Landsc Urban Plan 60:185–210. doi:10.1016/S0169-2046(02)00055-5
Burnham KP, Anderson DR (2002) Model selection and inference—a practical information—theoretic approach, 2nd edn. Springer-Verlag, New York
Capizzi D, Battistini M, Amori G (2002) Analysis of hazel dormouse Muscardinus avellanarius distribution in a Mediterranean fragmented woodland. Ital J Zool (Modena) 69:25–31
Capizzi D, Battistini M, Amori G (2003) Effects of habitat fragmentation and forest management on the distribution of the edible dormouse Glis glis. Acta Theriol (Warsz) 48:359–371
Celada C, Bogliani G, Gariboldi A, Maracci A (1994) Occupancy of isolated woodlots by the red squirrel Sciurus vulgaris in Italy. Biol Conserv 69:177–183. doi:10.1016/0006-3207(94)90057-4
Fahrig L (2003) Effects of habitat fragmentation on biodiversity. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 34:487–515. doi:10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.34.011802.132419
Favreau JM, Drew JA, Hess GR, Rubino MJ, Koch FH, Eschelback KA (2006) Recommendations for assessing the effectiveness of surrogate species approaches. Biodivers Conserv 15:3949–3969. doi:10.1007/s10531-005-2631-1
Fleishman E, Murphy DD, Brussard PF (2000) A new method for selection of umbrella species for conservation planning. Ecol Appl 10:569–579. doi:10.1890/1051-0761(2000)010[0569:ANMFSO]2.0.CO;2
Fornasari L, Casale P, Wauters L (1997) Red squirrel conservation: the assessment of a reintroduction experiment. Ital J Zool (Modena) 64:163–167
Gippoliti S, Amori G (2007) Beyond threatened species and reintroduction: establishing priorities for conservation and breeding programmes for European rodents in zoos. Int Zoo Yearb 41:194–202. doi:10.1111/j.1748-1090.2007.00002.x
Hosmer DW, Lemeshow S (2000) Applied logistic regression. Wiley, USA
IUCN (2007a) Elyomys quercinus. In: IUCN 2007 European mammal assessment. http://eceuropaeu/environment/nature/conservation/species/ema/. Accessed 11 May 2007
IUCN (2007b) Glis glis. In: IUCN 2007 European mammal assessment. http://eceuropaeu/environment/nature/conservation/species/ema/. Accessed 11 May 2007
IUCN (2007c) Sciurus vulgaris. In: IUCN 2007 European mammal assessment. http://eceuropaeu/environment/nature/conservation/species/ema/. Accessed 11 May 2007
Jenness J (2003) Identify features within distance id_within_distavx extension for ArcView 3x v 1b. Jenness Enterprises. www.jennessentcom/downloads/id_within_distzip
Jones-Walter LM, Corbet GB (1991) Glis glis. In: Corbet GB, Harris S (eds) The handbook of British mammals. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 264–267
Jurczyszyn M (2001) Reintroduction of the edible dormouse Glis glis in Sierakowski landscape park Poland preliminary results. Trakya Univ J Sci Res 22:111–114
Koper N, Schmiegelow FKA, Merril EH (2007) Residuals cannot distinguish between ecological effects of habitat amount and fragmentation implications for the debate. Landsc Ecol 22:811–820. doi:10.1007/s10980-007-9083-9
Koprowski JL (2005) The response of tree squirrels to fragmentation a review and synthesis. Anim Conserv 8:369–376. doi:10.1017/S1367943005002416
Lambeck RJ (1997) Focal species: a multi-species umbrella for nature conservation. Conserv Biol 11:849–856. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1739.1997.96319.x
Lindenmayer DB, Cunningham RB (1997) Patterns of co-occurrence among arboreal marsupials in the forests of central Victoria southeastern Australia. Austral Ecol 22:340–346. doi:10.1111/j.1442-9993.1997.tb00680.x
Lindenmayer DB, Manning A, Smith PL, McCarthy MA, Possingham HP, Fischer J (2002) The focal species approach and landscape restoration: a critique. Conserv Biol 16:338–345. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1739.2002.00450.x
Lurz PWW, Garson PJ, Wauters LA (1997) Effects of temporal and spatial variation in habitat quality on red squirrel dispersal behaviour. Anim Behav 54:427–435. doi:10.1006/anbe.1996.0486
MacKenzie DI, Nichols JD, Lachman GB, Droege S, Royle JA, Langtimm CA (2002) Estimating site occupancy when detection probability is less than one. Ecology 83:2248–2555
McGarigal K, Cushman S (2002) Comparative evaluation of experimental approaches to the study of habitat fragmentation. Ecol Appl 12:335–345. doi:10.1890/1051-0761(2002)012[0335:CEOEAT]2.0.CO;2
Morris P (1997) The edible dormouse Glis glis. An occasional publication of the Mammal Society, London
Mortelliti A, Boitani L (2008) Inferring red squirrel (Sciurus vulgaris) absence with hair tubes surveys: a sampling protocol. Eur J Wildl Res 54:353–356. doi:10.1007/s10344-007-0135-x
Rangel TFLVB, Diniz-Filho JAF, Bini LM (2006) Towards an integrated computational tool for spatial analysis in macroecology and biogeography. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 15:321–327. doi:10.1111/j.1466-822X.2006.00237.x
Rodriguez A, Andrèn H (2001) A comparison of Eurasian red squirrel distribution in fragmented landscapes. J Appl Ecol 36:649–662. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2664.1999.00426.x
Rodrigues ASL, Brooks TM (2007) Shortcuts for biodiversity conservation planning: the effectiveness of surrogates. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 38:713–737. doi:10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.38.091206.095737
Teerink BJ (1991) Hair of west-European mammals. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Wauters LA, Casale P, Dhondt AA (1994) Space use and dispersal of red squirrels in fragmented habitats. Oikos 69:140–146. doi:10.2307/3545294
Wauters L, Somers L, Dhondt A (1997) Settlement behaviour and population dynamics of reintroduced red squirrels Sciurus vulgaris in a park in Antwerp Belgium. Biol Conserv 82:101–107. doi:10.1016/S0006-3207(97)00007-4
Wikum DA, Shanholtzer GF (1978) Application of the Braun–Blanquet cover-abundance scale for vegetation analysis in land development studies. Environ Manage 2:323–329. doi:10.1007/BF01866672
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Cristina Cervone and Marco Negretto for help with fieldwork; this project was financed by the Province of Siena “Ufficio Risorse Faunistiche e Riserve Naturali”. Thanks to Joyce Keep for language revision.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix 1
Appendix 1
Summary of the distribution of three arboreal rodents species (M. avellanarius, G. glis and S. vulgaris) in the sampled sites in the province of Siena central Italy
Patch ID | Nestboxes | Hair tubes | Hectares | Proximity index (1,000 m) | Pn_factor | M. avellanarius | G. glis | S. vulgaris (2nd year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | 2 | 1 | 0.48 | 0.12 | −0.45 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
2 | 1 | 1 | 0.41 | 0.23 | −0.41 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
3 | 2 | 2 | 1.38 | 0.24 | −0.31 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
4 | 2 | 2 | 1.32 | 0.01 | −0.58 | 0 | n/a | 0 |
5 | 2 | 0 | 0.85 | 0.58 | −0.33 | 0 | n/a | n/a |
6 | 2 | 3 | 1.15 | 0.51 | −0.25 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
7 | 3 | 2 | 1.80 | 0.21 | −0.29 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
8 | 3 | 1 | 2.20 | 0.01 | −0.52 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
9 | 2 | 2 | 2.24 | 0.00 | −0.59 | 0 | n/a | 0 |
10 | 2 | 2 | 2.22 | 0.14 | −0.33 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
11 | 2 | 3 | 2.15 | 0.36 | −0.30 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
12 | 3 | 3 | 4.51 | 0.14 | −0.28 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
13 | 5 | 3 | 3.86 | 0.15 | −0.27 | 0 | n/a | 1 |
14 | 5 | 3 | 5.09 | 0.15 | −0.28 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
15 | 5 | 3 | 6.37 | 0.02 | −0.34 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
16 | 7 | 3 | 8.59 | 0.25 | −0.15 | 1 | n/a | 0 |
17 | 4 | 4 | 8.17 | 0.08 | −0.27 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
18 | 8 | 10 | 15.65 | 0.91 | −0.04 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
19 | 8 | 14 | 14.79 | 0.94 | −0.05 | 1 | n/a | 1 |
20 | 10 | 14 | 20.85 | 1.28 | −0.01 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
21 | 15 | 15 | 27.27 | 0.13 | −0.10 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
22 | 16 | 17 | 65.56 | 29.22 | 0.61 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
23 | 14 | 15 | 79.86 | 0.21 | −0.01 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
24 | * | 20 | 30,000 | 30.00 | 3.33 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
25 | 0 | 2 | 1.07 | 0.05 | −0.46 | n/a | n/a | 0 |
26 | 0 | 2 | 1.39 | 0.00 | −0.63 | n/a | 0 | 1 |
27 | 3 | 0 | 2.43 | 0.11 | −0.33 | 0 | n/a | n/a |
28 | 3 | 3 | 3.00 | 0.06 | −0.38 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
29 | 4 | 0 | 4.43 | 0.30 | −0.21 | 0 | 0 | n/a |
30 | * | 0 | 101.72 | 2.44 | 0.13 | 1 | 0 | n/a |
31 | 19 | * | 8,000 | 30.00 | 3.22 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
32 | 20 | * | 27,500 | 30.00 | 3.32 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mortelliti, A., Santulli Sanzo, G. & Boitani, L. Species’ surrogacy for conservation planning: caveats from comparing the response of three arboreal rodents to habitat loss and fragmentation. Biodivers Conserv 18, 1131–1145 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-008-9477-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-008-9477-2