Abstract
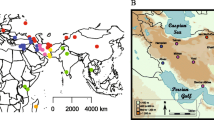
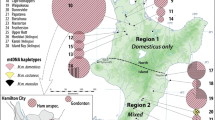
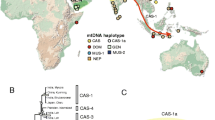
The expansion of Mus musculus domesticus from its origin has been studied in detail. The colonization routes and times depended on its commensal habits which favoured a rapid and recent dispersal, making it difficult to unravel the expansion pattern. The situation is still obscure in the central Mediterranean area. Mitochondrial D-loop was sequenced for 65 mice from the Aeolian Archipelago and the sixteen haplotypes identified were compared with the 528 available mouse haplotypes. The central Mediterranean phylogeography, the demographic history of the Aeolian mice and the relationships between mtDNA and karyotypes was investigate. Five lineages are present, belonging to five of the haplogroups previously described for the Mediterranean basin, and most individuals fall within the European haplogroups. The Archipelago was subjected to multiple colonizations and chromosomal and molecular data agree in indicating Sicily and Italy as possible sources of colonization in recent times. Nevertheless, the signatures of earlier colonizations might have been lost through extinction and admixing of mice due to human movements. Drastic events during the entire colonization process have led to the present-day random distribution of haplotypes. Furthermore, Salina emerges as an ancestral condition and no relation between karyotype composition and haplotype variability was highlighted.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auffray JC, Tchernov E, Nevo E (1988) Origine du commensalisme de la souris domestique Mus musculus domesticus vis-à-vis de l’homme. Comptes Rendus de l’Académie des Sciences de Paris 307:517–522
Berry RJ, Scriven PN (2005) The house mouse: a model and motor for evolutionary. Biol J Linn Soc 84:335–347
Bibb MJ, Van Etten RA, Wright CT, Walberg MW, Clayton DA (1981) Sequence and gene organization of mouse mitochondrial DNA. Cell 26:167–180
Bonhomme F, Orth A, Cucchi T, Rajabi-Maham H, Catalan J, Boursot P, Auffray JC, Britton-Davidian J (2011) Genetic differentiation of the house mouse around the Mediterranean basin: matrilineal footprints of early and late colonization. Proc R Soc B 278(1708):1034–1043
Boursot P, Din W, Anand R, Darviche D, Dod B, von Deimling F, Talwar GP, Bonhomme F (1996) Origin and radiation of the house mouse: mitochondrial DNA phylogeny. J Evol Biol 9:391–415
Britton-Davidian J, Nadeau JH, Croset H, Thaler L (1989) Genic differentiation and origin of Robertsonian populations of the house mouse (Mus musculus domesticus Rutty). Genet Res 53:29–44
Britton-Davidian J, Catalan J, Lopez J, Ganem G, Nunes C, Ramalhinho MG, Auffray JC, Searle JB, Mathias ML (2007) Patterns of genic diversity and structure in a species undergoing rapid chromosomal radiation: an allozyme analysis of house mice from the Madeira archipelago. Heredity 99:432–442
Burt G, Hauffe HC, Searle JB (2009) New metacentric population of the house mouse (Mus musculus domesticus) found in Valchiavenna, Northern Italy. Cytogenet Genome Res 12:260–265
Castiglia R, Annesi F, Capanna E (2005) Geographical pattern of genetic variation in the Robertsonian system of Mus musculus domesticus in central Italy. Biol J Linn Soc 84:395–405
Chesser RK, Baker RJ (1986) On factors affecting the fixation of chromosomal rearrangements and neutral genes: computer simulations. Evolution 40:625
Clement M, Posada D, Crandall KA (2000) TCS: a computer program to estimate gene genealogies. Mol Ecol 9:1657–1660
Cucchi T, Vigne JD, Auffray JC, Croft P, Peltenburg E (2002) Introduction involontaire de la souris domestique (Mus musculus domesticus) à Chypre dès le Néolithique précéramique ancien (fin IXe et VIIIe millénaires av J-C). C R Palevol 1:235–241
Cucchi T, Vigne JD, Auffray JC (2005) First occurrence of the house mouse (Mus musculus domesticus Schwarz and Schwarz, 1943) in the Western Mediterranean: a zooarchaeological revision of subfossil occurrences. Biol J Linn Soc 84:429–445
Excoffier L, Lischer HEL (2010) Arlequin suite v3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol Ecol Resour 10:564–567
Excoffier L, Smouse PE, Quattro JM (1992) Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among DNA haplotypes: application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data. Genetics 131:479–491
Förster DW, Gündüz I, Nunes AC, Gabriel S, Ramalhinho MG, Mathias ML, Britton-Davidian J, Searle JB (2009) Molecular insights into the colonization and chromosomal diversification of Madeiran house mice. Mol Ecol 18:4477–4494
Fu YX (1997) Statistical tests of neutrality of mutations against population growth, hitchhiking and background selection. Genetics 147:915–925
Gabriel S, Jóhannesdóttir F, Jones EP, Searle JB (2010) Colonization, mouse-style. BMC Biol 8:131
Gündüz I, Tez C, Malikov V, Vaziri A, Polyakov V, Searle JB (2000) Mitochondrial DNA and chromosomal studies of wild mice (Mus) from Turkey and Iran. Heredity 84:458–467
Gündüz I, Auffray JC, Britton-Davidian J, Catalan J, Ganem G, Ramalhinho MG, Mathias ML, Searle JB (2001) Molecular studies on the colonization of the Madeiran archipelago by house mice. Mol Ecol 10:2023–2029
Gündüz İ, Rambau RV, Tez C, Searle JB (2005) Mitochondrial DNA variation in the western house mouse (Mus musculus domesticus) close to its site of origin: studies in Turkey. Biol J Linn Soc 84:473–485
Hardouin EA, Chapuis JL, Stevens MI, van Vuuren JB, Quillfeldt P, Scavetta RJ, Teschke M, Tautz D (2010) House mouse colonization patterns on the sub-Antarctic Kerguelen Archipelago suggest singular primary invasions and resilience against re-invasion. BMC Evol Biol 10:325
Ho SYW, Phillips MJ, Cooper A, Drummond AJ (2005) Time dependency of molecular rate estimates and systematic overestimation of recent divergence times. Mol Biol Evol 22:1561–1568
Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F (2001) MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 17:754–755
Huson DH, Bryant D (2006) Application of phylogenetic networks in evolutionary studies. Mol Biol Evol 23:254–267
Jones EP, Van Der Kooij J, Solheim R, Searle JB (2010) Norwegian house mice (Mus musculus musculus/domesticus): distributions, routes of colonization and patterns of hybridization. Mol Ecol 19:5252–5264
Librado P, Rozas J (2009) DnaSP v. 5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 25:1451–1452
Nachman MW, Boyer SN, Searle JB, Aquadro CF (1994) Mitochondrial DNA variation and the evolution of Robertsonian chromosomal races of house mice, Mus domesticus. Genetics 136:1105–1120
Nylander JAA (2004) MrModeltest v2. Evolutionary Biology Center, Uppsala University, Uppsala
Piálek J, Hauffe HC, Searle JB (2005) Chromosomal variation in the house mouse. Biol J Linn Soc 84:535–563
Prager EM, Sage RD, Gyllensten U, Thomas WK, Hübner R, Jones CS, Noble L, Searle JB, Wilson AC (1993) Mitochondrial DNA sequence diversity and the colonization of Scandinavia by house mice from East Holstein. Biol J Linn Soc 50:85–122
Prager EM, Orrego C, Sage RD (1998) Genetic variation and phylogeography of central Asian and other house mice, including a major new mitochondrial lineage in Yemen. Genetics 150:835–861
Rajabi-Maham H, Orth A, Bonhomme F (2008) Phylogeography and postglacial expansion of Mus musculus domesticus inferred from mitochondrial DNA coalescent, from Iran to Europe. Mol Ecol 17:627–641
Ramos-Onsins SE, Rozas J (2002) Statistical properties of new neutrality tests against population growth. Mol Biol Evol 19:2092–2100
Riginos C, Nachman MW (1999) The origin of a Robertsonian chromosomal translocation in house mice inferred from linked microsatellite markers. Mol Biol Evol 16:1763–1773
Rogers A (1995) Genetic evidence for a Pleistocene population explosion. Evolution 49:608–615
Sage RD, Atchley WR, Capanna E (1993) House mice as models in systematic biology. Syst Biol 42:523–561
Schneider S, Excoffier L (1999) Estimation of demographic parameters from the distribution of pairwise differences when the mutation rates vary among sites: application to human mitochondrial DNA. Genetics 152:1079–1089
Searle JB, Jones CS, Gündüz I, Scascitelli M, Jones EP, Herman JS, Rambau RV, Noble LR, Berry RJ, Giménez MD, Jóhannesdóttir F (2009) Of mice and (Viking?) men: phylogeography of British and Irish house mice. Proc R Soc B 276:201–207
Solano E, Castiglia R, Corti M (2007) A new chromosomal race of the house mouse, Mus musculus domesticus, in the Vulcano Island—Aeolian Archipelago, Italy. Hereditas 144:75–77
Solano E, Castiglia R, Capanna E (2009) Chromosomal evolution of the house mouse, Mus musculus domesticus, in the Aeolian Archipelago (Sicily, Italy). Biol J Linn Soc 96:194–202
Tajima F (1989) The effect of change in population size on DNA polymorphism. Genetics 123:597–601
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The ClustalX windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 24:4876–4882
Tryfonopoulos GA, Chondropoulos BP, Fraguedakis-Tsolis SE (2005) The genus Mus as a model for evolutionary studies Mitochondrial DNA polymorphisms of the house mouse Mus musculus domesticus from Greece, focusing on the Robertsonian chromosomal system of north-west Peloponnese. Biol J Linn Soc 84:643–651
Valenzuela-Lamas S, Baylac M, Cucchi T, Vigne J (2011) House mouse dispersal in Iron Age Spain: a geometric morphometrics appraisal. Biol J Linn Soc 102:483–497
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thanks Giovanni Amori and Mauro Cristaldi that gently provide the samples of mice new to this study from outside the archipelago. Thanks are extended to Flavia Annesi for the helpful support in the lab work and to the two referees that provide helpful comments. E.S. research project was supported by the PhD funds (‘Sapienza’ Universita` di Roma).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Solano, E., Franchini, P., Colangelo, P. et al. Multiple origins of the western European house mouse in the Aeolian Archipelago: clues from mtDNA and chromosomes. Biol Invasions 15, 729–739 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-012-0322-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-012-0322-x