Abstract
Objectives
This study aimed to discuss the essential amino acid residues and catalytic mechanism of trans-epoxysuccinate hydrolase from Pseudomonas koreensis for the production of meso-tartaric acid.
Results
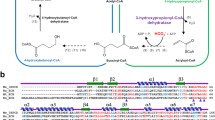
The optimum conditions of the enzyme were 45 °C and pH 9.0, respectively. It was strongly inhibited by Zn2+, Mn2+ and SDS. Michaelis–Menten enzyme kinetics analysis gave a Km value of 3.50 mM and a kcat of 99.75 s−1, with an exceptional EE value exceeding 99.9%. Multiple sequence alignment and homology modeling revealed that the enzyme belonged to MhpC superfamily and possessed a typical α/β hydrolase folding structure. Site-directed mutagenesis indicated H34, D104, R105, R108, D128, Y147, H149, W150, Y211, and H272 were important catalytic residues. The 18O-labeling study suggested the enzyme acted via two-step catalytic mechanism.
Conclusions
The structure and catalytic mechanism of trans-epoxysuccinate hydrolase were first reported. Ten residues were critical for its catalysis and a two-step mechanism by an Asp-His-Asp catalytic triad was proposed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen RH, Jakoby WB (1969) Tartaric acid metabolism. IX. Synthesis with tartrate epoxidase. J Biol Chem 244(8):2078–2084. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0021-9258(18)94369-3
Amrein BA, Bauer P, Duarte F, Carlsson ÅJ, Naworyta A, Mowbray SL, Widersten M, Kamerlin SCL (2015) Expanding the catalytic triad in epoxide hydrolases and related enzymes. ACS Catal 5(10):5702–5713. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.5b01639
Bahl CD, Madden DR (2012) Pseudomonas aeruginosa Cif defines a distinct class of α/β epoxide hydrolases utilizing a His/Tyr ring-opening pair. Protein Pept Lett 19(2):186–193. https://doi.org/10.2174/092986612799080392
Bahl CD, Morisseau C, Bomberger JM, Stanton BA, Hammock BD, O’Toole GA, Madden DR (2010) Crystal structure of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator inhibitory factor Cif reveals novel active-site features of an epoxide hydrolase virulence factor. J Bacteriol 192(7):1785–1795. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.01348-09
Bahl CD, Hvorecny KL, Morisseau C, Gerber SA, Madden DR (2016) Visualizing the mechanism of epoxide hydrolysis by the bacterial virulence enzyme Cif. Biochemistry 55(5):788–797. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.5b01229
Bao W, Pan H, Zhang Z, Cheng Y, Xie Z, Zhang J, Li Y (2013) Analysis of essential amino acid residues for catalytic activity of cis-epoxysuccinate hydrolase from Bordetella sp. BK-52. Appl Microbiol Biot 98:1641–1649. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5019-2
Bao W, Liao H, Chen Y, Huang Q, Huang W, Fang R, Liu S (2020) Isolation of a novel strain Aspergillus niger WH-2 for production of L(+)-tartaric acid under acidic condition. Biotechnol Lett 42:605–612. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-020-02799-z
Bitew MA, Wawegama NK, Newton HJ, Sansom FM (2019) Meso-tartrate inhibits intracellular replication of Coxiella burnetii, the causative agent of the zoonotic disease Q fever. Pathog Dis 77(8):ftz066. https://doi.org/10.1093/femspd/ftz066
Chan PWY, Yakunin AF, Edwards EA, Pai EF (2011) Mapping the reaction coordinates of enzymatic defluorination. J Am Chem Soc 133(19):7461–7468. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja200277d
Cheng Y, Wang L, Pan H, Bao W, Sun W, Xie Z, Zhang J, Zhao Y (2014) Purification and characterization of a novel cis-epoxysuccinate hydrolase from Klebsiella sp. that produces L(+)-tartaric acid. Biotechnol Lett 36:2325–2330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1614-2
Dong S, Liu X, Cui G, Cui Q, Wang X, Feng Y (2018) Structural insight into the catalytic mechanism of a cis-epoxysuccinate hydrolase producing enantiomerically pure D(-)-tartaric acid. Chem Commun 54(61):8482–8485. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8cc04398a
Dong S, Xuan J, Feng Y, Cui Q (2024) Deciphering the stereo-specific catalytic mechanisms of cis-epoxysuccinate hydrolases producing L(+)-tartaric acid. J Biol Chem 300(2):105635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2024.105635
Dutta S, Gellman AJ (2017) Enantiomer surface chemistry: conglomerate versus racemate formation on surfaces. Chem Soc Rev 46(24):7787–7839. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7cs00555e
Foster JW (1960) Microbiological preparation of meso-tartaric acid. US Patent 2947665
Heikinheimo P, Goldman A, Jeffries C, Ollis DL (1999) Of barn owls and bankers: a lush variety of alpha/beta hydrolases. Structure 7(6):R141–R146. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(99)80079-3
Khusnutdinova AN, Batyrova KA, Brown G, Fedorchuk T, Chai YS, Skarina T, Flick R, Petit AP, Savchenko A, Stogios P, Yakunin AF (2023) Structural insights into hydrolytic defluorination of difluoroacetate by microbial fluoroacetate dehalogenases. FEBS J 290(20):4966–4983. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.16903
Li F, Kong X, Chen Q, Zheng Y, Xu Q, Chen F, Fan L, Lin G, Zhou J, Yu H, Xu J (2018) Regioselectivity engineering of epoxide hydrolase: near-perfect enantioconvergence through a single site mutation. ACS Catal 8:8314–8317. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.8b02622
Loo B, Kingma J, Arand M, Wubbolts MG, Janssen DB (2006) Diversity and biocatalytic potential of epoxide hydrolases identified by genome analysis. Appl Environ Microb 72(4):2905–2917. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.72.4.2905-2917.2006
Martin WR, Foster JW (1955) Production of trans-epoxysyccinic acid by fungi and its microbiological conversion to meso-tartaric acid. J Bacteriol 70(4):405–414. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.70.4.405-414.1955
Mitusinska K, Wojsa P, Bzowka M, Raczynska A, Bagrowska W, Samol A, Kapica P, Gora A (2022) Structure-function relationship between soluble epoxide hydrolases structure and their tunnel network. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 20:193–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csbj.2021.10.042
Mowbray SL, Elfstrom LT, Ahlgren KM, Andersson CE, Widersten M (2006) X-ray structure of potato epoxide hydrolase sheds light on substrate specificity in plant enzymes. Protein Sci 15(7):1628–1637. https://doi.org/10.1110/ps.051792106
Nardini M, Ridder IS, Rozeboom HJ, Kalk KH, Rink R, Janssen DB, Dijkstra BW (1999) The X-ray structure of epoxide hydrolase from Agrobacterium radiobacter AD1: an enzyme to detoxify harmful epoxides. J Biol Chem 274(21):14579–14586. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.21.14579
Novak HR, Sayer C, Isupov MN, Paszkiewicz K, Gotz D, Spragg AM, Littlechild JA (2013) Marine Rhodobacteraceae L-haloacid dehalogenase contains a novel His/Glu dyad that could activate the catalytic water. FEBS J 280(7):1664–1680. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.12177
Pan H, Xie Z, Bao W, Cheng Y, Zhang J, Li Y (2011) Site-directed mutagenesis of epoxide hydrolase to probe catalytic amino acid residues and reaction mechanism. FEBS Lett 585(15):2545–2550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2011.07.006
Schuiten ED, Badenhorst CPS, Palm GJ, Berndt L, Lammers M, Mican J, Bednar D, Damborsky J, Bornscheuer UT (2021) Promiscuous dehalogenase activity of the epoxide hydrolase CorEH from Corynebacterium sp. C12. ACS Catal 11(10):6113–6120. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.1c00851
Varga G, Docsa T, Gergely P, Juhász L, Somsák L (2013) Synthesis of tartaric acid analogues of FR258900 and their evaluation as glycogen phosphorylase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 23(6):1789–1792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.01.042
Vasu V, Kumaresan J, Babu MG, Meenakshisundaram S (2012) Active site analysis of cis-epoxysuccinate hydrolase from Nocardia tartaricans using homology modeling and site-directed mutagenesis. Appl Microbiol Biot 93:2377–2386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3548-0
Wang Z, Wang Y, Su Z (2012) Purification and characterization of a cis-epoxysuccinic acid hydrolase from Nocardia tartaricans CAS-52, and expression in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biot 97:2433–2441. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4102-4
Wang JB, Ilie A, Yuan S, Reetz MT (2017) Investigating substrate scope and enantioselectivity of a defluorinase by a stereochemical probe. J Am Chem Soc 139(32):11241–11247. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.7b06019
Xuan J, Feng Y (2019) Enantiomeric tartaric acid production using cis-Epoxysuccinate hydrolase: history and perspectives. Molecules 24(5):903–914. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050903
Yamada T, Morisseau C, Maxwell JE, Argiriadi MA, Christianson DW, Hammock BD (2000) Biochemical evidence for the involvement of tyrosine in epoxide activation during the catalytic cycle of epoxide hydrolase. J Biol Chem 275(30):23082–23088. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M001464200
Zhang Z (2015) Isolation and heterologous expression of trans-epoxysuccinate hydrolase. Dissertation, Zhejiang University
Zhang J, Xie Z, Zhang Z, Pan H, Bao W (2016) The method for preparing meso-tartaric acid or its salt by Pseudomonas koreensis. Chinese Patent 103923866A
Zhang H, Tian S, Yue Y, Li M, Tong W, Xu G, Chen B, Ma M, Li Y, Wang J (2020a) Semirational design of fluoroacetate dehalogenase RPA1163 for kinetic resolution of α-fluorocarboxylic acids on a gram scale. ACS Catal 10(5):3143–3151. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.9b04804
Zhang L, De BC, Zhang W, Mandi A, Fang Z, Yang C, Zhu Y, Kurtan T, Zhang C (2020b) Mutation of an atypical oxirane oxyanion hole improves regioselectivity of the alpha/beta-fold epoxide hydrolase Alp1U. J Biol Chem 295(50):16987–16997. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA120.015563
Funding
This study was funded by the Huzhou Scientific and Technological Project (2022GZ56) and the Education of Zhejiang Province of China (Y202248484).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WNB and HFP contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by HXL, JFY and RLZ. The first draft of the manuscript was written by HXL and all authors commented on previous version of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, H., Pan, H., Yao, J. et al. Essential amino acid residues and catalytic mechanism of trans-epoxysuccinate hydrolase for production of meso-tartaric acid. Biotechnol Lett (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-024-03490-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-024-03490-3