Abstract
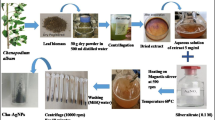
Aqueous black carpenter ant extract (ABCAE) was used to synthesize silver nanoparticles (AgNPs). The ABCAE was rich in water-soluble compounds such as hydrophilic polypeptides that behaved as both reducing and stabilizing agents for generating AgNPs from Ag+ ion precursors. The diameter of the observed AgNPs was mostly in the range of 20–60 nm. The AgNPs were tested as an antibacterial agent for the growth inhibition of two pathogenic bacteria (Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853, Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 27661) and one common bacteria (Escherichia coli K12 ATCC 10798). Disk diffusion test showed that the AgNPs selectively inhibited the growth of P. aeruginosa but not for the other two species, suggesting the potential application of the green-chemically synthesized AgNPs as a selective antibacterial agent without harming other beneficial bacteria.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
References
Abulude FO, Fagbayide SD (2017) Biochemical compositions of black carpenter ant, Camponotus pennsylvanicus (Hymenoptedra : Formicidae). Jahangirnagar Univ J Biol Sci 6:59–62. https://doi.org/10.3329/jujbs.v6i1.33732
Ahmed S, Ahmad M, Swami BL, Ikram S (2016) A review on plants extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications: a green expertise. J Adv Res 7:17–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2015.02.007
Cannon CA (1998) Nutritional ecology of the carpenter ant Camponotus pennsylvanicus (De Geer): macronutrient preference and particle consumption (Doctoral dissertation, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University). https://vtechworks.lib.vt.edu/bitstream/handle/10919/29447/Dissertation-etd.PDF?sequence=1
Cavallo JD, Hocquet D, Plesiat P, Fabre R, Roussel-Delvallez M, GERPA (Grouped’Etude de laRésistance de Pseudomonas aeruginosa auxantibiotiques) (2007) Susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to antimicrobials: a 2004 French multicentre hospital study. J Antimicrob Chemother 59:1021–1024. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkm076
CDC (2022) The biggest antibiotic-resistant threats in the US. In: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/biggest-threats.html. Accessed 4 Feb 2023
Chen T, Öçsoy I, Yuan Q, Wang R, You M, Zhao Z, Song E, Zhang X, Tan W (2012) One-step facile surface engineering of hydrophobic nanocrystals with designer molecular recognition. J Am Chem Soc 134:13164–13167. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja304115q
Chu JY, Espiritu RA (2022) Denatured crude protein extracts from the sea anemone Entacmaea quadricolor as capping agents for silver nanoclusters. Asian J Chem 34:740–744. https://doi.org/10.14233/ajchem.2022.23524
Demirbas A, Welt BA, Ocsoy I (2016) Biosynthesis of red cabbage extract directed Ag NPs and their effect on the loss of antioxidant activity. Mater Lett 179:20–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2016.05.056
Dogru E, Demirbas A, Altinsoy B, Duman F, Ocsoy I (2017) Formation of Matricaria chamomilla extract-incorporated Ag nanoparticles and size-dependent enhanced antimicrobial property. J Photochem Photobiol B 174:78–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2017.07.024
Ekrikaya S, Yilmaz E, Celik C, Demirbuga S, Ildiz N, Demirbas A, Ocsoy I (2021) Investigation of ellagic acid rich-berry extracts directed silver nanoparticles synthesis and their antimicrobial properties with potential mechanisms towards Enterococcus faecalis and Candida albicans. J Biotechnol 341:155–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2021.09.020
Feldhaar H, Straka J, Krischke M, Berthold K, Stoll S, Mueller MJ, Gross R (2007) Nutritional upgrading for omnivorous carpenter ants by the endosymbiont Blochmannia. BMC Biol 5:48. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7007-5-48
Ford MB, Mende K, Kaiser SJ, Beckius ML, Lu D, Stam J, Li P, Stewart L, Tribble DR, Blyth DM (2022) Clinical characteristics and resistance patterns of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from combat casualties. Mil Med 187:426–434. https://doi.org/10.1093/milmed/usab259
Gao J, Qu R, Tang B, Wang C, Ma Q, Sun C (2011) Control of the aggregation behavior of silver nanoparticles in polyurethane matrix. J Nanopart Res 13:5289–5299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-011-0515-8
Gul A, Fozia SA, Ahmad I, Khattak B, Ahmad M, Ullah R, Bari A, Ali SS, Alobaid A, Asmari MM, Mahmood HM (2021) Green synthesis, characterization, enzyme inhibition, antimicrobial potential, and cytotoxic activity of plant mediated silver nanoparticle using Ricinus communis leaf and root extracts. Biomolecules 11:206. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11020206
Hansen LD, Klotz JH (2005) Carpenter ants of the United States and Canada. Comstock Publishing Associates, Ithaca
He X, Gao L, Ma N (2013) One-step instant synthesis of protein-conjugated quantum dots at room temperature. Sci Rep 3:2825. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep02825
Jaiswal S, Duffy B, Jaiswal AK, Stobie N, McHale P (2010) Enhancement of the antibacterial properties of silver nanoparticles using β-cyclodextrin as a capping agent. Int J Antimicrob Agents 36:280–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2010.05.006
Klimchitskaya GL, Mostepanenko VM, Velichko EN (2020) Effect of increased stability of peptide-based coatings in the Casimir regime via nanoparticle doping. arXiv [cond-mat.mes-hall] https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.102.161405
Kumar M, Tomar M, Potkule J, Verma R, Punia S, Mahapatra A, Belwal T, Dahuja A, Joshi S, Berwal MK, Satankar V, Bhoite AG, Amarowicz R, Kaur C, Kennedy JF (2021) Advances in the plant protein extraction: mechanism and recommendations. Food Hydrocoll 115:106595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.106595
Laity PR, Gilks SE, Holland C (2015) Rheological behaviour of native silk feedstocks. Polymer (Guildf) 67:28–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2015.04.049
Leng Y, Fu L, Ye L, Li B, Xu X, Xing X, He J, Song Y, Leng C, Guo Y, Ji X, Lu Z (2016) Protein-directed synthesis of highly monodispersed, spherical gold nanoparticles and their applications in multidimensional sensing. Sci Rep 6:28900. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep28900
Moretti CL, Mattos LM, Calbo AG, Sargent SA (2010) Climate changes and potential impacts on postharvest quality of fruit and vegetable crops: a review. Food Res Int 43:1824–1832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2009.10.013
Muhle SA, Tam JP (2001) Design of Gram-negative selective antimicrobial peptides. Biochemistry 40:5777–5785. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi0100384
Nam KT, Lee YJ, Krauland EM, Kottmann ST, Belcher AM (2008) Peptide-mediated reduction of silver ions on engineered biological scaffolds. ACS Nano 2:1480–1486. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn800018n
Ocsoy I, Paret ML, Ocsoy MA, Kunwar S, Chen T, You M, Tan W (2013) Nanotechnology in plant disease management: DNA-directed silver nanoparticles on graphene oxide as an antibacterial against Xanthomonas perforans. ACS Nano 7:8972–8980. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn4034794
Oliveira RN, Mancini MC, de Oliveira FCS, Passos TM, Quilty B, da Thiré RMSM, McGuinness GB (2016) FTIR analysis and quantification of phenols and flavonoids of five commercially available plants extracts used in wound healing. Matér (Rio Jan) 21:767–779. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-707620160003.0072
Paramelle D, Sadovoy A, Gorelik S, Free P, Hobley J, Fernig DG (2014) A rapid method to estimate the concentration of citrate capped silver nanoparticles from UV–visible light spectra. Analyst 139:4855–4861. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4AN00978A
Schultheiss P, Nooten SS, Wang R, Wong MKL, Brassard F, Guénard B (2022) The abundance, biomass, and distribution of ants on Earth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 119:e2201550119. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2201550119
Şeker Karatoprak G, Aydin G, Altinsoy B, Altinkaynak C, Koşar M, Ocsoy I (2017) The effect of Pelargonium endlicherianum Fenzl. root extracts on formation of nanoparticles and their antimicrobial activities. Enzyme Microb Technol 97:21–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2016.10.019
Sharma S (2006) How to build an ant farm. In: wikiHow. https://www.wikihow.com/Build-an-Ant-Farm. Accessed 19 Apr 2023
Some S, Bulut O, Biswas K, Kumar A, Roy A, Sen IK, Mandal A, Franco OL, İnce İA, Neog K, Das S, Pradhan S, Dutta S, Bhattacharjya D, Saha S, Das Mohapatra PK, Bhuimali A, Unni BG, Kati A, Mandal AK, Yilmaz MD, Ocsoy I (2019) Effect of feed supplementation with biosynthesized silver nanoparticles using leaf extract of Morus indica L. V1 on Bombyx mori L. (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae). Sci Rep 9:14839. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-50906-6
Some S, Sarkar B, Biswas K, Jana TK, Bhattacharjya D, Dam P, Mondal R, Kumar A, Deb AK, Sadat A, Saha S, Kati A, Ocsoy I, Franco OL, Mandal A, Mandal S, Mandal AK, İnce İA (2020) Bio-molecule functionalized rapid one-pot green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their efficacy toward the multidrug resistant (MDR) gut bacteria of silkworms (Bombyx mori). RSC Adv 10:22742–22757. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA03451G
Song JY, Kim BS (2009) Rapid biological synthesis of silver nanoparticles using plant leaf extracts. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 32:79–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-008-0224-6
Strayer A, Ocsoy I, Tan W, Jones JB, Paret ML (2016) Low concentrations of a silver-based nanocomposite to manage bacterial spot of tomato in the greenhouse. Plant Dis 100:1460–1465. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-05-15-0580-RE
Upert G, Luther A, Obrecht D, Ermert P (2021) Emerging peptide antibiotics with therapeutic potential. Med Drug Discov 9:100078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100078
Vollath D, Fischer FD, Holec D (2018) Surface energy of nanoparticles—influence of particle size and structure. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 9:2265–2276. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.9.211
Wang J, Zhang Y, Jin N, Mao C, Yang M (2019) Protein-induced gold nanoparticle assembly for improving the photothermal effect in cancer therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:11136–11143. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b21488
Widdatallah MO, Mohamed AA, Alrasheid AA, Widatallah HA, Yassin LF, Eltilib SH, Ahmed SAR (2020) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Nigella sativa seeds and evaluation of their antibacterial activity. Adv Nanopart 09:41–48. https://doi.org/10.4236/anp.2020.92003
Zhu WL, Lan H, Park I-S, Kim JI, Jin HZ, Hahm K-S, Shin SY (2006) Design and mechanism of action of a novel bacteria-selective antimicrobial peptide from the cell-penetrating peptide Pep-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 349:769–774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.08.094
Acknowledgements
This work was performed under financial assistance from Southeastern Louisiana University, Troy University, and award 70NANB18H289 from U.S. Department of Commerce, National Institute of Standards and Technology. We also appreciate the TEM and SEM/EDS imaging assistance from Dr. Dongmei Cao at Louisiana State University.
Funding
This work was performed under main financial assistance from Southeastern Louisiana University, Troy University, and partial support from award 70NANB18H289 from U.S. Department of Commerce, National Institute of Standards and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JC and SL equally contributed to design and perform the experiments together and wrote the manuscript as co-authors. PW and JP helped in conducting experiments. DC helped in providing mathematical work for research. RE helped in preparing experiments, collecting initial research data and sample donations. JC, SL, JP and PW reviewed the manuscript. JC supervised the project as a corresponding author.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests. The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Research involving humans and animals statement
No Human (or human cell sample) has been used in this research. No vertebrate animals are used in this research.
Informed consent
No human participant is involved in this research.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, J.L., Liu, S., Wang, P. et al. Silver nanoparticles induced with aqueous black carpenter ant extract selectively inhibit the growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biotechnol Lett 45, 811–821 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-023-03386-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-023-03386-8