Abstract
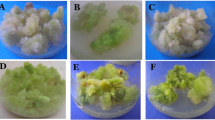
Finger millet [Eleusine coracana (L.) Gaertn.] is an important cereal because of its mineral-nutrition value. With the increasing demand, there is a pressing need to conserve it through biotechnological approaches. High-frequency somatic embryogenesis from seed-derived callus of E. coracana was developed on Murashige–Skoog (MS) medium supplemented with a combination of auxins [Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), 2,4-Dichlorophenoxy acetic acid (2,4-D)] and cytokinins [6-Benzylaminopurine (BAP), kinetin (KN)] in different concentrations, ranging from 0.1 to 5.0 mg L−1. Seeds cultured on this medium produced three different types of primary callus. Type I callus was very compact and dark brown, type II callus was light brownish and type III callus appeared whitish and light brown. All three types of calli had differential proliferation responses. Type II compact brown calli were obtained on the MS medium supplemented with 1.0 and 1.5 mg 2,4-Dichlorophenoxy acetic acid L−1 and 0.5 mg kinetin L−1. Friable yellowish embryogenic calli with a large number of somatic embryos were developed within 60 days after being transferred to auxins and cytokinin (1.0 and 1.5 mg 2,4-Dichlorophenoxy acetic acid L−1 and 0.5 mg Kinetin L−1) along with 200 mg casein hydrolysate L−1. Germination of somatic embryos on a half-strength MS medium supplemented with 0.1% Kinetin led to the development of healthy plantlets within 30 days. Genetic fingerprinting using random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) revealed high levels of genetic fidelity. The study provides methods and hormonal concentrations required to develop somatic embryos in E. coracana for its genetic improvement and conservation.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data generated and analyzed during this study are included in this article.
Abbreviations
- RAPD:
-
Random amplified polymorphic DNA
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- NAA:
-
1-Naphthalene acetic acid
- IAA:
-
Indole-3-acetic acid
- BAP:
-
6-Benzylaminopurine
- KN:
-
Kinetin
- CH:
-
Casein hydrolysate
- Glu:
-
Glutamine
- TDZ:
-
Thidiazuron
- EtBr:
-
Ethidium bromide
- NaoAc:
-
Sodium acetate
- EDTA:
-
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- CTAB:
-
Cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide
- TAE:
-
Tris–acetate-EDTA
- FAO:
-
Food and Agriculture Organization
- SDS:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate
- MS media:
-
Murashige and Skoog media
References
Ageel S, Elmeer K (2011) Effects of casein hydrolysates and glutamine on callus and somatic embryogenesis of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.). N Y Sci J 4(7):121–125
Arulselvi I, Krishnaveni S (2009) Effect of hormones, explants, and genotypes in vitro culturing of sorghum. J Biochem Technol 1(4):96–103
Chandra D, Chandra S, Sharma AK (2016) Review of Finger millet (Eleusine coracana (L) Gaertn.): a powerhouse of health benefiting nutrients. Food Sci Hum Wellness 5(3):149–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fshw.2016.05.004
Daniel DRHA, Caesar SA, Ramakrishnan M, Duraipandiyan V, Ignacimuthu S, Al-Dhabi NA (2018) Effect of l-glutamine and casein hydrolysate in the development of somatic embryos from cotyledonary leaf explants in okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L. monech)”. S Afr J Bot 114:223–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2017.11.014
Dosad S, Chawla HS (2015) In vitro plant regeneration from mature seeds of finger millet (Eleusine coracana) through somatic embryogenesis. Indian J Plant Physiol 20(4):360–367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40502-015-0191-2
FAO (2018) Future smart food Rediscovering hidden treasures of neglected and underutilized species for Zero Hunger in Asia Executive summary Bangkok, p 36. http://www.fao.org/3/I8907EN/i8907en.pdf
Garcia C, De Almeida AAF, Costa M, Britto D, Valle R, Royaert S, Marelli JP (2019) Abnormalities in somatic embryogenesis caused by 2, 4-D: an overview. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult (PCTOC) 137(2):193–212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-019-01569-8
Goldman JJ, Hanna WW, Fleming G, Ozais-akins P (2003) Fertile transgenic pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum (L.) R.Br.) plants recovered through microprojectile bombardment and phosphinothricin selection of apical meristem-, inflorescence-, and immature embryo-derived embryogenic tissues. Plant Cell Rep 21:999–1009. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-003-0615-8
Joshi BK (2017) Biotechnology for conservation and utilization of agricultural plant genetic resources in Nepal. J Nepal Agric Res Counc 3:49–59. https://doi.org/10.3126/jnarc.v3i1.17276
Khaleda L, Al-Forkan M (2006) Stimulatory effects of casein hydrolysate and proline in vitro callus induction and plant regeneration from five deepwater rice (Oryza sativa L.). Biotechnology 5(3):379–384. https://doi.org/10.3923/biotech.2006.379.384
Kidoido MM, Kasenge V, Mbowa S, Tenywa JS, Nyende P (2002) Socioeconomic factors associated with finger millet production in eastern Uganda. Afr Crop Sci J 10(1):111
Miah G, Rafii MY, Ismail MR, Puteh AB, Rahim HA, Asfaliza R, Latif MA (2013) Blast resistance in rice: a review of conventional breeding to molecular approaches. Mol Biol Rep 40(3):2369–2388. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-2318-0
Mohammed HI, Hamza NB (2018) Genetic diversity analysis of forty pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum (L.)R.Br) accessions from Sudan using agronomical descriptors and DNA molecular markers. Adv Biosci Biotechnol 9(07):322
M’ribu HK, Hilu KW (1994) Detection of interspecific and intraspecific variation in Panicum millets through random amplified polymorphic DNA. Theor Appl Genet 88(3–4):412–416. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00223653
Mukhopadhyay M, Bantawa P, Mondal TK, Nandi SK (2016) Biological and phylogenetic advancements of Gaultheria fragrantissima: economically important oil-bearing medicinal plant. Ind Crops Prod 81:91–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.11.042
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Nandhini RB, Rahul RN, Thilaga S, Rao NSP, Ganesh D (2013) Molecular distinction of C × R hybrid (Coffea congensis× Coffea canephora) from morphologically resembling male parent using rbcL and matK gene sequences. S Afr J Bot 88:334–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2013.08.011
Ngetich A, Mweu C, Ngugi M, Murakami A, Ojuolong H, Mbinda W (2018) Efficient plant regeneration protocol for finger millet [Eleusine coracana (L.) Gaertn] via somatic embryogenesis. Afr J Biotechnol 17(21):660–667. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB2018.16452
Oduori COA (2005) The importance and research status of finger millet in Africa. In: Paper presented at the Mcknight Foundation Collaborative Research Program Workshop on tef and finger millet: comparative genomics of the chloridoid cereals at the Biosciences for east and Central Africa (BECA) ILRI, Nairobi, Kenya, pp 28–30
Oduori COA (2008) Breeding investigations of finger millet characteristics including blast disease and striga resistance in Western Kenya. Dissertation
Pilatti V, Muchut SE, Uberti-Manassero NG, Vegetti AC, Reinheimer R (2018) Diversity, systematics, and evolution of Cynodonteae inflorescences (Chloridoideae–Poaceae). Syst Biodivers 16(3):245–259. https://doi.org/10.1080/14772000.2017.1392371
Rangan TS (1976) Growth and plant regeneration in plant tissue culture of some Indian millets; Paspalum scorbiculatum (L); Eleusine coracana (L.) Gaertn. and Pennisetum typhoideum. Perspflawzen Physiol 78:208–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-328X(73)80003-0
Rani V, Raina SN (2000) Genetic fidelity of organized meristem-derived micro propagated plants: a critical reappraisal. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 36(5):3199–3330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-000-0059-6
Sage RF, Zhu XG (2011) Exploiting the engine of C4 photosynthesis. J Exp Bot 62(9):2989–3000. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/err179
Satish L, Ceasar SA, Shilpha J, Rency AS, Rathinapriya P, Ramesh M (2015) Direct plant regeneration from in vitro-derived shoot apical meristems of finger millet (Eleusine coracana (L.) Gaertn.). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 51:192–200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-015-9672-2
Shingane S, Patil JV, Gomashe S, Chand D (2018) Assessing genetic diversity among Foxtail millet (Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv.) accessions using RAPD and ISSR markers. Int J Bio-Res Stress Manag 9(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.23910/IJBSM/2018.9.1.3C0574
Sood RKS, Prasad M (2020) An efficient Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation method for foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.). Plant Cell Rep 39:511–525. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-019-02507-w
Sood AK, Babu BK, Gaur VS, Pandey D, Kant L, Pattnayak A (2016) Gene discovery and advances in finger millet [Eleusine coracana (L.) Gaertn.] genomics: an important nutri-cereal of future. Front Plant Sci 7:1634. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01634
Thiru AN, Mohan R (1990) Tissue culture studies in ragi (Eleusine coracana(L.)Gaertn. Plant Cell Rep 18:93–96
Vasil IK (1987) Developing cell and tissue culture systems for the improvement of cereal and grass crops. J Plant Physiol 128:193–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0176-1617(87)80234-1
Vijayalakshmi D, Gowda KN, Jamuna KV, Ray BRM, Sajjan JT (2012) Empowerment of self-help group women through value addition of finger millet. J Dairy Foods Home Sci 31:223–226
Wakizukia T, Yamaguchi T (1987) The induction of enlarged apical domes invitro and multiple shoot formation from finger millet Eleusine coracana (L.). Ann Bot 60:331–336. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.aob.a087452
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Gandhi Krishi Vignan Kendra, Bangalore for providing finger millet seed samples of various genotypes. We also acknowledge Jawaharlal Nehru Memorial Fund, New Delhi and Department of Science & Technology, Promotion of University Research and Scientific Excellence (DST-PURSE), New Delhi, and Rashtriya Uchchattar Shiksha Abhiyan (RUSA) Ministry of Human Resource Development, Government of India for their financial support. We thank Dr. Ramu S Vemanna, Regional Centre for Biotechnology for the revision of the research paper.
Funding
This work was supported by Jawaharlal Nehru Memorial Fund, New Delhi (SU-1/124/2018-19/92) and Department of Science & Technology, Promotion of University Research and Scientific Excellence (DST-PURSE), New Delhi for their financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JV set up the experiment, carried out the entire experimental work, and analyzed the data. VR assisted the experiment. TS helped in preparing manuscript draft and interpretation of data. CS and GD (Research Guide) guided in setting up the experiment, data analysis, and manuscript preparation. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Venkatesan, J., Ramu, V., Sethuraman, T. et al. Assessing the genetic fidelity of somatic embryo-derived plantlets of finger millet by random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis. Biotechnol Lett 44, 1379–1387 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-022-03305-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-022-03305-3