Abstract
Objective
To produce valerenic acid (VA) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by engineering a heterologous synthetic pathway.
Result
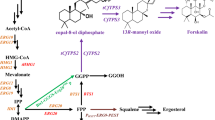
Valerena-4,7(11)-diene synthase (VDS) derived from Valeriana officinalis (valerian) was expressed in S. cerevisiae to generate valerena-4,7(11)-diene as the precursor of VA. By overexpressing the key genes of the mevalonate pathway ERG8, ERG12 and ERG19, and integrating 4 copies of MBP (maltose-binding protein)-VDS-ERG20 gene expression caskets into the genome, the production of valerena-4,7(11)-diene was improved to 75 mg/L. On this basis, the cytochrome P450 monooxygenase LsGAO2 derived from Lactuca sativa was expressed to oxidize valerena-4,7(11)-diene to produce VA, and the most effective VA production strain was used for fermentation. The yield of VA reached 2.8 mg/L in the flask and 6.8 mg/L in a 5-L bioreactor fed glucose.
Conclusions
An S. cerevisiae strain was constructed and optimized to produce VA, but the valerena-4,7(11)-diene oxidation by LsGAO2 is still the rate-limiting step for VA synthesis that needs to be further optimized in future studies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burke D, Dawson D, Stearns T (2000) Methods in yeast genetics: a Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory course manual (2000 edition). Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Plainview
Gietz RD, Schiestl RH, Willems AR, Woods RA (1995) Studies on the transformation of intact yeast cells by the LiAc/SS-DNA/PEG procedure. Yeast 11(4):355–360. https://doi.org/10.1002/yea.320110408
Ignea C, Cvetkovic I, Loupassaki S, Kefalas P, Johnson CB, Kampranis SC, Makris AM (2011) Improving yeast strains using recyclable integration cassettes, for the production of plant terpenoids. Microb Cell Fact 10(1):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-10-4
Kara M, Öztaş E, Boran T, Karaman EF, Veskoukis AS, Tsatsakis AM (2021) Ameliorative effects of the sesquiterpenoid valerenic acid on oxidative stress induced in HepG2 cells after exposure to the fungicide benomyl. Antioxidants 10(5):746. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10050746
Lu Q, Ding Y, Li Y, Lu Q (2020) 5-HT receptor agonist valerenic acid enhances the innate immunity signal and suppresses glioblastoma cell growth and invasion. Int J Biol Sci 16(12):2104–2115. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.44906
Murphy K, Kubin ZJ, Shepherd JN, Ettinger R (2010) Valeriana officinalis root extracts have potent anxiolytic effects in laboratory rats. Phytomedicine 17(8–9):674–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2009.10.020
Nguyen TD, Kwon M, Kim SU, Fischer C, Ro DK (2019) Catalytic plasticity of germacrene A oxidase underlies sesquiterpene lactone diversification. Plant Physiol 181(3):945–960. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.19.00629
Pyle BW, Tran HT, Pickel B, Haslam TM, Gao Z, MacNevin G, Vederas JC, Kim SU, Ro DK (2012) Enzymatic synthesis of valerena-4,7(11)-diene by a unique sesquiterpene synthase from the valerian plant (Valeriana officinalis). FEBS J 279(17):3136–3146. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08692.x
Ricigliano V, Kumar S, Kinison S, Brooks C, Nybo SE, Chappell J, Howarth DG (2016) Regulation of sesquiterpenoid metabolism in recombinant and elicited Valeriana officinalis hairy roots. Phytochemistry 125:43–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2016.02.011
Rodríguez-Cruz A, Romo-Mancillas A, Mendiola-Precoma J, Escobar-Cabrera JE, García-Alcocer G, Berumen LC (2020) Effect of valerenic acid on neuroinflammation in a MPTP-induced mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. IBRO Rep 8:28–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibror.2019.12.002
Wong J, d’Espaux L, Dev I, van der Horst C, Keasling J (2018) De novo synthesis of the sedative valerenic acid in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab Eng 47:94–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2018.03.005
Yeo YS, Nybo SE, Chittiboyina AG et al (2013) Functional identification of valerena-1, 10-diene synthase, a terpene synthase catalyzing a unique chemical cascade in the biosynthesis of biologically active sesquiterpenes in Valeriana officinalis. J Biol Chem 288(5):3163–3173. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.415836
Zeng BX, Yao MD, Wang Y, Xiao WH, Yuan YJ (2020) Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for enhanced dihydroartemisinic acid production. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 8:152. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.00152
Zhang C, Li M, Zhao GR, Lu W (2020) Harnessing yeast peroxisomes and cytosol acetyl-CoA for sesquiterpene α-humulene production. J Agric Food Chem 68(5):1382–1389. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b07290
Zinck GE, Chappell J (2021) Structurally guided reprogramming of valerenadiene synthase. Biochemistry 60(51):3868–3878. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.1c00523
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Key-Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province (Grant No. 2020B0303070002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Supplementary information
Methods for optimization of fermentation.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, M., Zhang, C., Wang, H. et al. Biosynthesis of valerenic acid by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Lett 44, 857–865 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-022-03264-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-022-03264-9