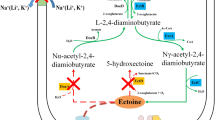
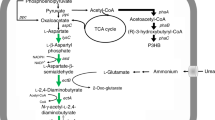
Abstract
Objectives
For the stress from fermenters, downstream processing equipment, and wastewater treatment to be alleviated, lowering salt-dependence in the ectoine synthesis process is of great significance in the moderately halotolerant Halomonas hydrothermalis Y2.
Results
In H. hydrothermalis Y2, the σ70- and σ38-controlled promoters of ectA are predicted to be involved in the osmotic regulation of ectoine synthesis. By substituting the ectA promoter with a promoter P265 that identified in the outer membrane pore protein E of H. hydrothermalis Y2, the salt dependence of ectoine synthesis was significantly decreased. In the 500-ml flask containing various NaCl contents, the engineered strain (p/Y2/△ectD/△doeA) showed a remarkably enhanced ability in ectoine synthesis, especially under lower saline stress. After a 36-h fed-batch fermentation in the 1-l fermenter, p/Y2/△ectD/△doeA synthesized 11.5 g ectoine l−1 in the presence of 60 g NaCl−1 l, with a high 0.32 g ectoine l−1 h−1 productivity, a specific productivity of 512.2 mg ectoine per g cell dry weight (CDW)−1, and an excretion ratio of 67 % ectoine.
Conclusions
As no impaired growth was observed in strain p/Y2/△ectD/△doeA while ectoine synthesis was increased, this promoter engineering strategy provides a practical protocol for lowering the salt-dependence of ectoine synthesis in this moderately halotolerant strain.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker J, Schäfer R, Kohlstedt M, Harder BJ, Borchert NS, Stöveken N, Wittmann C (2013) Systems metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for production of the chemical chaperone ectoine. Microb Cell Fact 12:110
Calderon MI, Vargas C, Rojo F, Iglesias-Guerra F, Csonka LN, Ventosa A, Nieto JJ (2004) Complex regulation of the synthesis of the compatible solute ectoine in the halophilic bacterium Chromohalobacter salexigens DSM 3043T. Microbiology 150:3051–3063
Cheng B, Meng Y, Cui Y, Li C, Tao F, Yin H, Yang C, Xu P (2016) Alkaline response of a halotolerant alkaliphilic Halomonas strain and functional diversity of its Na+(K+)/H+ antiporters. J Biol Chem 91:26056–26065
Czech L, Poehl S, Hub P, Stoeveken N, Bremer E (2018) Tinkering with osmotically controlled transcription allows enhanced production and excretion of ectoine and hydroxyectoine from a microbial cell factory. Appl Environ Microbiol 84:01772–01717
Hengge-Aronis R (2002) Stationary phase gene regulation: what makes an Escherichia coli promoter sigma S-selective? Curr Opin Microbiol 5:591–595
Jadhav K, Kushwah B, Jadhav I (2018) Insight into compatible solutes from halophiles: exploring significant applications in biotechnology. Microbial Bioprospecting for Sustainable Development, pp 978–981
Kuhlmann AU, Bremer E (2002) Osmotically regulated synthesis of the compatible solute ectoine in Bacillus pasteurii and related Bacillus spp. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:772–783
Kunte HJ (2006) Osmoregulation in bacteria: compatible solute accumulation and osmosensing. Environ Chem 3:94–100
Lee SJ, Gralla JD (2004) Osmo-regulation of bacterial transcription via poised RNA polymerase. Mol Cell 14:153–162
Li T, Li T, Ji W, Wang Q, Zhang H, Chen GQ, Lou C, Qi OY (2016) Engineering of core promoter regions enables the construction of constitutive and inducible promoters in Halomonas sp. Biotech J 11:219–227
Lugtenberg B, Boxtel RV, Verhoef C, Alphen WV (1978) Pore protein of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli K12. FEBS Lett 96:0–105
Nagayoshi C, Tokunaga H, Hayashi A, Harazono H, Hamasaki K, Ando A, Tokunaga M (2006) Efficient expression of haloarchaeal nucleoside diphosphate kinase via strong porin promoter in moderately halophilic bacteria. Protein Pept Lett 13:611–615
Oren A (2002) Halophilic microorganisms and their environments. Kluwer Academic Publishers, (Eds.). Dordrecht
Oren A (2018) Microbial life at high salt concentrations: phylogenetic and metabolic diversity. Saline Systems 4:1–13
Pejin B, Ciric A, Glamoclija J, Nikoli M, Sokovic M (2015) In vitro anti-quorum sensing activity of phytol. Nat Prod Res 29:374–377
Salvador M, Argandoña M, Pastor JM, Bernal V, Cánovas M, Csonka LN, Nieto JJ, Vargas C (2015) Contribution of RpoS to metabolic efficiency and ectoines synthesis during the osmo- and heat‐stress response in the halophilic bacterium Chromohalobacter salexigens. Env Microbiol Rep 7:301–311
Schwibbert K, Marin-Sanguino A, Bagyan I, Heidrich G, Lentzen G, Seitz H, Rampp M, Schuster SC, Klenk HP, Pfeiffer F, Oesterhelt D, Kunte HJ (2011) A blueprint of ectoine metabolism from the genome of the industrial producer Halomonas elongata DSM 2581T. Environ Microbiol 13:1973–1994
Seip B, Galinski EA, Kurz M (2011) Natural and engineered hydroxyectoine production based on the Pseudomonas stutzeri ectABCD-ask gene cluster. Appl Environ Microbiol 7:1368–1374
Stiller LM, Galinski EA, Emhj W (2018) Engineering the salt-inducible ectoine promoter region of Halomonas elongata for protein expression in a unique stabilizing environment. Genes 9:184
Typas A, Stella S, Johnson RC, Hengge R (2007) The σ35 sequence location and the Fis-sigma factor interface determine σS selectivity of the proP (P2) promoter in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 63:780–796
Wösten MMSM (1998) Eubacterial sigma-factors. FEMS Microbiol Rev 22:127–150
Yang C, Wang Z, Li Y, Niu Y, Du M, He X, Ma C, Tang H, Xu P (2010) Metabolic versatility of halotolerant and alkaliphilic strains of Halomonas isolated from alkaline black liquor. Bioresour Technol 101:6778–6784
Zhao Q, Li S, Lv P, Sun S, Ma C, Xu P, Su H, Yang C (2019) High ectoine production by an engineered Halomonas hydrothermalis Y2 in a decreased salinity medium. Microb Cell Fact 18:18412
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundations of China (Grant nos. 31870094 and 31670109).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. LS, SY and ZQ performed the experiments. YC and LS design the research. LS, ZQ, WW and DX contribute to data analysis. YC, SY, and LY wrote and revise the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Shang, Y., Zhao, Q. et al. Promoter engineering for high ectoine production in a lower saline medium by Halomonas hydrothermalis Y2. Biotechnol Lett 43, 825–834 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-021-03084-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-021-03084-3