Abstract
Objectives
This study on all-trans retinoic acid was designed to explore its effect on the ability of Fra-1 to cervical cancer cell development. The results show that all-trans retinoic acid enhances the effect of Fra-1 on inhibiting cervical cancer proliferation and the glucose consumption, its effect on the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, on the decreasing of lactic acid as well as ATP, and also influences the expression of MDM2/P53/P21 and LDHA.
Results
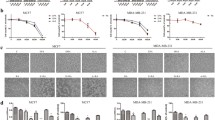
The results show that the expression of Fra-1 is higher in all-trans retinoic acid-treated cervical cancer. Flow cytometry and kit detection show that all-trans retinoic acid can enhance the ability of Fra-1 to lose the mitochondrial membrane potential, inhibit the glucose consumption and the production of lactic acid as well as ATP. CCK8 and colony formation assays indicate that all-trans retinoic acid enhances the ability of Fra-1 to inhibit cell proliferation. In addition, through Western blot analysis, it was determined that P53 and P21 were up-regulated, and MDM2 and LDHA were down-regulated.
Conclusion
The overall results of the study strongly suggest that all-trans retinoic acid enhances the effect of Fra-1 on inhibiting cervical cancer proliferation and metabolism in vitro, and also influences the expression of MDM2/P53/P21 and LDHA.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abildgaard C et al (2017) Inhibition of retinoic acid receptor beta signaling confers glycolytic dependence and sensitization to dichloroacetate in melanoma cells. Oncotarget 8:84210–84223
Belguise K et al (2005) FRA-1 expression level regulates proliferation and invasiveness of breast cancer cells. Oncogene 24:1434–1444
Bentivegna E et al (2016) Oncological outcomes after fertility-sparing surgery for cervical cancer: a systematic review. Lancet Oncol 17:e240–e253
Casalino L, De Cesare D, Verde P (2003) Accumulation of Fra-1 in ras-transformed cells depends on both transcriptional autoregulation and MEK-dependent posttranslational stabilization. Mol Cell Biol 23:4401–4415
Chinapayan SM, Prabhakaran P (2019) Anticancer effects of retinoic acid in cervical cancer cells. Teknologi 81:39–45
Du Y et al (2018) A novel all-trans retinoic acid derivative inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of myelodysplastic syndromes cell line SKM-1 cells via up-regulating p53. Int Immunopharmacol 65:561–570
Han Y et al (2019) Effects of FOSL1 silencing on osteosarcoma cell proliferation, invasion and migration through the ERK/AP-1 signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol 234:3598–3612
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144:646–674
He G et al (2005) Induction of p21 by p53 following DNA damage inhibits both Cdk4 and Cdk2 activities. Oncogene 24:2929–2943
Ishijima N et al (2015) Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase by retinoic acid sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to apoptosis induced by sorafenib. Cancer Sci 106:567–575
Kaiser A et al (1999) Fra-1: a novel target for retinoid action. FEBS Lett 448:45–48
Karin M, Liu Z, Zandi E (1997) AP-1 function and regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 9:240–246
Kustikova O et al (1998) Fra-1 induces morphological transformation and increases in vitro invasiveness and motility of epithelioid adenocarcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol 18:7095–7105
Li H, Wu X, Cheng X (2016) Advances in diagnosis and treatment of metastatic cervical cancer. J Gynecol Oncol 27:e43
Liberti MV, Locasale JW (2016) The Warburg effect: how does it benefit cancer cells? Trends Biochem Sci 41:211–218
Lu J et al (2013) All-trans retinoic acid upregulates the expression of p53 via Axin and inhibits the proliferation of glioma cells. Oncol Rep 29:2269–2274
Lu J, Tan M, Cai Q (2015) The Warburg effect in tumor progression: mitochondrial oxidative metabolism as an anti-metastasis mechanism. Cancer Lett 356:156–164
Myga-Nowak M et al (2011) Proliferation of cells and expression of RARs, RXRs and HPV viral E6 and E7 proteins in cervical cancer cell lines after treatment with ATRA. Ann Agric Environ Med 18:145–150
Narayanan BA et al (1998) The effect of all-trans and 9-cis retinoic acid on the steady state level of HPV16 E6/E7 mRNA and cell cycle in cervical carcinoma cells. Life Sci 63:565–573
Oridate N et al (1995) Inhibition of proliferation and induction of apoptosis in cervical carcinoma cells by retinoids: implications for chemoprevention. J Cell Biochem Suppl 23:80–86
Pimple S, Mishra G, Shastri S (2016) Global strategies for cervical cancer prevention. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol 28:4–10
Rattanasinchai C et al (2017) MLK3 regulates FRA-1 and MMPs to drive invasion and transendothelial migration in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Oncogenesis 6:e345
Rigobello MP et al (1999) Mitochondrial permeability transition and release of cytochrome c induced by retinoic acids. Biochem Pharmacol 58:665–670
Schmidt-Mende J et al (2006) Early mitochondrial alterations in ATRA-induced cell death. Cell Death Differ 13:119–128
Schwartzenberg-Bar-Yoseph F, Armoni M, Karnieli E (2004) The tumor suppressor p53 down-regulates glucose transporters GLUT1 and GLUT4 gene expression. Cancer Res 64:2627–2633
Shapiro IM et al (1994) Retinoic acid induces a shift in the energetic state of hypertrophic chondrocytes. J Bone Miner Res 9:1229–1237
Shi JF et al (2012) The burden of cervical cancer in China: synthesis of the evidence. Int J Cancer 130:641–652
Siegel R et al (2014) Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin 64:9–29
Tkach V et al (2003) Role of the Fos family members, c-Fos, Fra-1 and Fra-2, in the regulation of cell motility. Oncogene 22:5045–5054
Tripathy S et al (2016) All-trans-retinoic acid enhances mitochondrial function in models of human liver. Mol Pharmacol 89:560–574
Turner R, Tjian R (1989) Leucine repeats and an adjacent DNA binding domain mediate the formation of functional cFos-cJun heterodimers. Science 243:1689–1694
Vallejo A, Perurena N, Guruceaga E, Mazur PK et al (2017) An integrative approach unveils FOSL1 as an oncogene vulnerability in KRAS-driven lung and pancreatic cancer. Nat Commun 8:14294
Vander Heiden MG, DeBerardinis RJ (2017) Understanding the intersections between metabolism and cancer biology. Cell 168:657–669
Xiao SZ, Yi Y, Luo W et al (2015) Fra-1 is downregulated in cervical cancer tissues and promotes cervical cancer cell apoptosis by p53 signaling pathway in vitro. Int J Oncol 46:1677–1684
Xu DR, Huang S, Long ZJ, Chen JJ et al (2011) Inhibition of mitotic kinase Aurora suppresses Akt-1 activation and induces apoptotic cell death in all-trans retinoid acid-resistant acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. J Transl Med 9:74
Zhong G et al (2016) Fra-1 is upregulated in lung cancer tissues and inhibits the apoptosis of lung cancer cells by the P53 signaling pathway. Oncol Rep 35:447–453
Zhou YN, Luo W, Li Y, Xie H et al (2019) p53/Lactate dehydrogenase A axis negatively regulates aerobic glycolysis and tumor progression in breast cancer expressing wild-type p53. Cancer Sci 110:939–949
Funding
The Project of Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 2018JJ3782); China Scholarship Fund, CSC No. 201806375049; Postgraduate independent exploration and innovation project of central south university, Grant Nos. 2018zzts937, 2018zzts952, 2019zzts1055; Graduate research project of central south university, number: 2018dcyj075; Project of degree and postgraduate education and teaching reform in hunan province (JG2018A003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dou, Y., Huang, D., Zeng, X. et al. All-trans retinoic acid enhances the effect of Fra-1 to inhibit cell proliferation and metabolism in cervical cancer. Biotechnol Lett 42, 1051–1060 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-020-02847-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-020-02847-8