Abstract
Purpose
Numerous applications of compatible salts (osmolytes) as ectoine in food and pharmaceutical industries have been intensively increased nowadays. Decreasing the cost of industrial production of ectoine using low-cost cultivation media and improving the yield through modeling procedures are the main scopes of the present study.
Methods
Three statistical design experiments have been successfully applied for screening the parameters affecting the production process, studying the relations among parameters and optimizing the production using response surface methodology.
Results
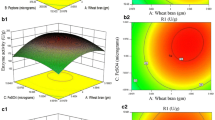
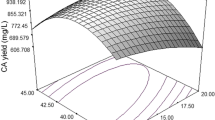
A novel semi-synthetic medium based on hydrolyzed corn gluten meal has been developed to cultivate moderate halophilic bacterial strains; Vibrio sp. CS1 and Salinivibrio costicola SH3, and support ectoine synthesis under salinity stress. Two regression equations describe the production process in the new medium have been formulated for each bacterial strain. Response surface optimizer of the central composite model predicts the maximum ectoine production is achieved at incubation time; 63.7 h, pH; 7.47 and salinity; 7.27% for Vibrio sp. CS1 whereas these variables should be adjusted at 56.95 h, 7.089 and 10.34%; on the same order regarding Salinivibrio costicola SH3. In application studies, 50 µg ectoine decreases RBCs hemolysis due to streptolysin O toxin by 21.7% within ten minutes. In addition, 2% ectoine succeeds to increase the viability of lactic acid bacteria in Yogurt as a classic example of functional food during the storage period (7 days).
Conclusion
The present study emphasizes on modeling the process of ectoine production by halophilic bacteria as well as its activity as a cryoprotectant agent.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akin SM (2005) Effects of inulin and different sugar levels on viability of probiotic bacteria and the physical and sensory characteristics of probiotic fermented ice-cream. Milchwissens Chaft 60(3):297–301
Arslan-Alaton I, Tureli G, Olmez-Hanci T (2009) Treatment of azo dye production wastewaters using Photo-Fenton-like advanced oxidation processes: optimization by response surface methodology. J Photochem Photobiol A 202(2):142–153
Ashraf GM, Greig NH, Khan TA, Hassan I, Tabrez S, Shakil S, Sheikh IA, Zaidi SK, Wali MA, Jabir NR, Firoz CK, Naeem A, Alhazza IM, Damanhouri GA, Kamal MA (2014) Protein misfolding and aggregation in Alzheimer’s disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targ 13(7):1280–1293
Baliarda A, Robert H, Jebbar M, Blanco C, Deschamps A, Le Marrec C (2003) Potential osmoprotectants for the lactic acid bacteria Pediococcus pentosaceus and Tetragenococcus halophila. Int J Food Microbiol 84(1):13–20
Bergmann S, David F, Franco-Lara E, Wittmann C, Krull R (2013) Ectoine production by Alkalibacillus haloalkaliphilus—bioprocess development using response surface methodology and model-driven strategies. Eng Life Sci 13(4):399–407
Bownik A, Stepniewska Z (2015) Protective effects of bacterial osmoprotectant ectoine on bovine erythrocytes subjected to staphylococcal alpha-haemolysin. Toxicon 99:130–135
Bownik A, Stępniewskam Z (2016) Ectoine as a promising protective agent in humans and animals. Arh Hig Rada Toksikol 67:260–265
Cunningham MW (2008) Pathogenesis of group A streptococcal infections and their sequelae. In: Finn A, Pollard AJ (eds) Hot topics in infection and immunity in Children IV. Advances in experimental medicine and biology, vol 609. Springer, New York
Dawson RMC, Elliot DC, Jones KM (1986) Data for biomedical research, 1st edn. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Ebrahimpour A, Abd Rahman RNZR, Ean Ch'ng DH, Basri M, Salleh AB (2008) A modeling study by response surface methodology and artificial neural network on culture parameters optimization for thermostable lipase production from a newly isolated thermophilic Geobacillus sp. strain ARM. BMC Biotechnol 8(1):96. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6750-8-96
Eshinimaev BT, Tsyrenzhapova IS, Khmelenina VN, Trotsenko YA (2007) Measurement of the content of the osmoprotectant ectoine in methylotrophic bacteria by means of normal-phase high performance liquid chromatography. Appl Biochem Microbiol 43(2):193–196
Fernández J, Redondo-Blanco S, Miguélez EM, Villar CJ, Clemente A, Lombó F (2015) Healthy effects of prebiotics and their metabolites against intestinal diseases and colorectal cancer. AIMS Microbiol 1(1):48–71
Graf R, Anzali S, Buenger J, Pfluecker F, Driller H (2008) The multifunctional role of ectoine as a natural cell protectant. Clin Dermatol 26(4):326–333
Guevarra RB, Barraquio VL (2015) Viable counts of lactic acid bacteria in philippine commercial yogurts. Int J Dairy Sci Process 2(5):24–28
Heuzé V, Tran G, Sauvant D, Renaudeau D, Lessire M, Lebas F (2018) Corn gluten meal. Feedipedia a programme by FAO. https://www.feedipedia.org/node/715
Hudson LE, McDermott CD, Stewart TP, Hudson WH, Rios D, Fasken MB, Corbettm AH, Lamb TJ (2016) Characterization of the probiotic yeast Saccharomyces boulardii in the healthy mucosal immune system. PLoS ONE 11(4):e0153351. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0153351
Kanapathipillai M, Lentzen G, Sierks M, Park CB (2005) Ectoine and hydroxyectoine inhibit aggregation and neurotoxicity of Alzheimer's beta-amyloid. FEBS Lett 579(21):4775–4780
Kolp S, Pietsch M, Galinski EA, Gütschow M (2006) Compatible solutes as protectants for zymogens against proteolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1764(7):1234–1242
Lentzen G, Schwarz T (2006) Extremolytes: natural compounds from extremophiles for versatile applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72(4):623–634
Li X, Chen X (2009) Drying of micro-encapsulated lactic acid bacteria—effects of trehalose and immobilization on cell survival and release properties. J Ocean Univ China 8(1):39–44
Li T, Qu A, Yuan X, Tan F, Li X, Wang T, Zhang L (2017) Response surface method optimization of ectoine fermentation medium with moderate halophilic bacteria Halomonas sp. H02. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 77:012019. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/77/1/012019
Marini A, Reinelt K, Krutmann J, Bilstein A (2014) Ectoine-containing cream in the treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis: a randomised, comparator-controlled, intra-individual double-blind, multi-center trial. Skin Pharmacol Physiol 27(2):57–65
Mei Y, Liu H, Zhang S, Yang M, Hu C, Zhang J, Shen P, Chen X (2017) Effects of salinity on the cellular physiological responses of Natrinema sp. J7-2. PLoS ONE 12(9):e0184974. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0184974
Michos A, Gryllos I, Hakansson A, Srivastava A, Kokkotou E, Wessels MR (2006) Enhancement of streptolysin O activity and intrinsic cytotoxic effects of the group A streptococcal toxin NAD-glycohydrolase. J Biol Chem 281(12):8216–8223
Omara AMA, Sharaf AM, El-Hela AA, Shahin AAM, El-Bialy HA, El-Fouly MZ (2019) Isolation and characterization of new ectoine-producers from various hypersaline ecosystems in Egypt. J Nucl Technol Appl Sci, in press
Ono H, Okuda M, Tongpim S, Imai K, Shinmyo A, Sakuda S, Kaneko Y, Murooka Y, Takano M (1998) Accumulation of compatible solutes, ectoine and hydroxyectoine, in a moderate halophile, Halomonas elongata KS3 isolated from dry salty land in Thailand. J Ferment Bioeng 85(4):362–368
Parwata P, Wahyuningrum D, Suhandono S, Hertadim R (2018) Production of ectoine by Halomonas elongata BK-AG25 using osmotic shock technique. Earth Environ Sci 209:012017. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/209/1/012017
Pastor JM, Salvador M, Argandoña M, Bernal V, Reina-Bueno M, Csonka LN, Iborra JL, Vargas C, Nieto JJ, Cánovas M (2010) Ectoines in cell stress protection: uses and biotechnological production. Biotechnol Adv 28:782–801
Reddy, N. R., Palmer, J. K., Pierson, M. D., & Bothast, R. J. (1983). Wheat straw hemicelluloses: composition and fermentation. J. Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 13, 1308e1313.
Sai-Ut S, Benjakul S, Sumpavapol P, Kishimura H (2014) Optimization of gelatinolytic enzyme production by B. amyloliquefaciens sp. H11 through Plackett–Burman design and response surface methodology. Int Aquat Res 6(1):59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40071-014-0059-5
Salar-García MJ, Bernal V, Pastor JM, Salvador M, Argandoña M, Nieto JJ, Vargas C, Cánovas M (2017) Understanding the interplay of carbon and nitrogen supply for ectoines production and metabolic overflow in high density cultures of Chromohalobacter salexigens. Microb Cell Fact. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-017-0643-7
Schwibbert K, Marin-Sanguino A, Bagyan I, Heidrich G, Lentzen G, Seitz H, Rampp M, Schuster SC, Klenk HP, Pfeiffer F (2581T) A blueprint of ectoine metabolism from the genome of the industrial producer Halomonas elongata DSM 2581T. Environ Microbiol 13(8):1973–1994
Shivanand P, Mugeraya G (2011) Halophilic bacteria and their compatible solutes—osmoregulation and potential applications. Curr Sci 100(10):1516–1521
Silva EAD, Albino LFT, Rostagno HS, Ribeiro Junior V, Vieira RA, Campos AMDA, Messias RKG (2012) Chemical composition and metabolizable energy values of feedstuffs for broiler chickens. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia 41:648–654
Slama I, Abdelly C, Bouchereau A, Flowers T, Savoure A (2015) Diversity, distribution and roles of osmoprotective compounds accumulated in halophytes under abiotic stress. Ann Bot 115:433–447
Tanimura K, Nakayama H, Tanaka T, Kondo A (2013) Ectoine production from lignocellulosic biomass-derived sugars by engineered Halomonas elongata. Biores Technol 142:523–529
Vipin and Abhishek, N. (2014) Isolation, purification and characterization of Streptolysin-O from Streptococci. Indian J Biotechnol Pharm Res 2(1):28–34
Weinisch L, Kühner S, Roth R, Grimm M, Roth T, Netz DJA, Pierik AJ, Filker S (2018) Identification of osmoadaptive strategies in the halophile, heterotrophic ciliate Schmidingerothrix salinarum. PLoS Biol 16(1):e2003892. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.2003892
Xia T, Zhu Y, Mu L, Zhang Z-F, Liu S (2016) Pulmonary diseases induced by ambient ultrafine and engineered nanoparticles in twenty first century. Natl Sci Rev 3:416–429. https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nww064
Zhang L, Mao S (2017) Application of quality by design in the current drug development. Asian J Pharm Sci 12(1):1–8
Zhu D, Niu L, Wang C, Nagata S (2007) Isolation and characterisation of moderately halophilic bacterium Halomonas ventosae DL7 synthesizing ectoine as compatible solute. Ann Microbiol 57(3):401–406
Acknowledgement
The authors gratefully acknowledge the National Center for Radiation Research and Technology, Egyptian Atomic Energy Authority; for financial support and facilities to accomplish this work.
Funding
There is no direct funding stream, but Egyptian Atomic Energy Authority provides financial support and facilities to accomplish this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Omara, A.M.A., Sharaf, A.EM.M., El-Hela, A.A. et al. Optimizing ectoine biosynthesis using response surface methodology and osmoprotectant applications. Biotechnol Lett 42, 1003–1017 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-020-02833-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-020-02833-0