Abstract
Objective
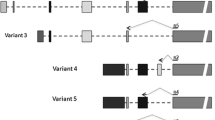
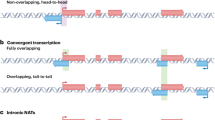
SOX9 is a key transcription factor with important roles in regulating proliferation and differentiation of various cell types. Dysregulation of SOX9 expression has been involved with pathogenesis of different developmental, degenerative, and neoplastic disorders. Natural antisense transcripts (NATs) are long non-coding RNAs with increasing significance in regulation of gene expression. However, the presence of a NAT at SOX9 locus has been so far unclear.
Result
We detected a natural antisense transcript at SOX9 locus (SOX9-NAT) through strand-specific RT-PCR. In contrast to SOX9 sense RNA (mRNA), SOX9-NAT was down-regulated in cancer tissues and cell lines compared with their normal counterparts. In addition, reciprocal to SOX9 mRNA, SOX9-NAT was also down-regulated in human embryonic stem cells in comparison with human fibroblasts in vitro.
Conclusion
The negative correlation between SOX9 mRNA and SOX9-NAT was confirmed by analyzing qPCR data, as well as RNA-Seq datasets of several human cancers. Our data suggest a functional role for SOX9-NAT in the regulation of SOX9 mRNA as a potential target in cancer treatment and regenerative medicine.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar-Medina M et al (2019) SOX9 stem-cell factor: clinical and functional relevance in cancer. J Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6754040
Balbin OA et al (2015) The landscape of antisense gene expression in human cancers. Genome Res 25:1068–1079
Bolandi Z, Hosseini Rad SMA, Soudi S, Hashemi SM, Ghanbarian H (2019) A simple and highly efficient method for transduction of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Biochem 120:1726–1734
Faghihi MA, Wahlestedt C (2009) Regulatory roles of natural antisense transcripts. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10:637–643. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2738
Ghanbarian H, Grandjean V, Cuzin F, Rassoulzadegan M (2011) A network of regulations by small non-coding RNAs: the P-TEFb kinase in development and pathology. Front Genet 2:95
Ghanbarian H, Wagner N, Michiels J-F, Cuzin F, Wagner K-D, Rassoulzadegan M (2017) Small RNA-directed epigenetic programming of embryonic stem cell cardiac differentiation. Sci Rep 7:41799
Jiang SS et al (2010) Upregulation of SOX9 in lung adenocarcinoma and its involvement in the regulation of cell growth and tumorigenicity. Clin Cancer Res 16:4363–4373. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-0138
Jo A et al (2014) The versatile functions of Sox9 in development, stem cells, and human diseases. Genes Dis 1:149–161
Kadaja M et al (2014) SOX9: a stem cell transcriptional regulator of secreted niche signaling factors. Genes Dev 28:328–341. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.233247.113
Keramati F, Seyedjafari E, Fallah P, Soleimani M, Ghanbarian H (2015) 7SK small nuclear RNA inhibits cancer cell proliferation through apoptosis induction. Tumor Biol 36:2809–2814
Lefebvre V, Dvir-Ginzberg M (2017) SOX9 and the many facets of its regulation in the chondrocyte lineage. Connect Tissue Res 58:2–14
Lei B, Zhang Y, Liu T, Li Y, Pang D (2016) Sox9 upregulation in breast cancer is correlated with poor prognosis and the CD44 (+)/CD24 (−/low) phenotype. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 9:7345–7351
Li J et al (2015) MicroRNA-494 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion of chondrosarcoma cells in vivo and in vitro by directly targeting SOX9. Oncotarget 6:26216
Lin S, Zhang L, Luo W, Zhang X (2015) Characteristics of antisense transcript promoters and the regulation of their activity. Int J Mol Sci 17:9
Liu N et al (2017) MicroRNA-101 inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion of human glioblastoma by targeting SOX9. Oncotarget 8:19244
Lü B et al (2008) Analysis of SOX9 expression in colorectal cancer. Am J Clin Pathol 130:897–904
Matheu A et al (2012) Oncogenicity of the developmental transcription factor Sox9. Cancer Res 72:1301–1315. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3660
Mokhberian N, Hashemi SM, Jajarmi V, Eftekhary M, Koochaki A, Ghanbarian H (2019) Sirt1 antisense transcript is down-regulated in human tumors. Mol Biol Rep 46(2):2299–2305
Pelechano V, Steinmetz LM (2013) Gene regulation by antisense transcription. Nat Rev Genet 14:880–893. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3594
Pritchett J, Athwal V, Roberts N, Hanley NA, Hanley KP (2011) Understanding the role of SOX9 in acquired diseases: lessons from development. Trends Mol Med 17:166–174
Richtig G et al (2017) SOX9 is a proliferation and stem cell factor in hepatocellular carcinoma and possess widespread prognostic significance in different cancer types. PLoS ONE 12:e0187814
Sashikawa Kimura M, Mutoh H, Sugano K (2011) SOX9 is expressed in normal stomach, intestinal metaplasia, and gastric carcinoma in humans. J Gastroenterol 46:1292–1299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-011-0443-5
Wang J et al (2017) Upregulation of microRNA-524-5p enhances the cisplatin sensitivity of gastric cancer cells by modulating proliferation and metastasis via targeting SOX9. Oncotarget 8:574
Wanowska E, Kubiak MR, Rosikiewicz W, Makałowska I, Szcześniak MW (2018) Natural antisense transcripts in diseases: from modes of action to targeted therapies. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 9:e1461
Yang B, Guo H, Zhang Y, Chen L, Ying D, Dong S (2011) MicroRNA-145 regulates chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by targeting Sox9. PLoS ONE 6:e21679
Zhang W, Cheng P, Hu W, Yin W, Guo F, Chen A, Huang H (2018) Inhibition of microRNA-384-5p alleviates osteoarthritis through its effects on inhibiting apoptosis of cartilage cells via the NF-κB signaling pathway by targeting SOX9. Cancer Gene Ther 25:326
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by a Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran (grant number: 14325). Our team appreciates the cellular and molecular biology research center, Tehran, Iran for providing space and facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.E., S.M.H., K.S., and H.G. comprehended and designed the study. M.E., S.M.H., N.M., Z.B., H.G., and S.M.-Y. performed the experiments. M.E., K.S., S.M.-Y., and H.G. analyzed the data and construed the results. M.E., N.M., Z.B., and H.G. prepared the manuscript. M.E., K.S., and H.G. reviewed during the preparation of manuscript and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest concerning the publication of this paper.
Ethical approval
All experiments performed in this study were in agreement with the ethical standards of the Ethics Committee at the Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eftekhary, M., Mohammadi-Yeganeh, S., Bolandi, Z. et al. A novel natural antisense transcript at human SOX9 locus is down-regulated in cancer and stem cells. Biotechnol Lett 42, 329–339 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-019-02774-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-019-02774-3