Abstract
Objectives
To develop a xylose-nonutilizing Escherichia coli strain for ethanol production and xylose recovery.
Results
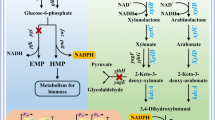
Xylose-nonutilizing E. coli CICIM B0013-2012 was successfully constructed from E. coli B0013-1030 (pta-ack, ldhA, pflB, xylH) by deletion of frdA, xylA and xylE. It exhibited robust growth on plates containing glucose, arabinose or galactose, but failed to grow on xylose. The ethanol synthesis pathway was then introduced into B0013-2012 to create an ethanologenic strain B0013-2012PA. In shaking flask fermentation, B0013-2012PA fermented glucose to ethanol with the yield of 48.4 g/100 g sugar while xylose remained in the broth. In a 7-l bioreactor, B0013-2012PA fermented glucose, galactose and arabinose in the simulated corncob hydrolysate to 53.4 g/l ethanol with the yield of 48.9 g/100 g sugars and left 69.6 g/l xylose in the broth, representing 98.6% of the total xylose in the simulated corncob hydrolysate.
Conclusions
By using newly constructed strain B0013-2012PA, we successfully developed an efficient bioprocess for ethanol production and xylose recovery from the simulated corncob hydrolysate.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anasontzis GE, Christakopoulos P (2014) Challenges in ethanol production with Fusarium oxysporum through consolidated bioprocessing. Bioengineered 5:393–395
Andersen RL, Jensen KM, Mikkelsen MJ (2015) Continuous ethanol fermentation of pretreated lignocellulosic biomasses, waste biomasses, molasses and syrup using the anaerobic, thermophilic bacterium Thermoanaerobacter italicus Pentocrobe 411. PLoS ONE 10:e0136060
Banerjee S, Mudliar S, Sen R, Giri B, Satpute D, Chakrabarti T, Pandey R (2010) Commercializing lignocellulosic bioethanol: technology bottlenecks and possible remedies. Biofuel Bioprod Bior 4:77–93
Bátori V, Ferreira JA, Taherzadeh MJ, Lennartsson PR (2015) Ethanol and protein from ethanol plant by-products using edible fungi Neurospora intermedia and Aspergillus oryzae. Biomed Res Int 2015:176371
Cao JL, Zhou L, Zhang L, Wang ZX, Shi GY (2010) Construction and fermentation of succinate-producing recombinant Escherichia coli. Chin J Appl Environ Biol 16:851–857
Cirino PC, Chin JW, Ingram LO (2006) Engineering Escherichia coli for xylitol production from glucose-xylose mixtures. Biotechnol Bioeng 95:1167–1176
Garcia Sanchez R, Karhumaa K, Fonseca C, Sànchez Nogué V, Almeida JR, Larsson CU, Bengtsson O, Bettiga M, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2010) Improved xylose and arabinose utilization by an industrial recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain using evolutionary engineering. Biotechnol Biofuels 3:13
Hasona A, Kim Y, Healy FG, Ingram LO, Shanmugam KT (2004) Pyruvate formate lyase and acetate kinase are essential for anaerobic growth of Escherichia coli on xylose. J Bacteriol 186:7593–7600
Ho NW, Chen Z, Brainard AP (1998) Genetically engineered Saccharomyces yeast capable of effective cofermentation of glucose and xylose. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:1852–1859
Ingram LO, Conway T, Clark DP, Sewell GW, Preston JF (1987) Genetic engineering of ethanol production in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:2420–2425
Jeffries TW (2006) Engineering yeasts for xylose metabolism. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17:320–326
Khankal R, Chin JW, Cirino PC (2008) Role of xylose transporters in xylitol production from engineered Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol 134:246–252
Kogje A, Ghosalkar A (2016) Xylitol production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae overexpressing different xylose reductases using non-detoxified hemicellulosic hydrolysate of corncob. 3. Biotech 6:127
Latif F, Rajoka MI (2001) Production of ethanol and xylitol from corn cobs by yeasts. Bioresour Technol 77:57–63
Ohta K, Beall DS, Mejia JP, Shanmugam KT, Ingram LO (1991) Metabolic engineering of Klebsiella oxytoca M5A1 for ethanol production from xylose and glucose. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:2810–2815
Puseenam A, Tanapongpipat S, Roongsawang N (2015) Co-expression of endoxylanase and endoglucanase in Scheffersomyces stipitis and its application in ethanol production. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 177:1690–1700
Rubin EM (2008) Genomics of cellulosic biofuels. Nature 454:841–845
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Song S, Park C (1997) Organization and regulation of the D-xylose operons in Escherichia coli K-12: XylR acts as a transcriptional activator. J Bacteriol 179:7025–7032
Sun JF, Xu M, Zhang F, Wang ZX (2004) Novel recombinant Escherichia coli producing ethanol from glucose and xylose. Acta Microbiol Sin 44:600–604
Sun JF, Tian KM, Shen W, Chen XZ, Wang ZX (2017) Genetic nature of xylose metabolism, differences between Escherichia coli strains. Chin J Food Ferment Ind 43:68–73
Treebupachatsakul T, Shioya K, Nakazawa H, Kawaguchi T, Morikawa Y, Shida Y, Ogasawara W, Okada H (2015) Utilization of recombinant Trichoderma reesei expressing Aspergillus aculeatus β-glucosidase I (JN11) for a more economical production of ethanol from lignocellulosic biomass. J Biosci Bioeng 120:657–665
Ur-Rehman S, Mushtaq Z, Zahoor T, Jamil A, Murtaza MA (2015) Xylitol: a review on bioproduction, application, health benefits, and related safety issues. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 55:1514–1528
van Maris AJ, Winkler AA, Kuyper M, de Laat WT, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT (2007) Development of efficient xylose fermentation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: xylose isomerase as a key component. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 108:179–204
Yoon SH, Mukerjea R, Robyt JF (2003) Specificity of yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) in removing carbohydrates by fermentation. Carbohydr Res 338:1127–1132
Zhang M, Eddy C, Deanda K, Finkelstein M, Picataggio S (1995) Metabolic engineering of a pentose metabolism pathway in ethanologenic Zymomonas mobilis. Science 267:240–243
Zhou L, Zuo ZR, Chen XZ, Niu DD, Tian KM, Prior BA, Shen W, Shi GY, Singh S, Wang ZX (2011) Evaluation of genetic manipulation strategies on D-lactate production by Escherichia coli. Curr Microbiol 62:981–989
Zhou L, Niu DD, Tian KM, Chen XZ, Prior BA, Shen W, Shi GY, Singh S, Wang ZX (2012) Genetically switched D-lactate production in Escherichia coli. Metab Eng 14:560–568
Acknowledgements
This research was supported financially by The Raising Program of Innovation Team for Tianjin Universities (TD12-5002).
Supporting information
Supplementary Table 1—Primers used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, J., Wang, J., Tian, K. et al. A novel strategy for production of ethanol and recovery of xylose from simulated corncob hydrolysate. Biotechnol Lett 40, 781–788 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-018-2537-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-018-2537-0