Abstract
Objectives
To explore the effects of Lin28A on progression of osteocarcinoma (OS) cells.
Results
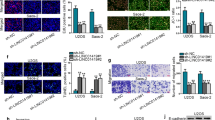
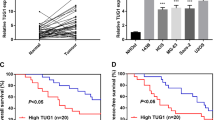
Lin28A mRNA and protein expressions were significantly increased in OS tissues compared with that in normal adjacent tissues. Expressions of Lin28A and long noncoding RNA MALAT1 were positively correlated. Patients with higher Lin28A expression had shorter overall survival. Moreover, Lin28A knockdown inhibited OS cells proliferation, migration, invasion and promoted cell apoptosis; Lin28A was found to harbor binding sites on MALAT1 sequences and associated with MALAT1, and increased MALAT1 stability and expression. Notably, the inhibition of Lin28A knockdown was attenuated or even reversed by MALAT1 overexpression.
Conclusions
RNA binding protein Lin28A could facilitate OS cells progression by associating with the long noncoding RNA MALAT1.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balzeau J, Menezes MR, Cao S, Hagan JP (2017) The LIN28/let-7 pathway in cancer. Front Genet 8:31
Beristain AG, Narala SR, Di Grappa MA, Khokha R (2012) Homotypic RANK signaling differentially regulates proliferation, motility and cell survival in osteosarcoma and mammary epithelial cells. J Cell Sci 125:943–955
Chou J, Wang B, Zheng T, Li X, Zheng L, Hu J, Zhang Y, Xing Y, Xi T (2016) MALAT1 induced migration and invasion of human breast cancer cells by competitively binding miR-1 with cdc42. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 472:262–269
Han X, Yang F, Cao H, Liang Z (2015) Malat1 regulates serum response factor through miR-133 as a competing endogenous RNA in myogenesis. FASEB J 29:3054–3064
Liu K, Huang J, Ni J, Song D, Ding M, Wang J, Huang X, Li W (2017) MALAT1 promotes osteosarcoma development by regulation of HMGB1 via miR-142-3p and miR-129-5p. Cell Cycle 16:578–587
Malakar P, Shilo A, Mogilevsky A, Stein I, Pikarsky E, Nevo Y, Benyamini H, Elgavish S, Zong X, Prasanth KV et al (2017) Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma development by SRSF1 upregulation and mTOR activation. Cancer Res 77:1155–1167
Nowak JS, Hobor F, Downie Ruiz Velasco A, Choudhury NR, Heikel G, Kerr A, Ramos A, Michlewski G (2017) Lin28a uses distinct mechanisms of binding to RNA and affects miRNA levels positively and negatively. RNA 23:317–332
Qi Y, Ooi HS, Wu J, Chen J, Zhang X, Tan S, Yu Q, Li YY, Kang Y, Li H et al (2016) MALAT1 long ncRNA promotes gastric cancer metastasis by suppressing PCDH10. Oncotarget 7:12693–12703
Shen H, Yang Y, Zhao L, Yuan J, Niu Y (2016) Lin28A and androgen receptor expression in ER-/Her2+ breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 156:135–147
Spreafico A, Schenone S, Serchi T, Orlandini M, Angelucci A, Magrini D, Bernardini G, Collodel G, Di Stefano A, Tintori C et al (2008) Antiproliferative and proapoptotic activities of new pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine derivative Src kinase inhibitors in human osteosarcoma cells. FASEB J 22:1560–1571
Tang Y, Jin X, Xiang Y, Chen Y, Shen CX, Zhang YC, Li YG (2015) The lncRNA MALAT1 protects the endothelium against ox-LDL-induced dysfunction via upregulating the expression of the miR-22-3p target genes CXCR2 and AKT. FEBS Lett 589:3189–3196
Wang T, Wang G, Hao D, Liu X, Wang D, Ning N, Li X (2015) Aberrant regulation of the LIN28A/LIN28B and let-7 loop in human malignant tumors and its effects on the hallmarks of cancer. Mol Cancer 14:125
Yu D, Zhang C, Gui J (2017) RNA-binding protein HuR promotes bladder cancer progression by competitively binding to the long noncoding HOTAIR with miR-1. Onco Targets Ther 10:2609–2619
Zhang Y, Dai Q, Zeng F, Liu H (2017) MALAT1 promotes the proliferation and metastasis of osteosarcoma cells by activating the Rac1/JNK pathway via targeting MiR-509. Oncol Res. https://doi.org/10.3727/096504017X14957939026111
Zheng L, Li X, Meng X, Chou J, Hu J, Zhang F, Zhang Z, Xing Y, Liu Y, Xi T (2016) Competing endogenous RNA networks of CYP4Z1 and pseudogene CYP4Z2P confer tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Mol Cell Endocrinol 427:133–142
Supporting information
Supplementary Table 1—PCR Primer sequences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Pang, J., Ji, B. et al. RNA binding protein Lin28A promotes osteocarcinoma cells progression by associating with the long noncoding RNA MALAT1. Biotechnol Lett 40, 493–500 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-017-2489-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-017-2489-9