Abstract
Objectives
To investigate the roles of miR-215 in high-grade glioma and to clarify the regulation of retinoblastoma 1 (RB1) by miR-215.
Results
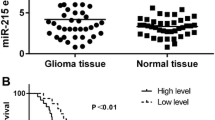
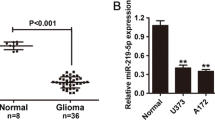
miR-215 is frequently up-regulated in high-grade glioma tissues. Increased miR-215 expression is significantly associated with World Health Organization grade (P < 0.01) tumor size (P < 0.05) and poor prognosis (P < 0.01). Over-expression of miR-215 promoted cell proliferation and knockdown of miR-215 inhibited cell proliferation in vitro. RB1 was identified as a direct and functional target of miR-215. RB1 is generally down-regulated in glioma tissues and its expression inversely correlated with miR-215, which is up-regulated in high-grade glioma tissues, and its expression was negatively correlated with miR-215.
Conclusions
The new miR-215/RB1 axis provides new insights into the molecular mechanism and treatment for glioma.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deng Y et al (2014) MiR-215 modulates gastric cancer cell proliferation by targeting RB1. Cancer Lett 342:27–35
Di Leva G, Croce CM (2010) Roles of small RNAs in tumor formation. Trend Mol Med 16:257–267
Gabriely G, Wurdinger T, Kesari S, Esau CC, Burchard J, Linsley PS, Krichevsky AM (2008) MicroRNA 21 promotes glioma invasion by targeting matrix metalloproteinase regulators. Mol Cell Biol 28:5369–5380
Goldhoff P et al (2012) Clinical stratification of glioblastoma based on alterations in retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein (RB1) and association with the proneural subtype. J Neuropathol Exper Neurol 71:83–89
Goodrich DW, Wang NP, Qian YW, Lee EY, Lee WH (1991) The retinoblastoma gene product regulates progression through the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Cell 67:293–302
Harbour JW, Dean DC (2000) Rb function in cell-cycle regulation and apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol 2:E65–E67
Hochberg FH, Atai NA, Gonda D, Hughes MS, Mawejje B, Balaj L, Carter RS (2014) Glioma diagnostics and biomarkers: an ongoing challenge in the field of medicine and science. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 14:439–452
Hu J et al (2016) MiR-215 is induced post-transcriptionally via HIF-drosha complex and mediates glioma-initiating cell adaptation to hypoxia by targeting KDM1B. Cancer Cell 29:49–60
Korenjak M, Brehm A (2005) E2F-Rb complexes regulating transcription of genes important for differentiation and development. Curr Opin Gen Dev 15:520–527
Liu F, You X, Chi X, Wang T, Ye L, Niu J, Zhang X (2014) Hepatitis B virus X protein mutant HBxDelta127 promotes proliferation of hepatoma cells through up-regulating miR-215 targeting PTPRT. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 444:128–134
Mu J et al (2013) Functional implications of microRNA-215 in TGF-beta1-induced phenotypic transition of mesangial cells by targeting CTNNBIP1. PLoS ONE 8:e58622
Nakamura M, Yonekawa Y, Kleihues P, Ohgaki H (2001) Promoter hypermethylation of the RB1 gene in glioblastomas. Lab Investig 81:77–82
Pichiorri F et al (2010) Downregulation of p53-inducible microRNAs 192, 194, and 215 impairs the p53/MDM2 autoregulatory loop in multiple myeloma development. Cancer Cell 18:367–381
Tong YQ et al (2015) MiR-215, an activator of the CTNNBIP1/beta-catenin pathway, is a marker of poor prognosis in human glioma. Oncotarget 6:25024–25033
Wei J, Gabrusiewicz K, Heimberger A (2013) The controversial role of microglia in malignant gliomas. Clin Dev Immunol 2013:285246
Wijnhoven BPL, Hussey DJ, Watson DI, Tsykin A, Smith CM, Michael MZ (2010) MicroRNA profiling of Barrett’s oesophagus and oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Br J Surg 97:853–861
Xue H et al (2016) MicroRNA-584-3p, a novel tumor suppressor and prognostic marker, reduces the migration and invasion of human glioma cells by targeting hypoxia-induced ROCK1. Oncotarget 7:4785–4805
Yuan J et al (2015) MiRNA-125a-5p inhibits glioblastoma cell proliferation and promotes cell differentiation by targeting TAZ. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 457:171–176
Zhu D et al (2015) Nidogen-1 is a common target of microRNAs MiR-192/215 in the pathogenesis of Hirschsprung’s disease. J Neurochem 134:39–46
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that they have no competing interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, X., Shi, B. miR-215 functions as an oncogene in high-grade glioma by regulating retinoblastoma 1. Biotechnol Lett 39, 1351–1358 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-017-2373-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-017-2373-7