Abstract
Objective
To identify new enzymatic bottlenecks of l-tyrosine pathway for further improving the production of l-tyrosine and its derivatives.
Result
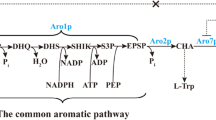
When ARO4 and ARO7 were deregulated by their feedback resistant derivatives in the host strains, the ARO2 and TYR1 genes, coding for chorismate synthase and prephenate dehydrogenase were further identified as new important rate-limiting steps. The yield of p-coumaric acid in the feedback-resistant strain overexpressing ARO2 or TYR1, was significantly increased from 6.4 to 16.2 and 15.3 mg l−1, respectively. Subsequently, we improved the strain by combinatorial engineering of pathway genes increasing the yield of p-coumaric acid by 12.5-fold (from 1.7 to 21.3 mg l−1) compared with the wild-type strain. Batch cultivations revealed that p-coumaric acid production was correlated with cell growth, and the formation of by-product acetate of the best producer NK-M6 increased to 31.1 mM whereas only 19.1 mM acetate was accumulated by the wild-type strain.
Conclusion
Combinatorial metabolic engineering provides a new strategy for further improvement of l-tyrosine or other metabolic biosynthesis pathways in S. cerevisiae.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bongaerts J, Kramer M, Muller U, Raeven L, Wubbolts M (2001) Metabolic engineering for microbial production of aromatic amino acids and derived compounds. Metab Eng 3:289–300
Curran KA, Leavitt JM, Karim AS, Alper HS (2013) Metabolic engineering of muconic acid production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab Eng 15:55–66
Duncan K, Edwards RM, Coggins JR (1988) The Saccharomyces cerevisiae ARO1 gene. An example of the co-ordinate regulation of five enzymes on a single biosynthetic pathway. FEBS Lett 241:83–88
Gold ND, Gowen CM, Lussier FX, Cautha SC, Mahadevan R, Martin VJ (2015) Metabolic engineering of a tyrosine-overproducing yeast platform using targeted metabolomics. Microb Cell Fact 14:73
Ikeda M (2006) Towards bacterial strains overproducing l-tryptophan and other aromatics by metabolic engineering. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 69:615–626
Ito H, Sakurai S, Tanaka T, Sato K, Enei H (1990) Genetic breeding of l-tyrosine producer from Brevibacterium lactofermentum. Agric Biol Chem 54:699–705
Jansen G, Wu CL, Schade B, Thomas DY, Whiteway M (2005) Drag & Drop cloning in yeast. Gene 344:43–51
Knop M, Siegers K, Pereira G, Zachariae W, Winsor B, Nasmyth K, Schiebel E (1999) Epitope tagging of yeast genes using a PCR-based strategy: more tags and improved practical routines. Yeast 15:963–972
Koopman F et al (2012) De novo production of the flavonoid naringenin in engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microb Cell Fact 11:155
Kyndt JA, Meyer TE, Cusanovich MA, Van Beeumen JJ (2002) Characterization of a bacterial tyrosine ammonia lyase, a biosynthetic enzyme for the photoactive yellow protein. FEBS Lett 512:240–244
Li M, Kildegaard KR, Chen Y, Rodriguez A, Borodina I, Nielsen J (2015) De novo production of resveratrol from glucose or ethanol by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab Eng 32:1–11
Lutke-Eversloh T, Stephanopoulos G (2007) l-tyrosine production by deregulated strains of Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75:103–110
Luttik MA, Vuralhan Z, Suir E, Braus GH, Pronk JT, Daran JM (2008) Alleviation of feedback inhibition in Saccharomyces cerevisiae aromatic amino acid biosynthesis: quantification of metabolic impact. Metab Eng 10:141–153
Mannhaupt G, Stucka R, Pilz U, Schwarzlose C, Feldmann H (1989) Characterization of the prephenate dehydrogenase-encoding gene, TYR1, from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene 85:303–311
Zheng L, Baumann U, Reymond JL (2004) An efficient one-step site-directed and site-saturation mutagenesis protocol. Nucleic Acid Res 32:e115
Acknowledgements
The work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31470004), the Sino-Swiss scientific and technological cooperation project supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2015DFG32140) and the National Basic Research Program of China (2011CBA00802).
Supporting information
Supplementary Table 1—Strains and plasmids used.
Supplementary Table 2—Primers used.
Supplementary Fig. 1—Schematic representation of the engineered strains.
Supplementary Fig. 2—Schematic representation of markless promoter replacement in S. cerevisaie.
Supplementary Fig. 3—The schematic maps of dual-promoter vectors pLC41 and pLC42 construction by marker substitution.
Supplementary Fig. 4—The qPCR analysis of gene expression levels of the engineered strains compared with NK-L70 strain.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, J., Liu, Q., Song, X. et al. Combinatorial analysis of enzymatic bottlenecks of l-tyrosine pathway by p-coumaric acid production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae . Biotechnol Lett 39, 977–982 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-017-2322-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-017-2322-5