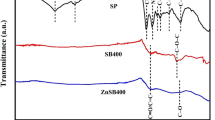
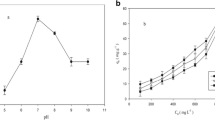
Abstract
Objective
To remove dibenzothiophene (DBT) and 4,6-dimethyl-dibenzothiophene (4,6-DMDBT) adsorbed on alumina, silica and sepiolite through biodesulfurization (BDS) using Rhodococcus Rhodochrous spp., that selectively reduce sulfur molecules without generating of gaseous pollutants.
Results
The adsorption of DBT and 4,6-DMDBT was affected by the properties of the supports, including particle size and the presence of surface acidic groups. The highest adsorption of both sulfur-containing organic molecules used particle sizes of 0.43–0.063 mm. The highest percentage removal was with sepiolite (80 % for DBT and 56 % for 4,6-DMDBT) and silica (71 % for DBT and 37 % for 4,6-DMDBT). This is attributed to the close interaction between these supports and the bacteria.
Conclusions
Biodesulfurization is effective for removing the sulfur-containing organic molecules adsorbed on inorganic materials and avoids the generation of gaseous pollutants.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baeza P, Bassi R, Villarroel M, Ojeda J, Araya P, Aguila G (2015) Adsorption of 4,6-dimethyldibenzothiophene over Cu/ZrO2. J Chil. Chem Soc 60:2817–2821
Bhatia S, Sharma DK (2010) Biodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene, its alkylated derivatives and crude oil by a newly isolated strain Pantoea agglomerans D23W3. Biochem Eng J 50:104–109
Dinamarca MA, Ibacache-Quiroga C, Baeza P, Galvez S, Villarroel M, Ojeda J (2010) Biodesulfurization of gas oil using inorganic supports biomodified with metabolically active cells immobilized by adsorption. Biores Technol 101:2375–2378
Dinamarca MA, Rojas A, Baeza P, Espinoza G, Ibacache-Quiroga C, Ojeda J (2014) Optimizing the biodesulfurization of gas oil by adding surfactants to immobilized cell systems. Fuel 116:237–241
Jeyachandran YL, Narayandassa SK, Mangalaraj D, Bao CY, Li W, Liao YM, Zhang C, Xiao LY, Chen WC (2006) A study on bacterial attachment on titanium and hydroxyapatite based films. Surf Coat Technol 201:3462–3474
Kilbane JJ II (2006) Microbial biocatalyst developments to upgrade fossil fuels. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17:305–314
Kim JH, Ma X, Zhou A, Song C (2006) Ultra-deep desulfurization and denitrogenation of diesel fuel by selective adsorption over three different adsorbents: a study on adsorptive selectivity and mechanism. Catal Today 111:74–83
Li W, Wang MD, Chen H, Shi Y (2006) Biodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene by growing cells of Gordonia sp. in batch cultures. Biotechnol Lett 28:1175–1179
Li W, Tang W, Liu Q, Xing J, Li Q, Wang D, Yang M, Li X, Liu H (2009) Deep desulfurization of diesel by integrating adsorption and microbial method. Biochem Eng J 44:297–301
Lu MC, Charisse LC, Wan MW, De Leon R, Arco S, Futalan C (2016) Adsorption of dibenzothiophene sulfone from fuel using chitosan-coated bentonite (CCB) as biosorbent. Desalin Water Treat 57:5108–5118
Maghsoudi S, Vossoughi M, Kheirolomoom A, Tanaka E, Katoh S (2001) Biodesulfurization of hydrocarbons and diesel fuels by Rhodococcus sp. strain P32C1. Biochem Eng J 8:151–156
Ojeda J, Escalona N, Fierro JLG, López-Agudo A, Gil-Llambías FG (2005) Effect of the preparation of Re/γ-Al2SO3 catalysts on the HDS and HDN of gasoil. Appl Catal A 281:25–30
Srivastav A, Srivastava VC (2009) Adsorptive desulfurization by activated alumina. J Hazard Mater 170:1133–1140
Tsai WT, Lai CW, Hsien KJ (2003) Effect of particle size of activated clay on the adsorption of paraquat from aqueous solution. J Colloid Interface Sci 263:29–34
Yee N, Fein JB, Daughney JC (2000) Experimental study of the pH, ionic strength, and reversibility behavior of bacteria–mineral adsorption. Geochim Cosmochim Ac 4:609
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Chilean government for financial support from CONICYT through FONDECYT Grant 1150544.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carvajal, P., Dinamarca, M.A., Baeza, P. et al. Removal of sulfur-containing organic molecules adsorbed on inorganic supports by Rhodococcus Rhodochrous spp.. Biotechnol Lett 39, 241–245 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2240-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2240-y