Abstract
Objectives
To induce natural genetic competence in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens isolates through overexpression of the master regulator, ComK, from B. subtilis (ComK Bsu ).
Results
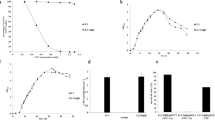
Plasmid pUBXC carrying the xylose-inducible comK expression cassette was constructed using plasmid pUB110 as a backbone. Plasmid pUBXC could be transferred from B. subtilis to B. amyloliquefaciens through plasmid pLS20-mediated biparental conjugation. After being induced by xylose, four B. amyloliquefaciens strains harbouring plasmid pUBXC developed genetic competence. Under optimal conditions, the transformation efficiencies of plasmid DNA ranged from 129 ± 20.6 to 1.7 ± 0.1 × 105 cfu (colony-forming units) per μg DNA, and the transformation efficiencies of PCR-assembled deletion constructs ranged from 3.2 ± 0.76 to 3.5 ± 0.42 × 104 cfu per μg DNA in the four tested strains.
Conclusion
Artificial induction of genetic competence through overexpressing ComK Bsu in B. amyloliquefaciens completed the tasks of replicative plasmid delivery and gene knockout via direct transformation of PCR-generated deletion cassettes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anagnostopoulos C, Spizizen J (1961) Requirements for transformation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 81:741–746
Chowdhury SP, Hartmann A, Gao XW, Borriss R (2015) Biocontrol mechanism by root-associated Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42-a review. Front Microbiol 6:780–790
Coukoulis H, Campbell LL (1971) Transformation in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. J Bacteriol 105:319–322
Duitman EH, Wyczawski D, Boven LG, Venema G, Kuipers OP, Hamoen LW (2007) Novel methods for genetic transformation of natural Bacillus subtilis isolates used to study the regulation of the mycosubtilin and surfactin synthetases. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:3490–3496
Härtl B, Wehrl W, Wiegert T, Homuth G, Schumann W (2001) Development of a new integration site within the Bacillus subtilis chromosome and construction of compatible expression cassettes. J Bacteriol 183:2696–2699
Hoffmann K, Wollherr A, Larsen M, Rachinger M, Liesegang H, Ehrenreich A, Meinhardt F (2010) Facilitation of direct conditional knockout of essential genes in Bacillus licheniformis DSM13 by comparative genetic analysis and manipulation of genetic competence. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:5046–5057
Itaya M, Sakaya N, Matsunaga S, Fujita K, Kaneko S (2006) Conjugational transfer kinetics of pLS20 between Bacillus subtilis in liquid medium. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 70:740–742
Jakobs M, Meinhardt F (2015) What renders Bacilli genetically competent? A gaze beyond the model organism. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:1557–1570
Koehler TM, Thorne CB (1987) Bacillus subtilis (natto) plasmid pLS20 mediates interspecies plasmid transfer. J Bacteriol 169:5271–5278
Koumoutsi A, Chen XH, Henne A, Liesegang H, Hitzeroth G, Franke P, Vater J, Borriss R (2004) Structural and functional characterization of gene clusters directing nonribosomal synthesis of bioactive cyclic lipopeptides in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain FZB42. J Bacteriol 186:1084–1096
Kovács ÁT, Smits WK, Mirończuk AM, Kuipers OP (2009) Ubiquitous late competence genes in Bacillus species indicate the presence of functional DNA uptake machineries. Environ Microbiol 11:1911–1922
Mirończuk AM, Kovács ÁT, Kuipers OP (2008) Induction of natural competence in Bacillus cereus ATCC14579. Microb Biotechnol 1:226–235
Ogura M, Yamaguchi H, Kobayashi K, Ogasawara N, Fujita Y, Tanaka T (2002) Whole-genome analysis of genes regulated by the Bacillus subtilis competence transcription factor ComK. J Bacteriol 184:2344–2351
Shevchuk NA, Bryksin AV, Nusinovich YA, Cabello FC, Sutherland M, Ladisch S (2004) Construction of long DNA molecules using long PCR-based fusion of several fragments simultaneously. Nucleic Acids Res 32:e19–e19
Van Sinderen D, Venema G (1994) comK acts as an autoregulatory control switch in the signal transduction route to competence in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 176:5762–5770
Veening JW, Smits W, Hamoen L, Kuipers O (2006) Single cell analysis of gene expression patterns of competence development and initiation of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis grown on chemically defined media. J Appl Microbiol 101:531–541
Vehmaanperä J (1988) Transformation of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens protoplasts with plasmid DNA. FEMS Microbiol Lett 49:101–105
Vehmaanperä J (1989) Transformation of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens by electroporation. FEMS Microbiol Lett 61:165–169
Wemhoff S, Meinhardt F (2013) Generation of biologically contained, readily transformable, and genetically manageable mutants of the biotechnologically important Bacillus pumilus. App Microbiol Biotechnol 97:7805–7819
Xu Z, Shao J, Li B, Yan X, Shen Q, Zhang R (2013) Contribution of bacillomycin D in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SQR9 to antifungal activity and biofilm formation. App Environ Microbiol 79:808–815
Xu J, Wang H, Zhu Z, Ji F, Yin X, Hong Q, Shi J (2016) Isolation and characterization of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens ZDS-1: exploring the degradation of Zearalenone by Bacillus spp. Food Control 68:244–250
Yan X, Yu H, Hong Q, Li S (2008) Cre/lox system and PCR-based genome engineering in Bacillus subtilis. App Environ Microbiol 74:5556–5562
Yuan J, Raza W, Huang Q, Shen Q (2011) Quantification of the antifungal lipopeptide iturin A by high performance liquid chromatography coupled with aqueous two-phase extraction. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 879:2746–2750
Zakataeva NP, Gronskiy SV, Sheremet AS, Kutukova EA, Novikova AE, Livshits VA (2007) A new function for the Bacillus PbuE purine base efflux pump: efflux of purine nucleosides. Res Microbiol 158:659–665
Acknowledgments
We appreciate Mitsuhiro Itaya from Mitsubishi Kagaku Institute of Life Science for providing plasmid pLS20cat. The authors would like to express their thanks to the financial support from 863 Plan (2014AA020543), 973 Plan (2015CB150505) and National Natural Science Foundation (31300099 and 31470225) of China.
Supporting information
Supplementary Table 1—Oligonucleotides used.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, XT., Ji, JB., Liu, YC. et al. Artificial induction of genetic competence in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens isolates. Biotechnol Lett 38, 2109–2117 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2194-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2194-0