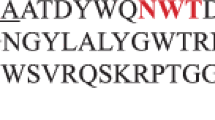Abstract
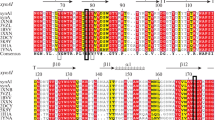
A recombinant xylanase gene (rxynUMB) from Ustilago maydis 521 was expressed in Pichia pastoris, and the enzyme was purified and characterized. Phylogenetic analysis demonstrated that rxynUMB belongs to glycosyl hydrolase family 11. The Trp84, Trp95, Glu93, and Glu189 residues are proposed to be present at the active site. The apparent molecular mass of the recombinant xylananse was approximately 24 kDa, and the optimum pH and temperature were 4.3 and 50 °C, respectively. Xylanase activity was enhanced by 166 and 115 % with Fe2+ and Mn2+, respectively. The biochemical properties of this recombinant xylanase suggest that it may be a useful candidate for a variety of commercial applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey P (1985) Microbial xylanolytic systems. Trends Biotechnol 3:286–290
Deesukon W, Nishimura Y, Sakamoto T, Sukhumsirichart W (2013) Purification, characterization of GH11 endo-β-1,4-xylanase from thermotolerant Streptomyces sp. SWU10 and overexpression in Pichia pastoris KM71H. Mol Biotechnol 54:37–46
Figueroa-Espinoza MC, Poulsen C, Soe JB, Zargahi MR, Rouau X (2004) Enzymatic solubilization of arabinoxylans from native, extruded, and high-shear-treated rye bran by different endo-xylanases and other hydrolyzing enzymes. J Agric Food Chem 52:4240–4249
Ghaffar A, Khan SA, Mukhtar Z, Rajoka MI, Latif F (2011) Heterologous expression of a gene for thermostable xylanase from Chaetomium thermophilum in Pichia pastoris GS115. Mol Biol Rep 38:3227–3233
McIntosh LP, Hand G, Johnson PE, Joshi MD, Korner M, Plesniak LA, Ziser L, Wakarchuk WW, Withers SG (1996) The pKa of the general acid/base carboxyl group of a glycosidase cycles during catalysis: A13C-NMR study of Bacillus circulans xylanase. Biochemistry 35:9958–9966
Mittal A, Nagar S, Kaur SJ, Kirti, Gupta VK (2012) Isolation, purification and characterization of alkali and thermostable xylanase from Bacillus sp. KS 09. Int J Res Dev Pharm Life Sci 1:63–68
Nair SG, Sindhu R, Shashidhar S (2008) Purification and biochemical characterization of two xylanases from Aspergillus sydowii SBS 45. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 149:229–243
O’Connell RJ, Panstruga R (2006) Inside a plant cell: establishing compatibility between plants and biotrophic fungi and oomycetes. New Phytol 171:699–718
Poon DK, Webster P, Withers SG (2003) Characterizing the pH-dependent stability and catalytic mechanism of the family 11 xylanase from the alkalophilic Bacillus agaradhaerens. Carbohydr Res 338:415–421
Shi H, Zhang Y, Zhong H, Huang YJ, Li X, Wang F (2014) Cloning, over-expression and characterization of a thermotolerant xylanase from Thermotoga thermarum. Biotechnol Lett 36:587–593
Xiong AS, Peng RH, Li X, Fan HQ, Yao QH, Guo MJ, Zhang SL (2003) Influence of signal peptide sequences on the expression of heterogeneous proteins in Pichia pastoris. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 35:154–160
Xiong AS, Yao QH, Peng RH, Li X, Fan HQ, Li Y, Cheng ZM (2004) A simple, rapid, high fidelity and cost-effective PCR based two-step DNA synthesis (PTDS) method for long gene sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 32:e98
Zhou C, Bai J, Deng S, Wang J, Zhu J, Wu M, Wang W (2008) Cloning of a xylanase gene from Aspergillus usamii and its expression in Escherichia coli. Bioresour Technol 99:831–838
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by the International Scientific and Technological Cooperation (13440701700), Agriculture Science Technology Achievement Transformation Fund (133919N1300), Key Project Fund of Shanghai Minhang Science and Technology Committee (2012MH059), Young Foundation of Shanghai Academy of Agricultural Science (2010–2014). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Supporting information
Supplementary Fig. 1 The optimal sequence derived for the wild-type xylanase gene, xynUMB, from Ustilago maydis 521.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, H., You, S., Zhu, B. et al. Characterization and high expression of recombinant Ustilago maydis xylanase in Pichia pastoris . Biotechnol Lett 37, 697–703 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1716-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1716-x