Abstract
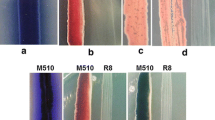
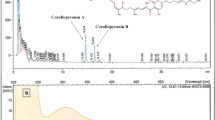
Prolific producers of natural products like streptomycetes and myxobacteria live in complex natural frameworks consisting of many microorganisms. Presumably intricate physiological and metabolic regulatory networks have evolved to enable the organisms to respond to intra- and interspecies interactions, e.g. biosynthesis of specific natural products is up-regulated due to competitors in the surrounding area. The soil-dwelling bacterium, Streptomyces coelicolor, produces the biologically-active compound, undecylprodigiosin (Red). Co-incubation with the corallopyronin A-producer, Corallococcus coralloides, was performed to explore the hypothesis that Red production can be enhanced by a myxobacterial competitor. Co-cultivation resulted in earlier onset and increased production of Red (60-fold increase of the intra-cellular concentration). Using different Corallococcus-derived extracts for elicitation, revealed that water-soluble factors triggered the enhanced production of Red which shows antimicrobial, immunosuppressive and anticancer properties.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angell S, Bench BJ, Williams H, Watanabe CM (2006) Pyocyanin isolated from a marine microbial population: synergistic production between two distinct bacterial species and mode of action. Chem Biol 13:1245–1246
Bassler BL, Losick R (2006) Bacterially speaking. Cell 125:237–246
Challis GL (2008) Mining microbial genomes for new natural products and biosynthetic pathways. Microbiology 154:1555–1569
Cueto M, Jensen PR, Kauffman C, Fenical W, Lobkovsky E, Clardy J (2001) Pestalone, a new antibiotic produced by a marine fungus in response to bacterial challenge. J Nat Prod 64:1444–1446
Erol O, Schäberle TF, Schmitz A, Rachid S, Gurgui C, El Omari M, Lohr F, Kehraus S, Piel J, Müller R, König GM (2010) Biosynthesis of the myxobacterial antibiotic corallopyronin A. ChemBioChem 11:1253–1265
Graupner K, Scherlach K, Bretschneider T, Lackner G, Roth M, Gross H, Hertweck C (2012) Imaging mass spectrometry and genome mining reveal highly antifungal virulence factor of mushroom soft rot pathogen. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 51:13173–13177
Ho TF, Ma CJ, Lu CH, Tsai YT, Wei YH, Chang JS, Lai JK, Cheuh PJ, Yeh CT, Tang PC, Tsai Chang J, Ko JL, Liu FS, Yen HE, Chang CC (2007) Undecylprodigiosin selectively induces apoptosis in human breast carcinoma cells independent of p53. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 225:318–328
Kang SG, Jin W, Bibb M, Lee KJ (1998) Actinorhodin and undecylprodigiosin production in wild-type and relA mutant strains of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) grown in continuous culture. FEMS Microbiol Lett 168:221–226
Kim YJ, Sa SO, Chang YK, Hong SK, Hong YS (2007) Overexpression of Shinorhizobium meliloti hemoprotein in Streptomyces lividans to enhance secondary metabolite production. J Microbiol Biotechnol 17:2066–2070
Liu P, Wang YY, Qi X, Gu Q, Geng M, Li J (2013) Undecylprodigiosin induced apoptosis in p388 cancer cells is associated with its binding to ribosome. PLoS ONE 8:e65381. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0065381
Luti KJ, Mavituna F (2011a) Streptomyces coelicolor increases the production of undecylprodigiosin when interacted with Bacillus subtilis. Biotechnol Lett 33:113–118
Luti KJ, Mavituna F (2011b) Elicitation of Streptomyces coelicolor with dead cells of Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus in a bioreactor increases production of undecylprodigiosin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90:461–466
Meschke H, Walter S, Schrempf H (2012) Characterization and localization of prodiginines from Streptomyces lividans suppressing Verticillium dahliae in the absence or presence of Arabidopsis thaliana. Environ Microbiol 14:940–952
Nett M, Ikeda H, Moore BS (2009) Genomic basis for natural product biosynthetic diversity in the actinomycetes. Nat Prod Rep 26:1362–1384
Oh DC, Jensen PR, Kauffman CA, Fenical W (2005) Libertellenones A-D: induction of cytotoxic diterpenoid biosynthesis by marine competition. Bioorg Med Chem 13:5267–5273
Pérez J, Muñoz-Dorado J, Braña AF, Shimkets LJ, Sevillano L, Santamaría RI (2011) Myxococcus xanthus induces actinorhodin overproduction and aerial mycelium formation by Streptomyces coelicolor. Microb Biotechnol 4:175–183
Petti RK (2009) Mixed fermentation for natural product drug discovery. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 83:19–25
Rigali S, Titgemeyer F, Barends S (2008) Feast or famine: the global regulator DasR links nutrient stress to antibiotic production by Streptomyces. EMBO Rep 9:670–675
Schäberle TF, Schiefer A, Schmitz A, König GM, Hoerauf A, Pfarr K (2013) Corallopyronin A—a promising antibiotic for treatment of filariasis. Int J Med Microbiol. doi:10.1016/j.ijmm.2013.08.010
Scherlach K, Hertweck C (2009) Triggering cryptic natural product biosynthesis in microorganisms. Org Biomol Chem 7:1753–1760
Schiefer A, Schmitz A, Schäberle TF, Specht S, Lämmer C, Johnston KL, Vassylyev DG, König GM, Hoerauf A, Pfarr K (2012) Corallopyronin A specifically targets and depletes essential obligate Wolbachia endobacteria from filarial nematodes in vivo. J Infect Dis 206:249–257
Schroeckh V, Scherlach K, Nützmann HW, Shelest E, Schmidt-Heck W, Schuemann J, Martin K, Hertweck C, Brakhage AA (2009) Intimate bacterial-fungal interaction triggers biosynthesis of archetypal polyketides in Aspergillus nidulans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:14558–14563
Williamson NR, Simonsen HT, Ahmed RA, Goldet G, Slater H, Woodley L, Leeper FJ, Salmond GP (2005) Biosynthesis of the red antibiotic, prodigiosin, in Serratia: identification of a novel 2-methyl-3-n-amylpyrrole (MAP) assembly pathway, definition of the terminal condensing enzyme, and implications for undecylprodigiosin biosynthesis in Streptomyces. Mol Microbiol 56:971–989
Williamson NR, Fineran PC, Leeper FJ, Salmond GPC (2006) The biosynthesis and regulation of bacterial prodiginines. Nat Rev Microbiol 4:887–899
Acknowledgments
We thank Seda Yaramis for technical assistance. This work was supported by grant KO 902/5-1 from the German Research Association (DFG).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schäberle, T.F., Orland, A. & König, G.M. Enhanced production of undecylprodigiosin in Streptomyces coelicolor by co-cultivation with the corallopyronin A-producing myxobacterium, Corallococcus coralloides . Biotechnol Lett 36, 641–648 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-013-1406-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-013-1406-0