Abstract
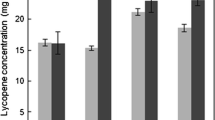
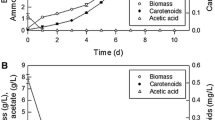
To prevent degradation of intracellular retinoids through in situ extraction from the cells, a two-phase culture system was performed. Several organic solvents, including n-alkanes, mineral oils and cosmetic raw materials, were applied as the extraction phase. Of the n-alkanes, n-decane had the highest retinoid production as 134 mg/l after 72 h. For mineral oil, light and heavy mineral oil gave retinoid productions of 158 and 174 mg/l after 96 h, respectively. Of other materials, isopropyl myristate gave the highest retinoid production of 181 mg/l. These results indicate that many types of oils can be applied for retinoid production, and optimization of the in situ extraction process will lead to further improve of economical production for the industrial purpose.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aono R (1998) Improvement of organic solvent tolerance level of Escherichia coli by overexpression of stress-responsive genes. Extremophiles 2:239–248
Hejazi MA, Wijffels RH (2003) Effect of light intensity on beta-carotene production and extraction by Dunaliella salina in two-phase bioreactors. Biomol Eng 20:171–175
Inoue A, Horikoshi K (1989) A pseudomonas thrives in high-concentrations of toluene. Nature 338:264–266
Jang HJ, Yoon SH, Ryu HK, Kim JH, Wang CL, Kim JY, Oh DK, Kim SW (2011) Retinoid production using metabolically engineered Escherichia coli with a two-phase culture system. Microb Cell Fact 10:59
Kim SK, Karadeniz F (2012) Biological importance and applications of squalene and squalane. Adv Food Nutr Res 65:223–233
Kleinegris DM, Janssen M, Brandenburg WA, Wijffels RH (2011) Continuous production of carotenoids from Dunaliella salina. Enzyme Microb Technol 48:253–259
Kuo CH, Chen HH, Chen JH, Liu YC, Shieh CJ (2012) High yield of wax ester synthesized from cetyl alcohol and octanoic acid by Lipozyme RMIM and Novozym 435. Int J Mol Sci 13:11694–11704
Leon R, Vila M, Hernanz D, Vilchez C (2005) Production of phytoene by herbicide-treated microalgae Dunaliella bardawil in two-phase systems. Biotechnol Bioeng 92:695–701
Martinez A, Bradley AS, Waldbauer JR, Summons RE, DeLong EF (2007) Proteorhodopsin photosystem gene expression enables photophosphorylation in a heterologous host. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:5590–5595
Mercier Chabardes (1994) Organometallic chemistry in industrial vitamin A and vitamin E synthesis. Pure Appl Chem 66:1509–1518
Nash JF, Gettings SD, Diembeck W, Chudowski M, Kraus AL (1996) A toxicological review of topical exposure to white mineral oils. Food Chem Toxicol 34:213–225
Nicolaou SA, Gaida SM, Papoutsakis ET (2010) A comparative view of metabolite and substrate stress and tolerance in microbial bioprocessing: from biofuels and chemicals, to biocatalysis and bioremediation. Metab Eng 12:307–331
Ramos JL, Duque E, Gallegos MT, Godoy P, Ramos-Gonzalez MI, Rojas A, Teran W, Segura A (2002) Mechanisms of solvent tolerance in gram-negative bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 56:743–768
Rawlings AV, Lombard KJ (2012) A review on the extensive skin benefits of mineral oil. Int J Cosmet Sci 34:511–518
Sabehi G, Loy A, Jung KH, Partha R, Spudich JL, Isaacson T, Hirschberg J, Wagner M, Beja O (2005) New insights into metabolic properties of marine bacteria encoding proteorhodopsins. PLoS Biol 3:e273
Sorg O, Antille C, Kaya G, Saurat JH (2006) Retinoids in cosmeceuticals. Dermatol Ther 19:289–296
Traul KA, Driedger A, Ingle DL, Nakhasi D (2000) Review of the toxicologic properties of medium-chain triglycerides. Food Chem Toxicol 38:79–98
Wang C, Yoon SH, Shah AA, Chung YR, Kim JY, Choi ES, Keasling JD, Kim SW (2010) Farnesol production from Escherichia coli by harnessing the exogenous mevalonate pathway. Biotechnol Bioeng 107:421–429
Yoon KW, Doo EH, Kim SW, Park JB (2008) In situ recovery of lycopene during biosynthesis with recombinant Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol 135:291–294
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant (NRF-2010-C1AAA001-0029084) from the National Research Foundation, the Intelligent Synthetic Biology Center of Global Frontier Project funded by the MEST (2011-0031964), and a grant from the Next-Generation BioGreen 21 Program (SSAC, Grant#: PJ009522003), RDA, Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Hui-Jeong Jang and Bo-Kyung Ha have contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jang, HJ., Ha, BK., Kim, JW. et al. Comparison of extraction phases for a two-phase culture of a recombinant E. coli producing retinoids. Biotechnol Lett 36, 497–505 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-013-1385-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-013-1385-1